Innovation Across Various Industries
Mar 09, 2024
By Ari Manor , CEO at ZOOZ
This is one in a series of articles that provide detailed and updated information about Innovation. In this specific article, which focuses on Innovation Across Various Industries, you can read about:
- Innovation in Entrepreneurship
- Why Innovation is Important In Entrepreneurship
- Innovation in Healthcare
- Why Innovation is Important in Healthcare
- Why Innovation in Healthcare is So Hard
- Innovation in Education
- Why Innovation is Important in Education
- Innovation in Marketing
- Innovation with Data
- Innovation for Equity
- Innovation for Justice
- Where Innovation Meets the Law
- What Innovation Changed the Textile Industry
- When Innovation Meets Fashion
- What Innovation Came About as a Result of Railroads
For additional articles about Innovation, see the Topic Menu.

Innovation in Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship and innovation are intrinsically linked, as entrepreneurs continuously seek new opportunities, develop creative solutions, and disrupt traditional business models. In today's competitive landscape, innovation is not just a competitive advantage; it's a survival imperative. Entrepreneurs who embrace innovation can differentiate their offerings, drive growth, and navigate through uncertainty more effectively. Whether it's introducing groundbreaking products, optimizing processes, or exploring new markets, innovation lies at the heart of entrepreneurial success.
Breakthrough Inventions for Entrepreneurship:
- WeWork: Redefining coworking spaces and revolutionizing the concept of shared office environments.
- Trello: Offering a visual project management tool that simplifies collaboration and task management for teams.
- Shopify: Empowering entrepreneurs to easily set up online stores and sell their products across multiple channels.
- Squarespace: Streamlining website building for entrepreneurs with easy-to-use templates and intuitive design tools.
- PayPal: Facilitating secure online payments, making it easier for businesses to manage transactions and grow their customer base.
 Case Study: Stripe's Seamless Payment Integration
Case Study: Stripe's Seamless Payment Integration
- Company: Stripe, San Francisco, USA (Founded in 2010)
- What Was Done: Stripe developed software that allows both private individuals and businesses to make payments over the internet. The platform simplifies the way businesses can incorporate payment processing into their websites and applications.
- Results/Impact: Stripe's technology has become instrumental in e-commerce by removing barriers to online payment processes, enabling businesses of all sizes to participate in the global economy. Their innovation has had a broad impact on digital entrepreneurship.
How to Apply Innovation for Entrepreneurship:
- Embrace Risk: Be willing to take calculated risks and experiment with new ideas, products, or business models.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Listen to customer feedback and iterate based on their needs and preferences to drive innovation.
- Agile Methodology: Adopt agile principles to rapidly test and iterate ideas, allowing for quick adaptation to market changes.
- Continuous Learning: Stay curious, seek knowledge from diverse sources, and invest in personal and professional development.
- Build a Diverse Team: Surround yourself with individuals from varied backgrounds and skill sets to foster innovation through diverse perspectives.
 Case Study: Kickstarter’s Crowdfunding Model
Case Study: Kickstarter’s Crowdfunding Model
- Company: Kickstarter, New York, USA (Launched in 2009)
- What Was Done: Kickstarter created a platform for crowdfunding, where individuals can fund projects and ventures in exchange for tiered rewards. It democratized the funding process for new creative projects and ventures.
- Results/Impact: Kickstarter has successfully funded a diverse range of projects from films, games, and music to art, technology, and design, becoming a vital tool for independent creators and entrepreneurs worldwide.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Entrepreneurship:
- Disruptive Potential: Successful entrepreneurial innovation often disrupts existing markets or creates entirely new ones.
- Bootstrapping Culture: Entrepreneurs often rely on resourcefulness and creativity to innovate with limited resources.
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: Innovation in entrepreneurship thrives on traits like resilience, adaptability, and a willingness to challenge the status quo.
- Iterative Process: Innovation in entrepreneurship is often an iterative journey, with frequent experimentation, feedback loops, and course corrections.
- Impactful Solutions: Entrepreneurial innovation aims to solve real-world problems and create value for customers, society, or the environment.
What to Avoid When Inventing for Entrepreneurship:
- Fear of Failure: Don't let the fear of failure prevent you from taking risks and pursuing innovative ideas.
- Ignoring Market Feedback: Pay attention to market signals and customer feedback to avoid building products or services with limited demand.
- Lack of Adaptability: Be open to pivoting or adjusting your strategy based on changing market conditions or new insights.
- Overlooking Legal Considerations: Ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations to avoid legal pitfalls that could derail your entrepreneurial journey.
- Isolation: Don't work in isolation; seek collaboration, mentorship, and networking opportunities to fuel your innovation efforts.
Innovation in entrepreneurship is not just about developing groundbreaking products or services; it's about cultivating a mindset of creativity, resilience, and adaptability. By embracing innovation, entrepreneurs can navigate through uncertainty, seize new opportunities, and ultimately, drive sustainable growth and success in their ventures.

Why Innovation is Important In Entrepreneurship
Innovation in entrepreneurship acts as the engine of modern business, fueling the growth of startups, invigorating corporates, and fostering competitive economies. It is the cornerstone of value creation and market advancement, catalyzing the development of novel products, services, and business models. In a landscape where change is the only constant, innovation within entrepreneurship ensures resilience, agility, and sustainable success.
Why is innovation in Entrepreneurship Crucial to Start-Ups
- Brand Differentiation: Innovation allows startups to differentiate their brand identity, creating unique selling propositions that distinguish them from competitors and draw attention to their value.
- Agility and Adaptability: Startups thrive on their ability to pivot quickly, and innovation is key to adapting to market changes, capitalizing on emerging opportunities, and staying ahead of industry trends.
- Personalized Customer Solutions: Innovative startups succeed by crafting personalized solutions that address specific customer needs, setting them apart in crowded marketplaces and building strong, loyal customer bases.
- Scalability and Growth: For startups, innovation is the pathway to scalability, opening doors to expand their market reach and grow their operations efficiently and effectively.
- Attracting Investment: Investors are drawn to startups that demonstrate innovative thinking, not just in their products but in their approach to business, increasing the potential for funding and support.
Why is Innovation in Internal Entrepreneurship Crucial to Corporates
- Sustaining Competitive Edge: Corporates rely on internal innovation to maintain a competitive edge, continuously improving and evolving to meet the ever-changing demands of the global market.
- Operational Efficiency: Innovation leads to improved processes and operational efficiency in corporates, optimizing performance, and reducing waste and costs.
- Market Leadership: By championing innovation, corporates can establish themselves as market leaders, setting industry standards and driving future trends.
- Employee Engagement: Innovative cultures within corporates drive employee engagement, encouraging creative thinking and problem-solving that contribute to job satisfaction and retention.
- Diversification of Products and Services: Internal entrepreneurship allows corporates to diversify their offerings, mitigating risks by spreading investments across a variety of innovative products and services.
Other Benefits of Innovation in Entrepreneurship
- Driving Economic Growth: Entrepreneurial innovation is a catalyst for economic growth, stimulating new industries, creating jobs, and contributing to national and global prosperity.
- Solving Complex Problems: Innovative entrepreneurs are often at the forefront of solving complex social and environmental problems, leveraging business acumen and creativity for the greater good.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Through innovation, entrepreneurs enhance customer experiences, delivering higher value, convenience, and satisfaction that foster brand loyalty and repeat business.
- Fostering Collaboration and Partnerships: Innovation often leads to new collaborations and strategic partnerships, broadening networks, and combining resources for amplified impact.
- Global Expansion: Innovative entrepreneurs have the potential to take their businesses global, breaking into new markets and cultural contexts with adaptable business models and products.
Consequences of Stagnant Entrepreneurship
- Diminished Market Relevance: Without innovation, businesses risk losing market relevance, unable to keep up with the pace of change and evolving consumer expectations.
- Lack of Investor Interest: Investors shy away from stagnant businesses, seeking dynamic entrepreneurs who demonstrate forward-thinking and innovation.
- Reduced Profit Margins: Businesses that fail to innovate often face shrinking profit margins, as they cannot differentiate their offerings or streamline their operations effectively.
- Inability to Attract Talent: Top talent gravitates towards innovative companies, leaving stagnant businesses struggling to attract and retain skilled professionals.
- Economic Stagnation: When entrepreneurship stagnates, so does economic growth, leading to a lack of new industries, fewer employment opportunities, and reduced competitiveness on a global scale.
Innovation in entrepreneurship is more than a buzzword; it's an essential ingredient for any business seeking longevity and success in the modern economy. It inspires, drives growth, and builds the foundation for companies that not only survive but thrive. By fostering an environment where innovation is embraced and encouraged, entrepreneurs can ensure that their ventures remain resilient and relevant in an ever-changing business landscape.

Innovation in Healthcare
Innovation in healthcare is vital for addressing the evolving needs of patients, improving clinical outcomes, and driving efficiency in healthcare delivery. From groundbreaking medical devices to transformative digital health solutions, innovations in healthcare have the potential to save lives, enhance patient experiences, and reduce healthcare costs. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, fostering a culture of innovation becomes increasingly essential for healthcare organizations, policymakers, and stakeholders.
Breakthrough Inventions for Healthcare
- Zipline: Utilizing drones to deliver medical supplies to remote and underserved areas, revolutionizing healthcare logistics.
- Butterfly Network: Transforming diagnostic imaging with a handheld, smartphone-connected ultrasound device, making medical imaging more accessible and affordable.
- CureVac: Pioneering messenger RNA (mRNA) technology for vaccine development, offering new possibilities for rapid vaccine production and customization.
- Sana Health: Introducing wearable devices that use neuromodulation therapy to alleviate chronic pain and improve sleep quality.
- Tempus: Leveraging artificial intelligence and big data analytics to personalize cancer treatment and improve clinical decision-making.
 Case Study: Proteus Digital Health's Ingestible Sensors
Case Study: Proteus Digital Health's Ingestible Sensors
- Company: Proteus Digital Health, Redwood City, USA (Founded in 2001)
- What Was Done: Proteus developed ingestible sensors that can be taken with medication, transmitting data to a patch worn on the patient's body and then to a mobile device, tracking medication adherence.
- Results/Impact: Although Proteus Digital Health filed for bankruptcy in 2020, its technology made strides in personalized medicine, providing valuable insights into patient compliance and the potential for tailored healthcare solutions.
How to Apply Innovation for Healthcare
- Invest in Research and Development: Allocate resources to research and development efforts to foster the discovery and development of innovative healthcare solutions.
- Collaborate Across Disciplines: Foster collaboration between healthcare providers, technologists, researchers, and patients to co-create solutions that address unmet needs and improve patient outcomes.
- Adopt Agile Practices: Embrace agile methodologies to enable rapid iteration, testing, and refinement of healthcare innovations, allowing for quick adaptation to evolving challenges and opportunities.
- Prioritize Patient-Centric Design: Place patients at the center of the innovation process, ensuring that healthcare solutions are accessible, user-friendly, and aligned with patient preferences and needs.
- Embrace Emerging Technologies: Explore emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, telemedicine, and genomics to unlock new possibilities for improving diagnosis, treatment, and care delivery.
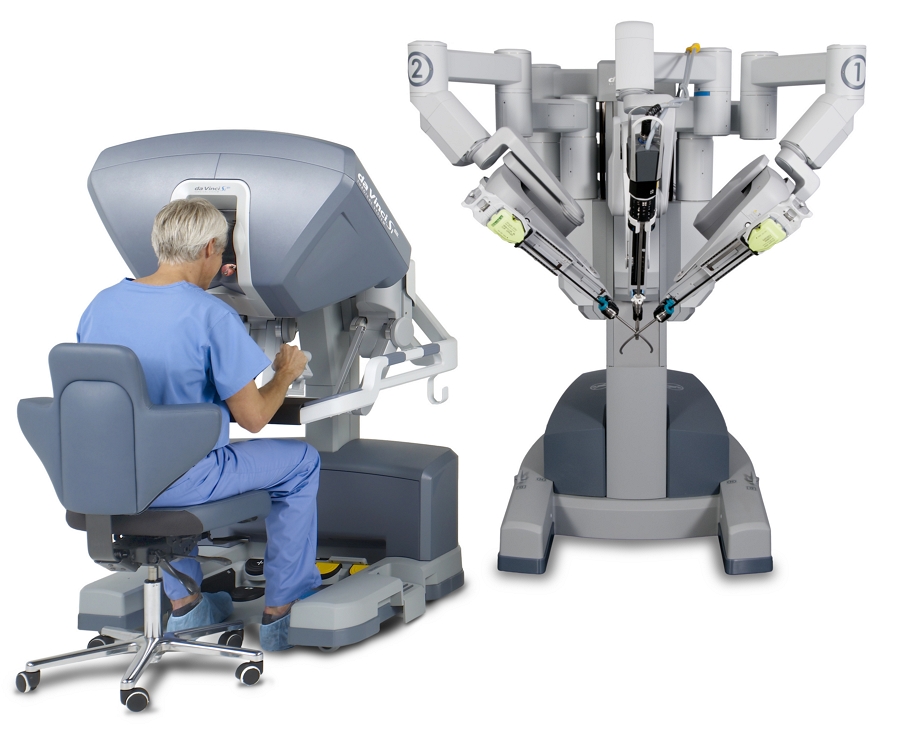 Case Study: Intuitive Surgical's da Vinci Surgical System
Case Study: Intuitive Surgical's da Vinci Surgical System
- Company: Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, USA
- Medical Device: The da Vinci Surgical System (FDA approval in 2000)
- What Was Done: Intuitive Surgical developed the da Vinci Surgical System, a robotic surgical system designed to facilitate complex surgery using a minimally invasive approach controlled by a surgeon from a console.
- Results/Impact: The da Vinci Surgical System has been widely adopted and has changed the way surgeries are performed, improving patient outcomes through less invasive surgical methods, resulting in shorter hospital stays and recovery times.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Healthcare
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Healthcare innovations are subject to rigorous regulatory scrutiny to ensure safety, efficacy, and compliance with healthcare standards and regulations.
- Ethical Considerations: Innovations in healthcare raise ethical questions related to patient privacy, data security, informed consent, and equitable access to healthcare services and technologies.
- Interdisciplinary Nature: Healthcare innovation often involves collaboration across diverse disciplines, including medicine, engineering, computer science, and behavioral science, to address complex healthcare challenges.
- Long Development Cycles: Healthcare innovations typically have long development cycles due to the need for extensive clinical testing, regulatory approval processes, and adoption by healthcare providers and patients.
- Note: Consequently, for healthcare innovations expect a delayed return on investment (ROI), often taking years to materialize, in contrast to quicker returns seen in other sectors.
- Note: Consequently, for healthcare innovations expect a delayed return on investment (ROI), often taking years to materialize, in contrast to quicker returns seen in other sectors.
- Global Impact: Healthcare innovations have the potential to have a profound global impact by addressing pressing healthcare challenges, improving health outcomes, and advancing public health initiatives.
What to Avoid When Inventing for Healthcare
- Overlooking Patient Needs: Ensure that healthcare innovations are aligned with patient needs, preferences, and values to maximize adoption and impact.
- Ignoring Regulatory Requirements: Stay informed about regulatory requirements and compliance standards to avoid delays, setbacks, or legal issues during the development and commercialization of healthcare innovations.
- Underestimating Implementation Challenges: Anticipate implementation challenges such as interoperability issues, workflow integration, reimbursement barriers, and resistance to change when introducing new healthcare technologies or practices.
- Neglecting Data Privacy and Security: Prioritize data privacy and security measures to protect patient confidentiality, prevent data breaches, and maintain trust in healthcare innovations and systems.
- Lack of Stakeholder Engagement: Involve stakeholders such as patients, healthcare providers, policymakers, insurers and payers, and industry partners throughout the innovation process to ensure relevance, feasibility, and sustainability of healthcare innovations.
Innovation in healthcare holds immense promise for transforming the future of medicine, improving patient outcomes, and advancing population health. By embracing a culture of innovation, healthcare stakeholders can drive progress, address unmet needs, and create a more resilient and responsive healthcare system for all.

Why Innovation is Important in Healthcare
Healthcare innovation serves as a critical catalyst for preventing premature death and improving longevity, while also enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals. By continually pushing the boundaries of medical research and technology, innovative advancements in healthcare address pressing challenges and drive positive outcomes for patients worldwide.
Why is innovation in healthcare crucial to increase longevity
- Preventing Death at Birth: Innovations in prenatal care, neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), and advanced medical imaging technologies help identify and address complications during pregnancy and childbirth, reducing infant mortality rates and increasing life expectancy from birth.
- Improving Treatments: Innovative treatments for life-threatening conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and infectious diseases have significantly improved survival rates and extended life expectancy for patients.
- Preventing Deaths Due to Treatments: Advancements in medical technology and pharmaceuticals help mitigate risks associated with surgeries, chemotherapy, and other intensive treatments, minimizing adverse effects and complications that could lead to premature death.
- Regenerative Medicine: Innovations in regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy, tissue engineering, and organ transplantation, hold promise for repairing and regenerating damaged tissues and organs, thereby extending lifespan.
- Precision Medicine: Tailored treatment strategies based on individual genetic makeup and molecular profiles enable more personalized and targeted interventions, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and prolonged lifespan.
- Health Maintenance Technologies: Innovations in health monitoring devices and wearable technology empower individuals to proactively manage their health, detect potential issues early, and adopt preventive measures to extend their lifespan.
- Lifestyle Interventions: Innovative approaches to promoting healthy lifestyles, such as digital health apps, personalized nutrition plans, and fitness trackers, encourage individuals to make positive behavior changes that contribute to longevity.
- Chronic Disease Management: Innovative healthcare models and technologies for managing chronic conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma, help patients maintain optimal health and prevent complications, thereby extending their lifespan.
Why is innovation in healthcare crucial to improve quality of life
- Advanced Therapies: Innovative medical treatments, such as minimally invasive surgeries and robotic-assisted procedures, minimize patient discomfort and recovery time, enhancing overall quality of life.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: Digital health innovations facilitate remote consultations and monitoring, providing convenient access to care and improving patient satisfaction.
- Assistive Technologies: Innovations like wearable devices and smart home technology enhance independence and functionality for individuals with disabilities or age-related limitations, thereby improving their quality of life.
- Mental Health Support: Innovative approaches to mental healthcare, including digital therapy platforms and telepsychiatry services, offer greater access to mental health support and treatment options, enhancing psychological well-being and overall quality of life.
- Patient-Centered Care: Healthcare innovation emphasizes patient engagement and shared decision-making, ensuring that care delivery is tailored to individual preferences and needs, leading to a more satisfying patient experience and improved quality of life.
- Note: It's important to consider potential trade-offs in patient-centered care. If patients personally choose treatments that ultimately fail, their resulting regret may lead to negative emotions and lower life quality.
- Note: It's important to consider potential trade-offs in patient-centered care. If patients personally choose treatments that ultimately fail, their resulting regret may lead to negative emotions and lower life quality.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery: Innovative rehabilitation therapies, assistive devices, and virtual reality technologies help individuals recover from injuries and surgeries more effectively, restoring function and independence and improving their overall quality of life.
- Social Support Systems: Innovations in community-based care models, peer support networks, and caregiver support services strengthen social connections and provide emotional support, contributing to improved well-being and quality of life.
- Palliative and End-of-Life Care: Innovative approaches to palliative care and end-of-life support prioritize patient comfort, dignity, and quality of life, ensuring compassionate care for individuals facing terminal illnesses and their families.
Other Benefits of Innovation in Healthcare
- Cost Reduction: Innovations in healthcare technology and delivery models streamline processes, optimize resource allocation, and reduce healthcare costs for patients and providers alike.
- Disease Prevention: Innovative public health interventions, such as community health initiatives, health education programs, and disease surveillance systems, help prevent the spread of infectious diseases and reduce the burden of chronic conditions.
- Global Health Equity: Advances in healthcare innovation promote equity by addressing disparities in access to healthcare services, improving health outcomes among vulnerable populations, and fostering international collaboration to tackle global health challenges.
- For example, the emergence of FemTech solutions is directly addressing the historical oversight in medical research where treatments, often tested predominantly on men, failed to account for women's unique physiological needs. By offering personalized healthcare services and products specifically designed for women, these innovations are significantly bridging the gap in healthcare access and outcomes, ensuring treatments are more effectively tailored to the distinct health profiles of women.
Case Study: Gender-Specific Dosing for Ambien (Zolpidem)
- Company: Sanofi-Aventis, Paris, France

- Treatment: Ambien (Zolpidem), 2013 Adjustment
- What Was Done: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced in 2013 that it was requiring manufacturers of zolpidem, a sleep aid marketed as Ambien among other names, to halve the recommended dose for women. This decision was based on new data showing that women metabolize zolpidem more slowly than men, resulting in higher morning blood levels that could increase the risk of impaired activities such as driving.
- Results/Impact: This adjustment in dosing recommendations was a significant shift towards recognizing and acting upon gender differences in pharmacokinetics (drug processing by the body). It highlighted the need for gender-specific research and dosing guidelines to ensure drug efficacy and safety for all patients. Following this decision, healthcare providers were advised to prescribe the lower dose for women to reduce the risk of next-morning impairment. This case represents an important step towards personalized medicine, acknowledging that men and women may require different treatment approaches for the same condition.
- For example, the emergence of FemTech solutions is directly addressing the historical oversight in medical research where treatments, often tested predominantly on men, failed to account for women's unique physiological needs. By offering personalized healthcare services and products specifically designed for women, these innovations are significantly bridging the gap in healthcare access and outcomes, ensuring treatments are more effectively tailored to the distinct health profiles of women.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: Breakthroughs in diagnostic imaging and pathology, such as AI-enhanced imaging and real-time data analysis, have increased the accuracy of diagnoses, leading to more effective treatment plans. These improvements may prevent deaths, enhance the quality of life, and have positive economic impacts.
- Robotic Assistance in Surgery: The integration of robotic technology in surgical procedures has enhanced precision, reduced patient recovery times, and minimized the likelihood of complications. This advancement also has the potential to improve life expectancy and quality of life, while reducing both direct and indirect healthcare costs.
- Expansion of Telemedicine: Continued innovation in telemedicine is expanding healthcare reach, allowing for specialist consultation and ongoing care management in underserved regions. This expansion has the potential to make healthcare more affordable and accessible, ultimately affecting mortality rates and quality of life.
Consequences of Stagnant Healthcare
- Unaddressed Health Emergencies: Without advancements, new diseases and health emergencies will emerge, and may remain unanswered, while increasing the risk of widespread disease outbreaks and pandemics.
- Rising Healthcare Costs: As population and life expectancy increase, stagnant healthcare services will inevitably lead to greater financial strain on individuals and healthcare systems.
- Worsening Health Inequalities: As socio-economic gaps grow, stagnant healthcare systems widen disparities, leaving more people with limited access to care.
- Technological Gaps Increase: A lack of innovation means healthcare services perform below their potential due to the absence of integrated technological advancements.
- Medical Workforce Challenges: Stagnation impacts the medical workforce, resulting in reduced morale, burnout, and a decline in the quality of healthcare professionals entering the field.
- Erosion of Trust: Patients may lose trust in the healthcare system due to its inability to adapt and innovate.
Healthcare innovation is not just a catalyst for enhancing longevity and quality of life; it is also a cornerstone for healthcare sustainability and equity. These advancements represent a commitment to not only addressing current medical challenges but also to anticipating future needs, ensuring all communities have access to the care and support they require for a healthier tomorrow.

Why Innovation in Healthcare is So Hard
Innovation in healthcare is a complex endeavor charged with challenges that span regulatory, financial, and cultural domains. Overcoming these hurdles is essential for driving meaningful progress and delivering transformative healthcare solutions. Let's delve into the challenges facing innovation in healthcare, the reasons that exacerbate these difficulties, and strategies to overcome them.
Challenges in Innovation in Healthcare
- Regulatory Hurdles: Stringent regulatory requirements, such as those imposed by the FDA, create barriers to entry for innovators, leading to prolonged approval processes and increased development costs.
- Resistance to Change: Healthcare professionals' reluctance to adopt new technologies or practices disrupts established workflows and slows the adoption of innovative solutions.
- Financial Barriers: Limited access to funding and resources impedes the development and implementation of innovative healthcare solutions, particularly for smaller organizations and startups.
- Fragmented Systems: Fragmentation within healthcare systems, including disjointed data systems and communication channels, complicates efforts to implement integrated care models and interoperable health IT solutions.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: The sensitive nature of healthcare data raises concerns about privacy and security, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures and adherence to strict data protection regulations.
- Medical Insurance Approval Challenges: Complex processes and stringent criteria for medical insurance approval create additional barriers for innovators, limiting the accessibility and affordability of innovative healthcare solutions for patients.
- Note: The introduction of innovative treatments that lower medical costs can sometimes conflict with the interests of insurers. This is because such advancements may result in reduced insurance premiums, impacting their profit margins.
Reasons that Add to These Difficulties
- Contaminated Evidence Base: Reliance on biased research findings or outdated clinical practices perpetuates ineffective treatment approaches, hindering innovation.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Insufficient investment in healthcare infrastructure limits the scalability and effectiveness of innovative solutions.
- Cultural Resistance: Deep-seated cultural norms within the healthcare industry resist change, hindering the adoption of innovative approaches.
- Limited Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Siloed approaches to innovation constrain creativity and limit the potential for groundbreaking solutions.
- Lack of Patient Engagement: Insufficient involvement of patients in the innovation process results in solutions that do not fully address patient needs or preferences.
How Startups Can Overcome These Issues
- Navigating Regulatory Challenges: Startups can leverage resources like regulatory consultants or accelerators specializing in healthcare to gain insights into navigating complex regulatory landscapes. Engaging in early communication with regulatory agencies to understand requirements and explore expedited pathways can also help.
- Embrace Agile Development: Startups should adopt agile development methodologies to iterate quickly, validate assumptions, and pivot when necessary. This approach allows for rapid adaptation to changing regulatory and market conditions.
- Seek Strategic Partnerships: Partnering with established healthcare organizations, academic institutions, or research centers can provide startups with access to expertise, resources, and networks that facilitate regulatory compliance and market access.
- Focus on MVP Development: Startups should prioritize developing minimum viable products (MVPs) to demonstrate proof of concept and gather feedback from stakeholders. This iterative approach allows startups to validate their solutions while conserving resources.
- Leverage Digital Health Platforms: Leveraging existing digital health platforms and interoperable solutions can help startups overcome infrastructure barriers and accelerate the adoption of their innovations. Cloud-based services and software-as-a-service (SaaS) models offer scalable and cost-effective solutions for data management and analytics.
- Invest in Compliance Expertise: Startups should invest in building internal expertise or partnering with compliance specialists to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and data privacy standards. Implementing robust compliance processes from the outset can streamline future regulatory submissions and audits.
- Stay Adaptive: Startups must remain adaptive in their approach, continuously monitoring regulatory developments, market trends, and customer feedback. Flexibility and responsiveness are key to navigating the dynamic healthcare landscape and overcoming regulatory hurdles.
- Utilize Real-World Evidence: Instead of relying solely on traditional clinical trials, startups can leverage real-world evidence and pragmatic study designs to generate data supporting the safety and efficacy of their innovations. Collaborating with healthcare providers to conduct pilot studies or observational research can strengthen the evidence base.
 Case Study: FDA Approval via Real-World Evidence
Case Study: FDA Approval via Real-World Evidence - Company: Pear Therapeutics, Boston, USA
- Date: reSET® & reSET-O®
- What Was Done: FDA Approval in 2017 and 2018
- What Was Done: Pear Therapeutics utilized real-world evidence alongside traditional clinical trials to gain FDA approval for its digital therapeutics platforms, reSET® and reSET-O®. These platforms are designed to assist in the treatment of substance use disorder and opioid use disorder, respectively. The company collaborated with healthcare providers to conduct observational studies and gather data on the platforms’ effectiveness in real-world settings.
- Results/Impact: The use of real-world evidence was instrumental in demonstrating the practical benefits and safety of reSET® and reSET-O®, leading to their approval by the FDA. This marked a significant milestone as one of the first instances of digital therapeutics receiving such approval. The evidence gathered provided strong support for the platforms’ efficacy in improving patient outcomes when used alongside standard care. As a result, these digital therapeutics have become accessible to a wider patient population, offering a novel approach to managing and treating substance use disorders.
In conclusion, while innovation in healthcare presents formidable challenges, addressing these obstacles is essential for driving progress and improving patient outcomes. By understanding the root causes of these difficulties and implementing strategies to overcome them, stakeholders across the healthcare ecosystem can foster a culture of innovation and realize the full potential of transformative healthcare solutions. Together, we can navigate the complexities of healthcare innovation and pave the way for a healthier future.
Innovation in Education
Innovation in education is essential for preparing students for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. With rapid advancements in technology, changes in workforce demands, and evolving educational paradigms, there's a growing need for innovative approaches to teaching, learning, and educational administration. Educational innovation encompasses a wide range of initiatives, including the development of new instructional methods, the integration of technology in the classroom, and the redesign of educational systems to promote equity, access, and lifelong learning.
Breakthrough Inventions for Education:
- Kahoot!: Gamified learning platform that engages students through quizzes, surveys, and games, making learning fun and interactive.
- Edmodo: Social learning network for teachers, students, and parents - to collaborate, share resources, and facilitate communication.
- Labster: Virtual laboratory simulations that enable students to conduct experiments and explore scientific concepts in a safe and immersive environment.
- Coursera: Offering online courses, specializations, and degrees from universities and colleges around the world, making higher education accessible to a global audience.
- Quizlet: Provides learning tools for students, including flashcards, study and game modes, making studying engaging and effective across a multitude of subjects.
 Case Study: Duolingo's Gamified Language Learning
Case Study: Duolingo's Gamified Language Learning
- Company: Duolingo, Pittsburgh, USA (Launched in 2012)
- What Was Done: Duolingo created a platform that uses gamification to teach languages. The app offers bite-sized lessons in a game-like format, making learning more interactive and engaging.
- Results/Impact: Duolingo has made language learning accessible to millions worldwide, promoting language education and cultural exchange. Its success illustrates the impact of innovative educational tools in global learning.
How to Apply Innovation for Education:
- Embrace Blended Learning: Integrate traditional face-to-face instruction with online and digital learning resources to create flexible and personalized learning experiences (e.g. – microlearning).
- Promote Student-Centered Learning: Empower students to take ownership of their learning by providing opportunities for inquiry-based learning, project-based learning, and self-directed learning.
- Harness Educational Technology: Leverage educational technology tools such as learning management systems, interactive whiteboards, and educational apps to enhance teaching effectiveness and student engagement.
- Foster Collaborative Learning: Facilitate collaboration, teamwork, and peer learning opportunities to promote critical thinking, communication skills, and social-emotional development.
- Cultivate a Culture of Innovation: Encourage educators to experiment with new teaching methods, pedagogical approaches, and instructional technologies to foster creativity, curiosity, and lifelong learning among students.
 Case Study: ClassDojo's Classroom Communication
Case Study: ClassDojo's Classroom Communication
- Company: ClassDojo, San Francisco, USA (Launched in 2011)
- What Was Done: ClassDojo developed an educational technology communication app. It connects primary school teachers, students, and families through communication features like photos, videos, and messages to share classroom moments.
- Results/Impact: ClassDojo has fostered a positive culture and community between teachers, students, and parents. The platform is used in 95% of U.S. K-8 schools and in 180 countries, enhancing the educational experience by promoting engagement and collaboration.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Education:
- Customization and Personalization: Educational innovation seeks to tailor learning experiences to meet the unique needs, interests, and learning styles of individual students, fostering personalized learning pathways and differentiated instruction.
- Note: When applying personalized education, factors to consider include age, gender, generation, language, cultural background, learning style, prior knowledge, motivation levels, disabilities or special needs, socio-economic status, country or region of residence, digital literacy, career interests, educational goals, and psychological factors such as attention span and memory capacity.
- Note: When applying personalized education, factors to consider include age, gender, generation, language, cultural background, learning style, prior knowledge, motivation levels, disabilities or special needs, socio-economic status, country or region of residence, digital literacy, career interests, educational goals, and psychological factors such as attention span and memory capacity.
- Interdisciplinary Integration: Educational innovation encourages interdisciplinary collaboration and integration across subjects, disciplines, and learning domains to promote holistic and interconnected learning experiences.
- Lifelong Learning Focus: Educational innovation emphasizes the importance of continuous learning and skill development throughout life to adapt to changing societal needs and technological advancements.
- Equity and Inclusion: Educational innovation aims to address disparities in educational access, quality, and outcomes by promoting equitable opportunities for all learners, regardless of their background, abilities, or socioeconomic status.
- Community and Global Engagement: Educational innovation promotes community partnerships, global connections, and real-world applications of learning to enrich educational experiences and foster civic engagement and global citizenship.
What to Avoid When Inventing for Education:
- Ignoring Pedagogical Principles: Ensure that educational innovations align with evidence-based pedagogical principles and learning theories to promote effective teaching and learning outcomes.
- Overreliance on Technology: Avoid overemphasizing technology as a substitute for effective teaching practices and human interaction, recognizing that technology should enhance, not replace, the role of educators and facilitators in the learning process.
- Neglecting Accessibility and Inclusivity: Consider the diverse needs, abilities, and backgrounds of learners and ensure that educational innovations are accessible, inclusive, and responsive to diverse learners' needs.
- Resistance to Change: Address resistance to change among educators, students, and stakeholders by fostering a culture of innovation, providing professional development opportunities, and communicating the benefits and rationale for educational innovations.
- Lack of Evaluation and Assessment: Conduct ongoing evaluation and assessment of educational innovations to measure their effectiveness, identify areas for improvement, and inform evidence-based decision-making and continuous improvement efforts.
Innovation in education holds the promise of transforming teaching and learning, empowering educators, inspiring students, and preparing them for success in an increasingly complex and interconnected world. By embracing innovation and creativity in education, we can create more engaging, equitable, and effective learning experiences that unlock the full potential of every learner.

Why Innovation is Important in Education
Innovation in education is instrumental in shaping the future of learning, equipping students with the skills, knowledge, and values needed to thrive in an ever-evolving world. By fostering creativity, critical thinking, and adaptability, innovative approaches to education empower learners to navigate complex challenges and unlock their full potential. Let's explore why innovation is crucial in education and how it drives positive outcomes for students, educators, and society as a whole.
Why is Innovation in Education Crucial to Enhance Learning and Knowledge
- Personalized Learning: Innovative educational technologies, such as adaptive learning platforms and AI-powered tutoring systems, tailor instruction to individual learning styles and preferences, optimizing learning outcomes and knowledge retention.
- Project-Based Learning: Embracing project-based learning approaches fosters hands-on exploration, collaboration, and problem-solving skills, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios and deepen their understanding of concepts.
- Experiential Learning Opportunities: Innovations like virtual reality (VR) simulations, augmented reality (AR) experiences, and immersive learning environments provide immersive and engaging learning experiences that enhance comprehension and retention of complex concepts.
- Global Connectivity: Digital platforms and online learning communities connect students and educators across geographical boundaries, facilitating cross-cultural exchange, collaboration, and exposure to diverse perspectives, thereby enriching learning experiences.
- Gamification and EdTech Tools: Gamified learning platforms and educational apps leverage game mechanics and interactive elements to make learning engaging and enjoyable, motivating students to actively participate and pursue mastery of academic content.
Why is Innovation in Education Crucial to Enhance Values and Motivation:
- Character Development: Innovative educational programs and initiatives prioritize the holistic development of students, fostering essential values such as empathy, resilience, and integrity, which are integral to success in academic and professional contexts.
- Growth Mindset Cultivation: Promoting a growth mindset through innovative teaching practices encourages students to embrace challenges, learn from failure, and persist in the face of obstacles, fostering a positive attitude towards learning and personal development.
- Inclusive Learning Environments: Equity-centered innovations in education aim to address systemic barriers and create inclusive learning environments where all students feel valued, supported, and empowered to succeed, regardless of their backgrounds or abilities.
- Student Agency and Empowerment: Empowering students as active participants in their learning journey through self-directed inquiry, choice-based assignments, and project ownership promotes autonomy, self-efficacy, and intrinsic motivation.
- Real-World Relevance: Integrating real-world contexts, issues, and challenges into the curriculum through innovative teaching methods and community partnerships enhances student engagement, relevance, and motivation to learn, bridging the gap between classroom learning and practical application.
Other Benefits of Innovation in Education
- Lifelong Learning Culture: Fostering a culture of innovation in education cultivates a lifelong learning mindset among students, educators, and communities, enabling continuous growth, adaptation, and skill development in a rapidly changing world.
- Teacher Professional Development: Investing in innovative professional development programs and resources empowers educators to embrace new pedagogical approaches, technologies, and instructional strategies that enhance their effectiveness and job satisfaction.
- Social and Emotional Learning (SEL): Integrating SEL competencies, such as self-awareness, social awareness, and responsible decision-making, into the curriculum through innovative teaching practices promotes emotional well-being, resilience, and positive social interactions among students.
- Community Engagement and Collaboration: Leveraging community partnerships and innovative outreach initiatives strengthens school-community connections, fosters mutual trust and respect, and enriches learning experiences through authentic, real-world connections.
- Career Readiness and Future Preparedness: Equipping students with 21st-century skills, including digital literacy, critical thinking, and collaboration, through innovative educational programs ensures they are well-prepared for success in higher education, careers, and civic engagement.
Consequences of Stagnant Education
- Inadequate Preparation for Future Challenges: Stagnant education systems fail to equip students with the skills, knowledge, and competencies needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving world, leaving them ill-prepared for future academic, professional, and personal challenges.
- Achievement Gaps and Inequities: A lack of innovation exacerbates existing achievement gaps and inequities in education, perpetuating systemic barriers that hinder access to quality learning opportunities and limit upward mobility for marginalized students.
- Disengagement and Dropout Rates: Monotonous, outdated instructional methods and irrelevant curriculum content contribute to student disengagement, boredom, and apathy, increasing the risk of dropout and underachievement, particularly among vulnerable student populations.
- Skills Mismatch and Unemployment: Failure to adapt educational practices to meet the changing demands of the labor market results in a skills mismatch, where graduates lack the competencies required for available job opportunities, leading to unemployment and underemployment.
- Diminished Innovation and Economic Growth: A stagnant education system stifles creativity, innovation, and entrepreneurship, depriving societies of the talent, ideas, and solutions needed to drive economic growth, social progress, and global competitiveness.
In conclusion, innovation in education is not merely a means to enhance learning outcomes or academic achievement; it is a fundamental driver of social change, economic prosperity, and human flourishing. By embracing innovative approaches to teaching, learning, and educational leadership, we can create transformative learning experiences that empower individuals to reach their full potential, contribute meaningfully to society, and shape a brighter future for generations to come.

Innovation in Marketing
Innovation in marketing is essential for businesses to stay competitive, relevant, and responsive to changing consumer preferences and market dynamics. With the advent of digital technology, social media, and data analytics, traditional marketing approaches are being revolutionized, giving rise to new strategies, channels, and customer engagement models. Successful marketing innovation involves creatively leveraging emerging technologies, data-driven insights, and customer-centric approaches to deliver personalized, memorable, and impactful brand experiences.
Breakthrough Inventions for Digital Marketing
- ChatGPT Ads: AI-powered advertising platform that generates personalized ad copy based on user preferences, behaviors, and interactions.
- Voice Search Optimization: Optimization strategies for voice search queries to enhance brand visibility and accessibility in voice-enabled devices and virtual assistants.
- Augmented Reality Try-Ons: AR technology that enables consumers to virtually try on products like clothing, accessories, or cosmetics before making a purchase.
- Blockchain-based Loyalty Programs: Decentralized loyalty programs that use blockchain technology to track and reward customer engagement and brand advocacy transparently and securely.
- Interactive Billboards: Leveraging high-tech features in billboards, such as touch screens, QR codes, and augmented reality, to create engaging and memorable experiences in public spaces.
- TikTok Brand Takeovers: Short-form video advertising format that allows brands to showcase their products or services through immersive, full-screen ads.
 Case Study: HubSpot's Inbound Marketing Software
Case Study: HubSpot's Inbound Marketing Software
- Company: HubSpot, Cambridge, USA (Founded in 2006)
- What Was Done: HubSpot offers a full platform of marketing, sales, customer service, and CRM software, plus the methodology, resources, and support to help businesses grow better.
- Results/Impact: HubSpot has been instrumental in shifting business marketing strategies from traditional outbound methods to inbound marketing, attracting customers through content tailored to them.
Non-digital Breakthroughs in Traditional Marketing
Despite the dominance of digital channels, the following inventions demonstrate the enduring value and innovation within non-digital marketing as well.
- Experiential Pop-Up Events: Brands create temporary, immersive experiences in physical locations to engage directly with consumers, generating buzz and fostering a deeper emotional connection.
- Note: Nowadays, creating buzz invariably incorporates marketing channels like Facebook and Twitter. Therefore, advertisers should be savvy in facilitating and promoting social media engagement as an integral part of physical campaigns.
- Note: Nowadays, creating buzz invariably incorporates marketing channels like Facebook and Twitter. Therefore, advertisers should be savvy in facilitating and promoting social media engagement as an integral part of physical campaigns.
- Scent Marketing: Leveraging the power of smell to enhance brand identity and customer experience, businesses use strategic scents within physical spaces to evoke specific emotions, memories, and perceptions, thereby influencing purchasing decisions.
- Handwritten Direct Mail: Personalizing direct mail campaigns with handwritten notes to stand out in the recipient's mailbox, creating a personal touch that increases engagement and response rates.
- Guerrilla Marketing Tactics: Innovative and unconventional marketing strategies that create immersive, unexpected experiences in the real world, generating buzz and virality.
- In-depth Interviews: Utilizing detailed, personal interviews with consumers to gain profound insights into their preferences, behaviors, and attitudes, informing more targeted and effective marketing strategies.
- Ambient Advertising: Creative use of the environment to present ads in unexpected places, turning everyday objects and locations into compelling advertisements that capture attention in a subtle yet impactful way.
 Example: Ambient Advertising
Example: Ambient Advertising- Brand: Mondo Pasta
- Message: So good you can't let go!
- Agency: Jung von Matt
- Location: Hamburg, Germany
- More about this: Here
How to Apply Innovation for Marketing
- Embrace Data-driven Insights: Leverage data analytics, machine learning, and predictive modeling to gain deeper insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and trends, enabling more targeted and personalized marketing campaigns.
- Adopt Agile Marketing Practices: Embrace agile marketing methodologies and iterative testing to rapidly prototype, launch, and optimize marketing initiatives in response to real-time feedback and market dynamics.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Prioritize customer-centricity and focus on delivering seamless, personalized, and omni-channel brand experiences that exceed customer expectations and foster brand loyalty.
- Experiment with Emerging Technologies: Explore emerging technologies such as AR, VR, AI, and IoT to create immersive, interactive, and memorable brand experiences that captivate and engage consumers.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Foster cross-functional collaboration and partnerships between marketing, product development, sales, and customer service teams to align strategies, share insights, and deliver integrated brand experiences across the customer journey.
Case Study: Canva's Democratization of Design
- Company: Canva, Sydney, Australia (Launched in 2013)

- What Was Done: Canva developed a user-friendly graphic design tool that offers a drag-and-drop interface and a vast library of templates. It has enabled anyone to create professional-quality graphic designs.
- Results/Impact: Canva has changed the way small businesses, entrepreneurs, and even individuals approach graphic design for marketing, enabling the creation of high-quality visual content without the need for extensive design skills.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Marketing
- Measurable Impact and ROI: Marketing innovation is results-driven and focused on delivering measurable business impact and return on investment (ROI) through metrics such as customer acquisition, engagement, retention, and lifetime value.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Marketing innovation requires a culture of continuous learning, adaptation, and agility, where marketers embrace change, iterate on ideas, and learn from successes and failures.
- Creative Experimentation and Risk-taking: Marketing innovation involves creative experimentation, risk-taking, and a willingness to challenge conventional wisdom and explore new ideas, strategies, and channels.
- Dynamic and Evolving Landscape: Marketing innovation thrives in a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape characterized by technological advancements, shifting consumer behaviors, and emerging market trends.
- Ethical and Responsible Practices: Marketing innovation prioritizes ethical and responsible practices, including transparency, privacy, data security, and compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices.
What to Avoid When Inventing for Marketing:
- Ignoring Customer Insights: Avoid overlooking or disregarding customer insights, feedback, and preferences when developing marketing strategies, campaigns, and messaging.
- Overlooking Brand Authenticity: Ensure that marketing innovations align with the brand's values, identity, and promise to maintain authenticity, credibility, and trust with consumers.
- Neglecting Omnichannel Integration: Avoid siloed or disjointed marketing efforts by ensuring seamless integration and consistency across multiple channels, touchpoints, and interactions.
- Relying Solely on Technology: Guard against over-reliance on technology or automation at the expense of human connection, empathy, and emotional resonance in marketing communications and experiences.
- Losing Sight of Long-term Goals: Maintain a balance between short-term tactics and long-term strategic objectives in marketing innovation, avoiding short-sighted approaches that sacrifice long-term brand equity or customer relationships for immediate gains.
Innovation in marketing holds the potential to revolutionize how businesses connect with consumers, build brand awareness, and drive growth in an increasingly digital, connected, and competitive marketplace. By embracing creativity, data-driven insights, and customer-centricity, marketers can unlock new opportunities, break through traditional barriers, and shape the future of marketing in the digital age.

Innovation with Data
Innovation with data has emerged as a cornerstone of modern business strategy, empowering organizations to harness the power of data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to drive informed decision-making, enhance operational efficiency, and unlock new opportunities for growth and differentiation. With the exponential growth of data generated from various sources such as social media, IoT devices, and digital transactions, organizations are increasingly investing in innovative technologies, tools, and methodologies to extract actionable insights, drive predictive analytics, and optimize business processes across industries and sectors.
Breakthrough Inventions for Data Innovation:
- Snowflake Data Cloud: Data cloud platform that enables organizations to securely store, manage, and analyze massive volumes of data from disparate sources in real-time.
- DataRobot Automated Machine Learning: Automated machine learning platform that democratizes AI and empowers organizations to build, deploy, and manage predictive models without requiring extensive data science expertise.
- Databricks Unified Analytics Platform: Unified analytics platform that combines data engineering, data science, and machine learning capabilities to accelerate innovation and collaboration across data-driven teams.
- Tableau Augmented Analytics: Augmented analytics platform that leverages AI and natural language processing to automate data analysis, visualization, and insights generation for business users.
- Alation Data Catalog: Data catalog and governance platform that enables organizations to discover, catalog, and collaborate on data assets while ensuring data quality, security, and compliance.
 Case Study: Palantir's Data Integration Platforms
Case Study: Palantir's Data Integration Platforms
- Company: : Palantir Technologies, Denver, USA (Founded in 2003)
- What Was Done: Palantir develops software that integrates, manages, and secures data, assisting organizations in data-driven decision-making. Their platforms are used for data analytics in various sectors including government, healthcare, and finance.
- Results/Impact: Palantir has played a critical role in fraud detection, disease tracking, and cybersecurity. Their software aids in uncovering patterns and insights hidden in complex data sets, influencing significant decisions and strategies.
How to Apply Innovation for Data:
- Define Clear Objectives: Start by defining clear business objectives and use cases for data innovation initiatives to ensure alignment with organizational goals and priorities.
- Access Exclusive Data Sources: Ensure acquisition of exclusive and distinctive data collections, emphasizing the importance of proprietary information that sets your analytics apart from competitors.
- Invest in Data Infrastructure: Build robust data infrastructure and architecture that can scale, integrate diverse data sources, and support advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning capabilities.
- Leverage Advanced Analytics: Embrace advanced analytics techniques such as predictive modeling, prescriptive analytics, and anomaly detection to extract actionable insights and drive data-driven decision-making.
- Promote Data Literacy: Foster a culture of data literacy and continuous learning within the organization by providing training, resources, and tools to empower employees at all levels to understand, interpret, and leverage data effectively.
- Collaborate Across Functions: Encourage cross-functional collaboration between data science, IT, business operations, and other departments to identify opportunities, share insights, and drive innovation with data-driven solutions.
Case Study: Looker's Business Intelligence and Big Data Analytics
- Company: Looker, Santa Cruz, USA
- Timeline: Founded in 2012, Acquired by Google in 2020
- What Was Done: Looker provided an innovative platform for data exploration and insights, enabling businesses to capture and analyze data from multiple sources and make data-driven decisions.
- Results/Impact: Looker allows smaller companies to harness the power of big data, leading to smarter business operations and strategies. Despite its acquisition, Looker's beginnings as a small company showcase the impactful innovation in data handling and visualization.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Data
- Data-driven Decision Making: Data innovation prioritizes evidence-based decision-making, enabling organizations to move from intuition and gut feeling to data-driven insights and analytics.
- Continuous Iteration and Improvement: Data innovation involves a process of continuous iteration, experimentation, and improvement, where organizations refine and optimize their data strategies, models, and algorithms over time.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Data innovation thrives on interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together diverse expertise, perspectives, and skill sets from fields such as data science, statistics, computer science, and domain-specific domains.
- Ethical and Responsible Data Use: Data innovation emphasizes ethical and responsible data use, including privacy protection, data security, transparency, and fairness in algorithmic decision-making.
- Agility and Adaptability: Data innovation requires agility and adaptability to rapidly respond to changing business requirements, market dynamics, and technological advancements while staying ahead of the competition.
What to Avoid When Inventing with Data:
- Ignoring Data Quality: Avoid overlooking data quality issues such as inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and biases that can undermine the reliability and validity of data-driven insights and decisions.
- Overlooking Privacy and Compliance: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA to safeguard customer privacy and mitigate legal and reputational risks associated with data misuse or mishandling.
- Neglecting Security Measures: Implement robust data security measures such as encryption, access controls, and threat detection to protect sensitive data assets from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats.
- Underestimating Change Management: Recognize the importance of change management and stakeholder buy-in when implementing data innovation initiatives, as resistance to change or lack of adoption can hinder success and ROI.
- Failing to Measure Impact: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure the impact and effectiveness of data innovation efforts, ensuring accountability, transparency, and continuous improvement.
Innovation with data holds the promise of unlocking new insights, opportunities, and value across organizations, industries, and sectors. By embracing a culture of data-driven innovation, organizations can gain a competitive advantage, drive business growth, and navigate the complexities of the digital age with confidence and agility.

Innovation for Equity
Innovation for equity and inclusion encompasses a range of initiatives, strategies, and solutions aimed at addressing systemic inequalities, promoting social justice, and ensuring fair and inclusive access to opportunities, resources, and services for all individuals and communities. It encompasses efforts to dismantle barriers to equity, including those related to race, gender, socioeconomic status, disability, and other dimensions of diversity, while fostering a culture of inclusivity, belonging, and empowerment. By harnessing the power of innovation, organizations, governments, and communities can drive positive change, advance equity agendas, and create a more just and equitable world for future generations.
Breakthrough Inventions for Equity:
- EqualAI: A platform that uses artificial intelligence to detect and mitigate bias in algorithms, decision-making processes, and digital experiences, promoting fairness and inclusivity in AI applications.
- Note: Note: Numerous AI and ML-based systems are developed using datasets that carry intrinsic biases related to gender, skin color, age, geographic location, and access, among others, leading to biased recommendations and outcomes for certain groups. EqualAI addresses and rectifies these biases, ensuring more equitable and fair AI applications.
- Note: Note: Numerous AI and ML-based systems are developed using datasets that carry intrinsic biases related to gender, skin color, age, geographic location, and access, among others, leading to biased recommendations and outcomes for certain groups. EqualAI addresses and rectifies these biases, ensuring more equitable and fair AI applications.
- Kiva: An online crowdfunding platform that facilitates microloans to entrepreneurs in underserved communities, empowering individuals to start or grow their businesses and achieve economic independence.
- Community Fridges: Community-led initiatives that provide free access to fresh food and essential supplies in food deserts and low-income neighborhoods, addressing food insecurity and promoting equitable access to nutritious food.
- DIAL Open Source Solutions: Open-source software solutions developed by the Digital Impact Alliance (DIAL) to improve access to digital tools and technologies for underserved populations in developing countries, enabling them to participate in the digital economy.
- Accessible Public Transportation: Innovations in public transportation design and infrastructure, such as low-floor buses, wheelchair ramps, and audiovisual announcements, to enhance accessibility and mobility for people with disabilities and elderly individuals.
Case Study: Salesforce's 1-1-1 Philanthropic Model
- Company: Salesforce, San Francisco, USA (Established in 1999)
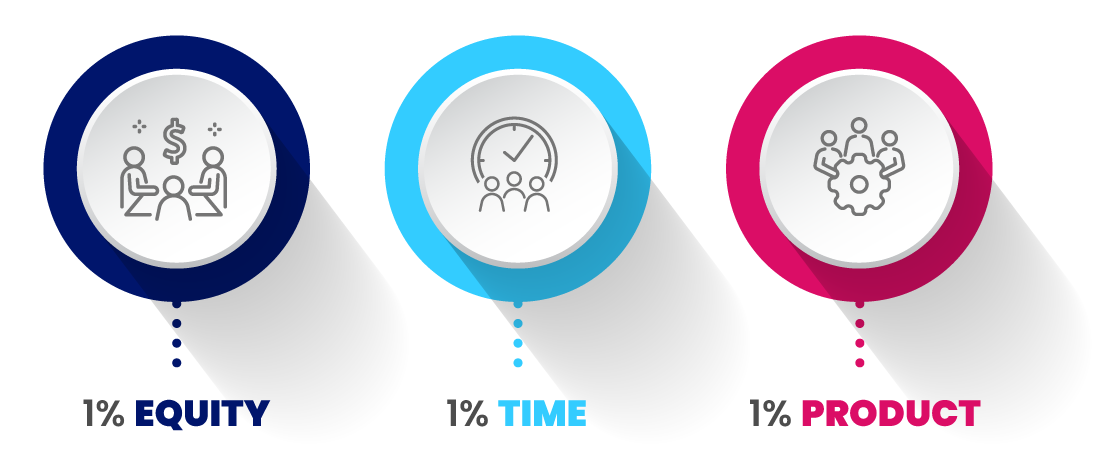
- What Was Done: Salesforce has pioneered the 1-1-1 model of philanthropy, which commits the company to contribute one percent of product, one percent of equity, and one percent of employee hours back to the community.
- Results/Impact: Salesforce's approach to corporate philanthropy has not only led to substantial community investment and involvement but has also set a precedent for other companies to incorporate equity into their business models, inspiring a trend towards social corporate responsibility.
How to Apply Innovation for Equity:
- Center Marginalized Voices: Prioritize the voices, perspectives, and needs of marginalized communities in the design, development, and implementation of equity initiatives to ensure relevance, authenticity, and impact.
- Note: Marginalized groups may represent significant portions of society, defined not by their numbers but by the presence of systemic biases against them. For instance, FemTech aims to counteract biases facing women, who constitute over half of the global population, demonstrating that marginalization is determined by common treatment rather than sheer population size.
- Note: Marginalized groups may represent significant portions of society, defined not by their numbers but by the presence of systemic biases against them. For instance, FemTech aims to counteract biases facing women, who constitute over half of the global population, demonstrating that marginalization is determined by common treatment rather than sheer population size.
- Collaborate Across Sectors: Foster partnerships and collaborations between government agencies, nonprofits, businesses, and community organizations to leverage collective resources, expertise, and networks to address equity challenges holistically.
- Use Data for Equity: Utilize data-driven approaches, including disaggregated data analysis and equity impact assessments, to identify disparities, measure progress, and inform evidence-based policy and program interventions.
- Promote Inclusive Innovation: Embrace human-centered design principles, participatory approaches, and co-creation methodologies to develop inclusive products, services, and solutions that meet the diverse needs of all stakeholders.
- Advocate for Policy Change: Advocate for policy reforms, legislative changes, and institutional reforms that advance equity agendas, dismantle systemic barriers, and promote social justice at local, national, and global levels.
Case Study: Warby Parker's Buy a Pair, Give a Pair Program
- Company: Warby Parker, New York, USA (Launched in 2010)

- What Was Done: Warby Parker initiated a program where for every pair of glasses sold, a pair is distributed to someone in need, integrating a social mission directly into their business model.
- Results/Impact: The program has been hugely successful, with millions of pairs of glasses distributed worldwide. This initiative has not only helped address visual impairment in underserved populations but also established Warby Parker as a leader in socially responsible entrepreneurship.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Equity:
- Community Empowerment: Innovation for equity empowers individuals and communities to actively participate in decision-making processes, advocate for their rights, and drive social change from the grassroots level.
- Intersectional Approach: Equity innovation recognizes and addresses the intersectionality of social identities and experiences, acknowledging that individuals may face multiple forms of discrimination and oppression based on race, gender, class, sexuality, disability, and other intersecting factors, not just one.
- Cultural Competence: Equity innovation emphasizes cultural competence, humility, and responsiveness, recognizing and respecting diverse cultural norms, values, and traditions in designing and delivering equitable solutions.
- Systems Change: Equity innovation seeks to address root causes of inequity by challenging and transforming systemic structures, policies, and practices that perpetuate injustice and inequality in society.
- Long-Term Impact: Equity innovation aims to achieve sustainable, long-term impact by fostering systemic change, building resilience, and creating pathways for social mobility and economic empowerment for marginalized populations.
What to Avoid When Innovating for Equity:
- Tokenism: Avoid superficial inclusion of marginalized groups just to look inclusive. Ensure they're genuinely involved, represented, and have a say in decisions.
- Colorblindness: Avoid approaches that overlook the significance of race, ethnicity, and diversity in achieving fair outcomes. Ignoring these aspects can unintentionally support biases and maintain inequality.
- Savior Complex: Steer clear of narratives that depict privileged groups as the sole rescuers of marginalized communities, as this can perpetuate a sense of superiority and unequal power dynamics.
- Charity Mentality: Move beyond just offering temporary help to marginalized groups. Focus on tackling the root causes of inequality and encourage empowerment and independence.
- Failure to Listen: Ensure you actively listen and give importance to the voices and needs of marginalized communities in equity efforts, to avoid creating solutions that are irrelevant, ineffective, or harmful to those they intend to serve.
Innovation for equity represents a powerful force for social change and transformation, offering a pathway to build more inclusive, just, and resilient societies for all. By embracing innovative approaches, fostering collaboration, and advocating for systemic change, we can create a future where equity is not just an aspiration but a reality for everyone, regardless of their background, identity, or circumstances.

Innovation for Justice
Innovation for justice encompasses a wide range of initiatives, technologies, and strategies aimed at advancing fairness, access, and effectiveness within the legal system. It seeks to address systemic barriers to justice, including inequities in legal representation, access to information, procedural complexities, and disparities in outcomes based on socioeconomic status, race, gender, or other factors. By leveraging technology, data, and collaborative approaches, innovation for justice endeavors to enhance legal processes, increase transparency, and empower individuals to navigate the legal system more effectively, ultimately promoting the rule of law and upholding fundamental rights and liberties.
Breakthrough Inventions for Justice
- Legal Aid Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots, such as DoNotPay, that provide legal assistance, guidance, and resources to individuals facing legal issues, including landlord-tenant disputes, traffic tickets, and consumer rights violations, democratizing access to legal information and support.
- Blockchain for Legal Identity: Blockchain-based solutions, like ID2020, that enable secure and verifiable digital identity management, particularly for marginalized populations, refugees, and stateless individuals, enhancing access to essential services, legal protections, and economic opportunities.
- Online Dispute Resolution Platforms: Platforms like Modria (now part of Tyler Technologies) that offer online mediation and arbitration services for resolving civil disputes, small claims, and family matters, streamlining case management, reducing backlog, and improving access to justice for litigants.
- Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment: Tools like COMPAS (Correctional Offender Management Profiling for Alternative Sanctions) that use algorithms and data analytics to assess the risk of recidivism and inform sentencing decisions, aiming to mitigate bias, promote fairness, and optimize resource allocation within the criminal justice system.
- Community-Based Restorative Justice Programs: Innovations in restorative justice practices, such as Community Conferencing, which engage victims, offenders, and community members in collaborative dialogue, healing, and accountability processes, fostering reconciliation, rehabilitation, and community resilience.
 Case Study: Ravel Law's Legal Analytics Software
Case Study: Ravel Law's Legal Analytics Software
- Company: Ravel Law, San Francisco, USA (Founded in 2012)
- Owner: Acquired by LexisNexis in 2017
- What Was Done: Ravel Law developed an advanced legal analytics platform that uses AI to provide lawyers with strategic insights into court opinions and the behavior of judges.
- Results/Impact: Ravel Law's innovation has equipped attorneys with tools to make more informed decisions, strategize on cases, and anticipate outcomes, enhancing the pursuit of justice through data-driven insights.
How to Apply Innovation for Justice
- Promote Legal Empowerment: Empower individuals and communities to understand their rights, access legal information, and navigate the legal system through legal literacy programs, community outreach, and technology-enabled self-help tools.
- Leverage Open Data: Open and transparent data initiatives can enhance accountability, facilitate research and analysis, and inform evidence-based policy-making and advocacy efforts to address systemic injustices and gaps in legal services.
- Invest in Technology: Invest in research, development, and deployment of technology solutions, including AI, blockchain, and data analytics, to improve legal service delivery, enhance efficiency, and expand access to justice for underserved populations.
- Strengthen Legal Aid: Expand funding, resources, and infrastructure for legal aid organizations, pro bono networks, and public defenders to provide free or low-cost legal assistance to individuals and communities in need, ensuring equal access to justice regardless of income or status.
- Foster Cross-Sector Collaboration: Foster partnerships and collaborations between legal professionals, technology experts, civil society organizations, government agencies, and academic institutions to co-create innovative solutions, share best practices, and drive systemic change in the justice sector.
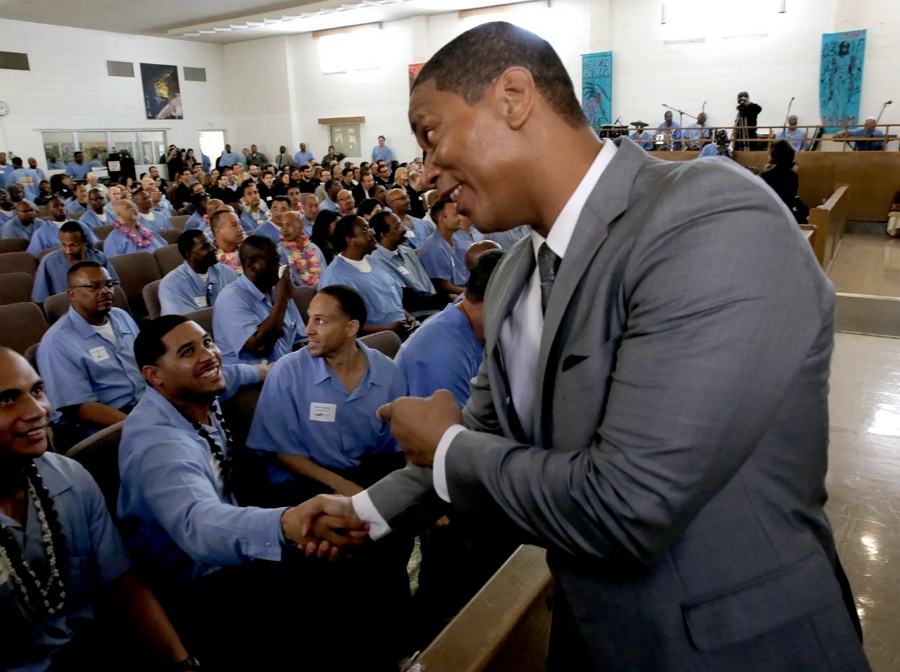 Case Study: The Last Mile’s Education Program in Prisons
Case Study: The Last Mile’s Education Program in Prisons
- Company: The Last Mile, San Francisco, USA (Founded in 2010)
- What Was Done: The Last Mile created the first computer programming curriculum for prisoners in the United States, providing education and vocational training to incarcerated individuals.
- Results/Impact: The program has significantly reduced recidivism rates for participants and has helped many formerly incarcerated individuals start careers in tech, demonstrating that education and opportunity can effectively contribute to justice reform.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Justice
- Human-Centered Design: Prioritize the needs, experiences, and perspectives of end-users, including litigants, legal professionals, and marginalized communities, in designing and implementing justice innovations to ensure relevance, usability, and effectiveness.
- Procedural Fairness: Emphasize procedural fairness, transparency, and accountability in legal processes and decision-making, including judicial proceedings, alternative dispute resolution mechanisms, and law enforcement practices, to uphold the rule of law and public trust in the justice system.
- Cultural Competence: Recognize and respect diverse cultural norms, values, and legal traditions in justice innovations, particularly in multicultural and pluralistic societies, to ensure equitable access to justice and promote cultural sensitivity and responsiveness.
- Trauma-Informed Approaches: Integrate trauma-informed principles and practices into legal services, including victim support, offender rehabilitation, and court proceedings, to address the impact of trauma on individuals' interactions with the legal system and promote healing and recovery.
- Community Engagement: Engage communities, stakeholders, and affected populations in participatory decision-making, policy development, and implementation of justice innovations to build trust, foster collaboration, and promote social cohesion and collective action.
What to Avoid When Innovating for Justice
- Marginalizing Stakeholder Voices: Avoid marginalizing or excluding the voices, experiences, and expertise of affected communities, justice practitioners, and civil society organizations in the design, development, and implementation of justice innovations, which can undermine legitimacy, trust, and social acceptance of reforms.
- Tech-Driven Solutions: Avoid over-reliance on technology as a panacea for complex justice challenges, recognizing the limitations and potential biases inherent in algorithmic decision-making and digital platforms, and the importance of human oversight and accountability.
- One-Size-Fits-All Approaches: Avoid adopting standardized or uniform justice solutions that fail to account for the diverse needs, contexts, and legal systems of different communities, cultures, and jurisdictions, and may exacerbate existing disparities and inequities.
- Disregarding Ethical Considerations: Avoid compromising ethical principles, human rights, and constitutional protections in the pursuit of justice innovations, including privacy, due process, and non-discrimination, to prevent unintended consequences and harm to vulnerable populations.
- Underestimating Implementation Challenges: Avoid underestimating the complexities and challenges of implementing justice innovations in real-world settings, including legal, institutional, cultural, and political barriers, and the need for ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation to ensure effectiveness and sustainability.
Innovation for justice holds the potential to transform legal systems, empower marginalized communities, and advance human rights and social justice agendas worldwide. By embracing human-centered design, leveraging technology, fostering collaboration, and upholding ethical standards, we can create more equitable, inclusive, and effective justice systems that uphold the rule of law, protect fundamental rights, and promote dignity and equality for all.

Where Innovation Meets the Law
The intersection of innovation and law is a complex and dynamic terrain where the cutting edge of human creativity meets the principles of regulation. The legal system, often perceived as traditional and resistant to change, plays a critical role in nurturing and shaping the trajectory of innovation. It provides the structure and protection that innovations need to flourish while ensuring public interests are safeguarded. The balance struck here is crucial for progress, as it can either stimulate or stifle the innovative spirit.
Innovation in Creating Laws
- Predictive Lawmaking: Applying data analytics to predict the impact of laws and shape them proactively.
- Automated Legal Drafting: Using AI to draft legislation and legal documents, increasing efficiency and reducing human error.
- Crowdsourced Legislation: Utilizing technology to involve the public in the legislative process, making it more participatory and inclusive.
- Blockchain for Record-Keeping: Implementing blockchain to enhance the transparency and traceability of legal documents.
- Smart Contracts: Automating contract execution in the blockchain to ensure self-enforcing legal agreements.
Innovation in Enforcing Laws
- Tech-Enhanced Surveillance: Integrating advanced technologies into surveillance to deter crime and enhance the investigative process.
- Digital Forensics: Evolving the field of forensics to tackle cybercrime, employing advanced technologies to trace digital activities.
- AI in Legal Analysis: Leveraging AI to assist in case analysis, evidence sorting, and legal research to support law enforcement.
- Online Dispute Resolution: Offering digital platforms for resolving disputes, making justice more accessible and efficient.
- E-Policing Tools: Developing new tools for law enforcement agencies to improve public safety and responsiveness.
 Case Study: Implementing ShotSpotter in Chicago
Case Study: Implementing ShotSpotter in Chicago
- Organization: ShotSpotter at Chicago, USA (Rolled out in 2012)
- What Was Done: The City of Chicago, in partnership with ShotSpotter (a NASDAQ listen company), implemented an advanced e-policing tool designed to detect and locate gunfire in real-time. ShotSpotter uses acoustic sensors placed across the city to instantly analyze sounds, identify gunshots, and alert law enforcement agencies with precise locations of shootings, often before any calls to 911 are made.
- Results/Impact: The implementation of ShotSpotter in Chicago led to a notable improvement in the police department's ability to respond quickly to gun violence incidents. According to reports, the system enabled law enforcement to arrive at shooting scenes more promptly and efficiently, sometimes even before being notified by the public. This rapid response capability has been credited with saving lives and has contributed to a more proactive approach to gun violence in the city. Additionally, the data collected by ShotSpotter has been used to analyze shooting patterns, helping to deploy resources more strategically and work towards preventing violence before it happens.
Trade-off between Conservatism and Reformism in Law Regulatory
- Sandboxes: Allowing limited testing of innovations in a controlled environment to assess the need for new regulations.
- Adaptive Legislation: Creating laws that can adapt to technological progress without needing constant amendments.
- Precedent vs. Innovation: Balancing the respect for legal precedent with the need for new legal paradigms to regulate unprecedented technologies.
- Data Privacy vs. Open Data: Navigating the tension between protecting individual privacy and promoting the openness of data for innovation.
- Ethics in Innovation: Ensuring that the drive for innovation is balanced with ethical considerations and societal values.
Case Study: Clio's Cloud-Based Legal Practice Management
- Company: Clio, Vancouver, Canada (Launched in 2007)
- What Was Done: Clio offers cloud-based legal practice management software to help law firms manage their operations, with tools for case management, billing, client intake, and more.
- Results/Impact: Clio has become a leader in transforming legal practices worldwide. Their platform has streamlined operations for law firms, enhancing efficiency, client service, and profitability. The impact of Clio's innovation is evident in its widespread adoption, with legal professionals in over 90 countries relying on its comprehensive suite of tools. The company's success highlights the potential of cloud technology to revolutionize traditionally conservative industries by improving access to information and services.
International Law in the Age of Global Innovation
- Global Innovation Collaboration: Creating legal frameworks that support international research and development partnerships.
- Global IP Enforcement: Harmonizing intellectual property laws to protect innovations across borders.
- Cross-Border Data Flow Regulations: Navigating the complexities of data sovereignty and international data transfer rules.
- Tech Export Controls: Implementing regulations on the export of sensitive technologies to balance innovation with national security.
- International Cybersecurity Standards: Establishing shared cybersecurity protocols to safeguard innovations in a connected world.
Legal Tech Startups: Disrupting the Legal Industry
- Blockchain for Legal Contracts: Utilizing blockchain to create and enforce tamper-proof contracts.
- Legal Process Automation: Streamlining routine legal tasks with automation to increase efficiency and save costs.
- E-Discovery Innovations: Enhancing the process of electronic discovery in litigation with new software solutions.
- AI-Powered Legal Research: Developing platforms that use AI to revolutionize how legal research is conducted.
- Online Legal Services: Providing accessible legal advice and services through online platforms.
 Case Study: LegalZoom's Online Legal Services
Case Study: LegalZoom's Online Legal Services
- Company: LegalZoom, Glendale, USA (Launched in 2001)
- What Was Done: LegalZoom was one of the first companies to provide online legal services such as document preparation and filing, offering an accessible alternative to traditional legal consultation.
- Results/Impact: LegalZoom has served millions of customers, disrupting the legal industry by making legal services more accessible and affordable, and influencing the way legal support is provided.
Legal Aspects of Inventions
- Intellectual Property Rights: Safeguarding inventors’ creations to encourage continued innovation and fair competition in the marketplace.
- Patent Law Evolution: Continuous updates to patent laws to better protect technological advancements and software innovations.
- Licensing Agreements: Crafting agreements that allow for the sharing of innovations while protecting proprietary interests.
- Liability Issues: Addressing the complexities of liability in new technologies, such as AI decision-making and autonomous vehicles.
- Compliance Standards: Establishing standards to ensure new products and innovations align with existing laws and ethical guidelines.
Intellectual Property in the Digital Age
- IP and Open Source: Balancing protection of IP with the benefits of open-source collaboration.
- User-Generated Content Rights: Determining ownership and liability for user-generated content on digital platforms.
- Patenting Software Innovations: Defining and refining the patentability of software and algorithms.
- Digital Copyright Challenges: Addressing the implications of digital sharing and content reproduction on copyright law.
- Trademarks in Cyberspace: Managing and enforcing trademarks in the digital marketplace.
The dance between innovation and law is intricate, requiring a nuanced understanding of both the promise of new technologies and the importance of regulation. While the law can act as a sturdy framework within which innovation can safely and confidently progress, it must also be flexible enough to evolve with the rapid pace of technological change.
What Innovation Changed the Textile Industry
The textile industry has seen numerous transformative innovations over its long history, but few have had as profound an impact as the Industrial Revolution's spinning jenny and the modern era's digital printing techniques.
The Spinning Jenny
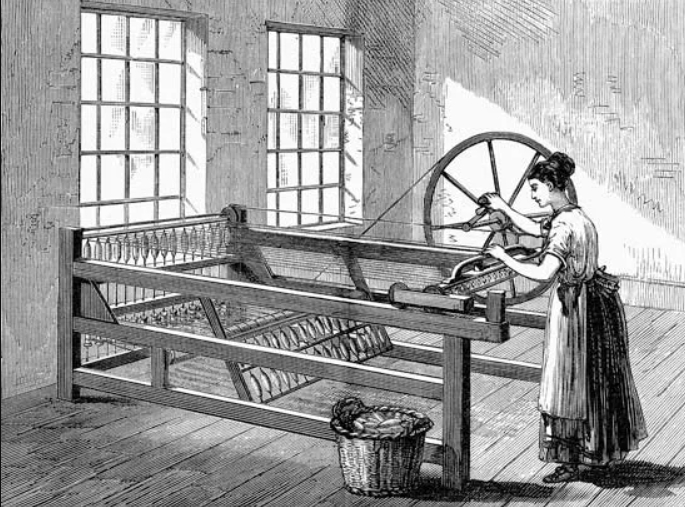 The spinning jenny, invented in 1764 by James Hargreaves in Lancashire, England, revolutionized the production of yarn, including cotton fiber, enabling one worker to spin multiple spools at once and greatly increasing the efficiency of the textile industry. This invention was a key development in the Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain and soon spread to other parts of the world. It not only changed how textiles were produced but also had widespread social implications, leading to the growth of factories and the urban workforce.
The spinning jenny, invented in 1764 by James Hargreaves in Lancashire, England, revolutionized the production of yarn, including cotton fiber, enabling one worker to spin multiple spools at once and greatly increasing the efficiency of the textile industry. This invention was a key development in the Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain and soon spread to other parts of the world. It not only changed how textiles were produced but also had widespread social implications, leading to the growth of factories and the urban workforce.
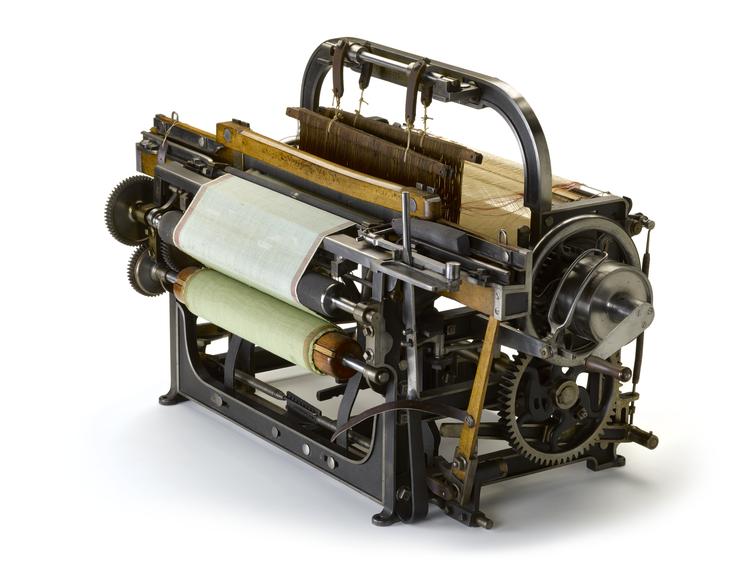
Power Looms
Following on the heels of the spinning jenny were power looms, which mechanized the process of weaving cloth. Invented by Edmund Cartwright in 1785, these looms further boosted production capacity and reduced the manual labor required to create textiles, leading to mass production and the establishment of textile factories as centers of manufacturing.
Synthetic Dyes
The mid-19th century saw the development of synthetic dyes, which replaced the traditional natural dyes. This innovation provided a broader range of colors and more colorfast textiles (resistant to fading), profoundly affecting the fashion and fabric industries.
Synthetic Fibers
The creation of synthetic fibers like nylon, polyester, and acrylic in the 20th century offered alternatives to natural fibers like cotton, wool, and silk. These synthetic fibers have become staples in clothing production due to their durability and lower cost. Interestingly, within today's fashion landscape, fabrics that demand more maintenance and care, such as silk and cashmere, are often considered more luxurious compared to cotton, wool, and certainly synthetic fibers.
Digital Printing
 In the modern era, digital printing technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, allowing for the precise and cost-effective printing of complex designs on fabric. This technology enables small runs of custom textiles, which has significantly lowered the barriers to entry for small designers and has led to the democratization of fashion and textile design.
In the modern era, digital printing technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, allowing for the precise and cost-effective printing of complex designs on fabric. This technology enables small runs of custom textiles, which has significantly lowered the barriers to entry for small designers and has led to the democratization of fashion and textile design.
Automation and Robotics
The latest advancements in automation and robotics are currently transforming the textile industry. Automated cutting machines, computerized knitting machines, and AI-driven design tools are increasing production speed and allowing for more personalized and sustainable manufacturing processes, including the capability for mass customization.
Sustainability Innovations
Moreover, the textile industry is embracing sustainable practices, with innovations such as recycled fabrics, waterless dye technologies, and closed-loop recycling systems that aim to reduce the environmental footprint of textile production.
The evolution of the textile industry is a testament to the pivotal role innovation plays in driving economic growth, societal shifts, and environmental sustainability. These transformative innovations have not only reshaped manufacturing processes but have also redefined the fashion landscape and consumer behaviors. The industry's embrace of digital and sustainable innovations continues to push the boundaries of what's possible, ensuring that the fabric of society remains as vibrant and diverse as the textiles it produces.

When Innovation Meets Fashion
The convergence of innovation and fashion has ushered in a new era of creativity, sustainability, and consumer engagement within the industry. From groundbreaking advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques to innovative retail experiences and digital platforms, fashion innovation continues to redefine the way we create, consume, and interact with clothing and accessories.
Breakthroughs in Fashion Innovation
- 3D Printing: Revolutionizing garment production by enabling on-demand manufacturing, customization, and intricate design possibilities.
- Velox: Introduces 3D-printed shoes made from sustainable materials, reducing waste and offering unique, customizable designs.
- Velox: Introduces 3D-printed shoes made from sustainable materials, reducing waste and offering unique, customizable designs.
- Augmented Reality Fitting Rooms: Enhancing the in-store shopping experience by allowing customers to virtually try on clothes before making a purchase.
- Topshop's Virtual Fitting Room app: Enables shoppers to see how clothes fit and look at them using augmented reality technology.
- Topshop's Virtual Fitting Room app: Enables shoppers to see how clothes fit and look at them using augmented reality technology.
- Smart Clothing: Integrating technology into garments to enhance functionality, performance, and comfort.
- Misfit Wearables: Launches Swarovski Shine, a collection of activity trackers disguised as stylish jewelry, blending fashion with fitness.
- Misfit Wearables: Launches Swarovski Shine, a collection of activity trackers disguised as stylish jewelry, blending fashion with fitness.
- Fashion Rental Platforms: Redefining the concept of ownership by offering subscription-based services that allow customers to rent designer clothing and accessories.
- Rent the Runway: Offers a wide selection of designer dresses and accessories for rent, providing affordable luxury and reducing fashion waste.
- Rent the Runway: Offers a wide selection of designer dresses and accessories for rent, providing affordable luxury and reducing fashion waste.
- Sustainable Fabrics: Pioneering eco-friendly materials derived from renewable sources or recycled materials to address environmental concerns.
- Re:newcell: Develops Circulose, a fiber made from recycled textiles, offering a closed-loop solution for sustainable fashion production.
- Re:newcell: Develops Circulose, a fiber made from recycled textiles, offering a closed-loop solution for sustainable fashion production.
 Case Study:
Case Study:
Rothy's Sustainable Fashion Footwear
- Company: Rothy’s, San Francisco, USA (Launched in 2016)
- What Was Done: Rothy’s developed a line of fashionable shoes using recycled materials. The shoes are 3D-knitted from recycled plastic water bottles, combining sustainable practices with design and comfort.
- Results/Impact: Rothy’s has transformed over 100 million plastic bottles into stylish footwear and accessories, gaining a loyal customer base and raising industry standards for sustainable production in fashion.
Leaders in Fashion Innovation
- Stella McCartney: Champions sustainable fashion practices and cruelty-free materials, leading the way in ethical and eco-conscious design.
- Farfetch: Revolutionizes luxury retail through its online marketplace and augmented reality shopping experiences, connecting consumers with global boutiques and designers.
- Eileen Fisher: Embraces circularity and sustainability in fashion through initiatives like Renew, which repurposes old garments into new designs.
- Gucci: Embraces digital innovation with its augmented reality app and virtual try-on experiences, enhancing customer engagement and brand loyalty.
- Adidas: Pushes the boundaries of sportswear innovation with groundbreaking technologies such as 4D printing (3D + changes with time as a response to the environment) and recycled materials.
 Case Study: Adidas's BOOST Technology
Case Study: Adidas's BOOST Technology- Company: Adidas AG, Herzogenaurach, Germany (BOOST launched in 2013)
- What Was Done: Adidas introduced BOOST technology, which uses thermoplastic polyurethane to create a more durable and responsive sole in their running shoes. This innovation has redefined the company's sports footwear line.
- Results/Impact: BOOST technology has been highly successful, leading to increased sales for Adidas running shoes and creating a new standard for comfort and performance in sports footwear, influencing the entire industry.
Iconic Fashion Products: A Historical Perspective
- The Little Black Dress (LBD): Popularized by Coco Chanel in the 1920s, the Little Black Dress became a fashion staple due to its versatility, elegance, and the ability to transcend trends and seasons, making it an essential piece in every woman's wardrobe.
- Denim Jeans: Originally designed as durable workwear for miners in the late 19th century, denim jeans were popularized by Levi Strauss & Co. They evolved into a symbol of youth culture in the 1950s and have since become a ubiquitous garment across the globe, celebrated for their comfort and durability.
- The Push-Up Bra: Introduced by Frederick Mellinger, the founder of Frederick's of Hollywood, in the late 1940s, the push-up bra revolutionized women's lingerie by enhancing the appearance of the bustline. It combined fashion and function, offering both support and a desirable silhouette.
- The Mini Skirt: Credited to designer Mary Quant in the 1960s, the mini skirt was a radical departure from the conservative fashion of previous decades. Its daring hemline symbolized freedom, rebellion, and the youth culture of the era, making it an iconic piece of fashion history.
- Sneakers for Everyday Wear: The transformation of sneakers from purely athletic footwear to a fashion statement for everyday wear marks a significant innovation in fashion. Brands like Converse, Adidas, and Nike have been at the forefront of this transition, with the Adidas Stan Smiths and Nike Air Jordans becoming cultural icons that blend comfort, style, and sports heritage.
How to Apply Fashion Innovation
- Embrace Sustainable Practices: Incorporate eco-friendly materials, ethical sourcing, and transparent supply chains into fashion production processes.
- Invest in Technology: Explore cutting-edge technologies such as 3D printing, augmented reality, and wearable tech to enhance product design, manufacturing, and customer experiences.
- Foster Collaboration: Partner with technology companies, startups, and industry innovators to exchange ideas, share resources, and drive collective innovation in fashion.
- Consumer-Centric Design: Prioritize consumer needs, preferences, and feedback when developing new products, services, and shopping experiences.
- Experiment and Iterate: Embrace a culture of experimentation, iteration, and continuous improvement to stay ahead of evolving trends, preferences, and market demands.
Unique Characteristics of Fashion Innovation
- Creative Fusion: Blending elements of art, technology, culture, and sustainability to create innovative fashion concepts and designs.
- Disruptive Impact: Challenging traditional norms, practices, and business models within the fashion industry to drive positive change and social impact.
- Expressive Potential: Empowering individuals to express their identity, values, and beliefs through fashion choices that resonate with their personal style and ethos.
- Experiential Engagement: Creating immersive and memorable shopping experiences that captivate consumers, foster emotional connections, and drive brand loyalty.
- Collaborative Ecosystems: Building partnerships and alliances across industries, disciplines, and communities to co-create and co-innovate solutions that address complex challenges in fashion.
What to Avoid When Innovating in Fashion
- Greenwashing: Beware of superficial or misleading sustainability claims that do not align with genuine efforts to reduce environmental impact and improve social responsibility.
- Technological Gimmicks: Avoid gimmicky or overly complex technology implementations that detract from the core value proposition or user experience of fashion products.
- Lack of Diversity and Inclusion: Ensure representation and inclusivity in design, marketing, and decision-making processes to avoid perpetuating stereotypes or excluding marginalized communities.
- Short-Term Thinking: Resist the temptation to prioritize short-term gains or trends over long-term sustainability, ethical practices, and brand integrity.
- Overlooking Practicality: In the textile and fashion industries, innovations that enhance the functionality and practical use of garments often have more lasting value than fleeting design trends
- Discover further insights in "Systematic Innovation in the Textile Industry," an article that draws from our expertise at ZOOZ consulting.
- Our journey in spearheading Systematic Innovation processes has spanned across numerous global textile manufacturers, such as Bagir (tailored suits), Delta Galil and Gibor-Sabrina (underwear).
- For an in-depth look at functional innovation, explore the success story of Bagir.
- Resistance to Change: Embrace innovation and adaptability to stay relevant in a rapidly evolving fashion landscape, avoiding complacency or resistance to transformative shifts in consumer behavior, technology, or market dynamics.
Fashion innovation serves as a catalyst for creativity, sustainability, and positive change within the industry, driving advancements in design, technology, and consumer experiences. By embracing sustainability, investing in technology, fostering collaboration, prioritizing consumer needs, and maintaining a commitment to ethical practices, fashion brands can lead the way in shaping a more inclusive, responsible, and innovative future for the industry.

What Innovation Came About as a Result of Railroads
The development and expansion of railroads were pivotal in the industrialization of the modern world, catalyzing numerous innovations in transportation, communication, and industry. Railroads not only transformed the physical landscape but also the technological and economic fabric of society.
Standard Time Zones
 One of the most significant innovations prompted by the expansion of railroads was the establishment of standard time zones. Prior to railroads, time was determined locally, with cities setting their clocks based on the position of the sun. However, this system was impractical for scheduling trains that traveled across vast distances. The adoption of standardized time zones in the 19th century enabled synchronized train schedules, improving efficiency and safety in rail transport.
One of the most significant innovations prompted by the expansion of railroads was the establishment of standard time zones. Prior to railroads, time was determined locally, with cities setting their clocks based on the position of the sun. However, this system was impractical for scheduling trains that traveled across vast distances. The adoption of standardized time zones in the 19th century enabled synchronized train schedules, improving efficiency and safety in rail transport.
Steel Production
The demand for durable railroad tracks spurred innovations in steel production, notably the Bessemer process. This method allowed for the mass production of steel, which was stronger and more flexible than iron. The availability of inexpensive steel had far-reaching effects, fueling advancements in construction, manufacturing, and even the automotive industry.
Telegraph System
 The need for efficient communication across long distances led to the widespread use of the telegraph alongside railroad lines. This innovation allowed for instant communication between distant stations, revolutionizing the way information was transmitted and making railroads safer and more reliable.
The need for efficient communication across long distances led to the widespread use of the telegraph alongside railroad lines. This innovation allowed for instant communication between distant stations, revolutionizing the way information was transmitted and making railroads safer and more reliable.
Freight Management Systems
Railroads necessitated the development of sophisticated freight management and logistics systems. Innovations such as the containerization of cargo simplified the loading and unloading process, reduced damage to goods, and streamlined the transfer of freight between railroads and other modes of transportation.
Safety Innovations
The increased use of railroads led to the invention of numerous safety mechanisms, including the air brake system by George Westinghouse. Prior to this, braking was a manual and inconsistent process. The air brake system enabled simultaneous and more effective braking across all train cars, significantly reducing the risk of accidents.
Electric Railways
The introduction of electric railways marked a significant shift from steam-powered locomotives, leading to faster, cleaner, and more efficient trains. This innovation paved the way for modern subway systems and electrified rail networks, transforming urban transportation.
Railway Signaling Systems
To manage the growing complexity of rail networks, advanced signaling systems were developed. These systems controlled train movements, preventing collisions and ensuring the efficient use of tracks.
Railroads were the arteries of the industrial age, and the innovations they inspired have left an indelible mark on the world. From revolutionizing timekeeping to sparking advancements in steel production and safety, the legacy of railroads extends far beyond the tracks. These innovations not only facilitated the expansion of rail transport but also propelled society into the modern era, underscoring the profound impact of railroads on global development.
Systematic innovation
Interested in getting help with systematic innovation processes and developing new products and services?
Contact us: info@zooz.co.il ,+972-9-958-5085
Innovation Articles
- Innovation overview
- Innovation management
- Innovation methods
- Innovation tools
- Innovation and creativity
- Innovation and other disciplines
- Innovation in organizations
- Innovation career
- Innovation importance
- Innovation goals
- Innovation values
- Inspiration for innovation
- Innovation education
- Product innovation
- Service innovation
- Technological innovation
- Innovation examples
- Innovations across various industries
- Innovation glossary (200 terms)





