Innovation Career
Feb 27, 2024
By Ari Manor , CEO at ZOOZ

This is one in a series of articles that provide detailed and updated information about Innovation. In this specific article, which focuses on Innovation Career, you can read about:
- Entrepreneur
- Innovation Manager
- Why Innovation Management is Important
- Innovation Team
- Innovation Jobs
- Innovation Jobs Near Me
- Innovation to Transform Education Training
- Innovation Job Titles
- Innovation Officer
- Innovation Leader
- Innovation Training
- Innovation Workshops
For additional articles about Innovation, see the Topic Menu.

Entrepreneur
Entrepreneurs are visionary individuals who identify opportunities, take calculated risks, and create innovative solutions to address unmet needs or challenges in society. As drivers of economic growth and agents of change, entrepreneurs play a vital role in shaping the future by introducing new products, services, and business models that disrupt existing industries and drive progress. Their entrepreneurial spirit and relentless pursuit of innovation fuel innovation ecosystems, inspire others, and create value for customers, investors, and society at large.
Typical entrepreneurship skills include
- Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: Entrepreneurs must be able to identify and analyze problems effectively and develop innovative solutions. For instance, the founders of Airbnb exemplify critical thinking by reimagining lodging, turning empty spaces in homes into accommodations for travelers.
- Risk Management: Effective entrepreneurs assess and manage risks, not shy away from them. Spanx founder Sara Blakely's investment of her life savings into creating comfortable shapewear is an example of calculated risk-taking.
- Networking: Building a strong network is essential for entrepreneurial success. Reid Hoffman, co-founder of LinkedIn, leveraged his connections to create the world's largest professional network, showcasing the power of strategic networking.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Entrepreneurs need to adapt to changing markets and customer needs. Netflix’s Reed Hastings shifted from DVD rentals to streaming, demonstrating adaptability in business.
- Leadership and Management: Successful entrepreneurs must lead and manage teams effectively. Mark Zuckerberg's leadership in scaling Facebook from a college network to a global platform highlights the importance of management skills.
- Financial Literacy: Understanding finances is crucial for making informed business decisions Jeff Bezos displayed this skill by strategically reinvesting profits back into Amazon, focusing on long-term growth over immediate profit.
- Marketing and Sales: Entrepreneurs should excel at marketing their products and closing sales. The success of Kylie Jenner's cosmetics line illustrates the impact of strong marketing and sales skills.
- Innovation and Creativity: Constant innovation is key to staying competitive. Elon Musk’s ventures like Tesla and SpaceX underscore the significance of creativity in entrepreneurship.
- Persistence and Resilience: Overcoming setbacks is a vital entrepreneurial skill. Steve Jobs' return to Apple and his subsequent revival of the company into a tech giant exemplifies the resilience needed in entrepreneurship.
- Negotiation: Strong negotiation skills can lead to better deals and opportunities. Oprah Winfrey's ability to negotiate partnerships and contracts has been central to building her media empire.
Entrepreneurs stand at the helm of innovation, their unique blend of vision, courage, and ingenuity propelling society forward. In their relentless pursuit of progress, these trailblazers not only shape industries but also foster the growth of global economies and inspire the spirit of enterprise in others.

Innovation Manager
An Innovation Manager plays a pivotal role in steering an organization’s creative capabilities towards strategic business objectives.
The Responsibilities of the Inovation Manager
- Vision and Leadership: Setting the vision for innovation within the company and leading the charge to inspire a culture of continuous improvement and creative thinking.
- Strategy Development: Crafting strategies that align with business goals and determining the best paths for innovation efforts, whether in products, services, processes, or business models.
- Process Management: Overseeing the innovation process from ideation to execution, ensuring that it's efficient, effective, and adheres to the company's strategic direction.
- Collaboration Facilitation: Acting as a liaison between different departments, external partners, and stakeholders to foster collaboration and cross-pollination of ideas.
- Portfolio Management: Managing the portfolio of innovation projects, prioritizing initiatives based on potential impact, and ensuring a balanced mix of incremental and disruptive innovation efforts.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring that projects have the necessary resources, from funding to expertise, and managing those resources wisely to maximize return on investment.
- Metrics and Analysis: Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) for innovation and analyzing the performance of innovation activities to inform future decisions.
- Change Advocacy: Championing change and helping to overcome resistance by clearly articulating the benefits and value of innovation initiatives.
Innovation Manager Position
- Scope: The position of an Innovation Manager can be either full-time or part-time, depending on the organization's size, industry, and the capacity of innovation activities it undertakes. However, it is essential that this role occupies at least 25% of a full-time position to ensure sufficient attention and momentum is maintained in the innovation process.
- Skills: An Innovation Manager should possess highly analytical skills to manage external screenings and idea banks effectively. Additionally, the innovation manager needs excellent communication and soft skills to navigate organizational barriers, foster a culture of innovation, and motivate team members and peers to engage in innovative activities.
- Size and Type of Organizations: Organizations of all sizes and types can benefit from having an Innovation Manager, especially those in rapidly evolving sectors were staying ahead of technological trends and market demands is critical. While larger corporations may require a dedicated full-time position, smaller firms or startups might start with a part-time role or incorporate these responsibilities into a broader managerial position.
- Experience and Education Required: Typically, an Innovation Manager should have a background in business, management, or a related field, with a bachelor's degree being a minimum requirement. Many also hold advanced degrees such as an MBA or masters in innovation management. Relevant experience in project management, R&D, product development, or strategic planning is crucial. It's also beneficial for Innovation Managers to have a solid understanding of the industry they're working in, along with experience in managing cross-functional teams and implementing change.
In essence, the Innovation Manager's role is to bridge the gap between innovative ideas and their successful implementation, requiring a blend of strategic insight, leadership qualities, and a deep understanding of both market and technological trends, making it one of the most dynamic and influential positions in today's corporate landscape.

Why Innovation Management is Important
Innovation management is critical because it structures the process of bringing new and creative ideas to life, which is fundamental for any business that seeks to grow, remain competitive, and avoid stagnation.
Why Innovation Management Matters
- Alignment with Strategic Goals: Innovation management ensures that new ideas align with the company's strategic objectives, thereby supporting focused growth and value creation.
- Resource Optimization: By managing innovation, organizations can allocate their resources more effectively, ensuring that the best ideas receive the necessary investment of time and capital.
- Risk Reduction: Innovation management helps to identify potential risks early in the development process, allowing for better risk mitigation and increasing the likelihood of success.
- Market Responsiveness: Effective innovation management enables a company to respond quickly to market changes, customer needs, and technological advancements, keeping it ahead of competitors.
- Culture of Continuous Improvement: It fosters a culture where continuous improvement is valued and sought after, encouraging employees to constantly look for ways to enhance products, services, and processes.
- Sustainable Competitive Advantage: By regularly introducing innovative products, services, or processes, a company can establish and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: A strong focus on innovation attracts talent looking to work in dynamic and forward-thinking environments, and it keeps employees engaged by providing opportunities for creativity and problem-solving.
Applying Systematic Innovation
Innovation management is not just about generating creative ideas; it's about translating those ideas into tangible outcomes that drive business success. It's a discipline that requires coordination, investment, and a strategic approach to harness the creative capabilities of an organization effectively.
Here at ZOOZ Consulting, after leading innovation and strategic processes in hundreds of organizations across many countries, we have developed a methodology for managing all aspects of innovation systematically to reduce risk and improve outcomes. This methodology, known as Systematic Innovation™, incorporates lessons we've learned during our 25 years of experience in the field of business innovation.
The Systematic Innovation methodology includes a comprehensive framework for innovation, as well as highly effective tools, principles, and methods for ongoing innovation management at all stages of the innovation process, as follows:
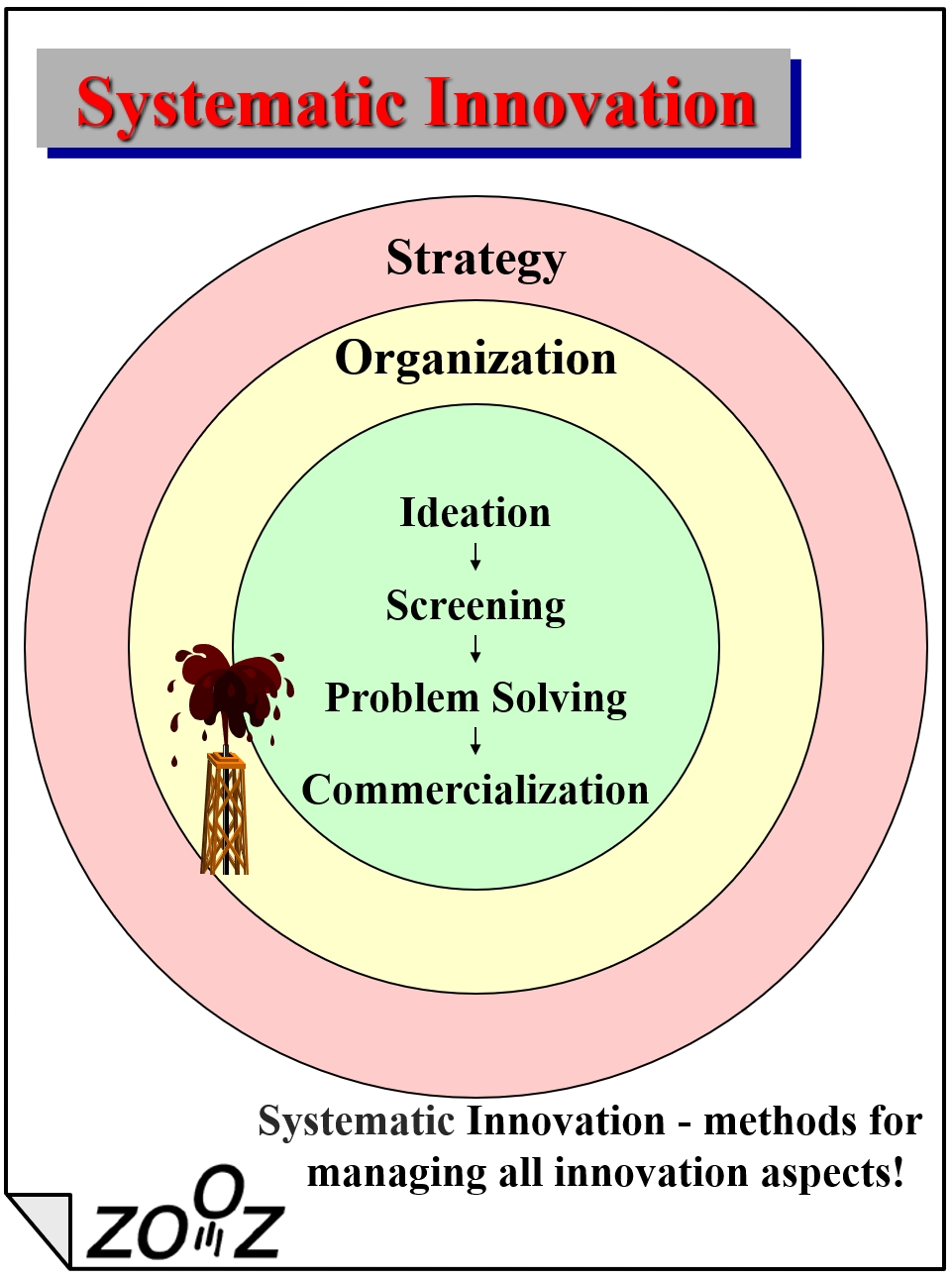 Strategic Infrastructure (a framework for the innovation efforts):
Strategic Infrastructure (a framework for the innovation efforts):- Ensuring there is (or devising) a business strategy that innovation should support.
- Defining a strategy for innovation – goals, innovation focus, fields to innovate in, etc.
- Working on disruptive business strategy – strategic growth paths, blue ocean strategy, etc.
- Organizational Infrastructure (setting up an innovation culture):
- Defining, advancing, and guiding the innovation workforce – Innovation manager, think tanks, etc.
- Providing on-the-job training and nurturing required skills, using systematic tools and methods.
- Offering mass-training to employees to enhance organizational creativity (“Invent in Yourself” Days).
- Assimilating tools to shape an innovation culture (Six thinking hat, Idea Banks, and more)
- Idea Funnel (leading innovation sessions and assimilating dedicated tools and methods):
- Idea generation – we use SIT, SCAMPER, TRIZ, and more, according to the needs.
- Screening – internal screening, external screening via concept testing.
- Problem-solving – using SIT and TRIZ methodologies to overcome technical and logistic issues.
- Commercialization – developing innovative packaging and display solutions, and highly creative ads.
For further detail about Systematic Innovation, read the following articles:
- Building The Future - Insights and recommendations for on innovation management.
- How Do You Make an Organization Innovative? – Organizational aspects of innovation management.
If you need help in applying Systematic Innovation in your organization, contact us.
We offer Systematic Innovation workshops anywhere on the globe.

Innovation Team
An Innovation Team is a cross-functional group within an organization that is tasked with driving innovation. This team is often composed of individuals from various departments and levels of expertise, bringing diverse perspectives to the table.
Key Functions and Responsibilities of Innovation Teams
- Idea Generation: Brainstorming and developing new ideas that could translate into successful products, services, or processes.
- Prototyping and Testing: Creating prototypes of potential products or models of new services and conducting tests to evaluate feasibility and market potential.
- Market Research: Conducting research to understand market needs, trends, and the competitive landscape to ensure that innovations are relevant and targeted.
- Collaboration: Working with other teams and external partners to develop and refine ideas and bring different skill sets and knowledge bases to the innovation process.
- Project Management: Overseeing innovation projects from conception through to completion, ensuring they meet timelines, budget constraints, and objectives.
- Communication: Keeping all stakeholders informed of the team’s progress, challenges, and successes to maintain transparency and support throughout the organization.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Learning from both successes and failures to continuously improve the innovation process.
Typical Positions in an Innovation Team
- Innovation Manager
- Responsibilities: Oversees the innovation process from ideation to execution, develops innovation strategy aligned with business goals, and fosters a culture of innovation.
- Required Skills: Strong leadership, strategic thinking, project management, and communication skills.
- Education and Experience: Bachelor’s degree in business or related field; MBA or master's in innovation management preferred. Experience in project management, R&D, or strategic planning is advantageous.
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
- Responsibilities: Leads the company’s technological research and development (R&D), aligns technology-related decisions with the organization's goals, and explores new technological opportunities.
- Required Skills: Deep technical knowledge, strategic planning, leadership, and the ability to drive technology innovation.
- Education and Experience: Typically requires a degree in computer science, engineering, or related field, along with extensive experience in IT and technology development.
- Researcher
- Responsibilities: Conducts market and technology research to identify trends and opportunities, supports product development with factual insights.
- Required Skills: Analytical skills, proficiency in research methodologies, attention to detail.
- Education and Experience: Degree in market research, business, or a technical field. Experience in research roles within the industry.
- Product Manager
- Responsibilities: Manages the development and marketing strategy of products from conception through lifecycle management to ensure they meet customer needs and company goals.
- Required Skills: Product development, market analysis, customer engagement, cross-functional team leadership.
- Education and Experience: Bachelor’s degree in business, marketing, or related technical field, with experience in product development and management.
Types of Think Tanks for Advancing Innovation
- Strategic Innovation Team
- Composition: Management (and sometimes the board is invited as well).
- Focus: Developing long-term innovation strategies that align with the company's overarching goals, identifying new market opportunities, and ensuring the sustainability of innovation efforts.
- Optimal size: 5-15 people (pending on the management team size).
- Product and Service Innovation Team – for Idea Generation
- Composition: Marketing professionals, with some operational and/or technological people to confirm feasibility of ideas.
- Focus: Innovating around new or existing products and services to meet evolving market needs, improving customer experience, and ensuring the feasibility of ideas.
- Optimal size: 8-12 people (diversity in opinions and ideas, while still enabling efficient discussions)
- Technological Problem-Solving Team
- Composition: CEO, CTO/Operation, Marketing Manager, Innovation manager, and another manager from the marketing department.
- Focus: Internal screening, Idea bank management, execution and advancing specific project.
- Optimal size: 5 people (Internal screening and execution do not require a bigger team)
- Process Innovation Team
- Composition: Operations and process management experts./li>
- Focus: Streamlining and improving internal processes, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and implementing new tools and technologies to support operational excellence.
In conclusion, the formation and effective management of an Innovation Team are crucial for fostering a culture of continuous improvement and creativity within any organization. By assembling a diverse group of individuals equipped with the right skills, experience, and perspectives, and by clearly defining roles, responsibilities, and focus areas, organizations can significantly enhance their capacity for innovation.
Whether it's through generating groundbreaking ideas, developing and testing new products and services, conducting thorough market research, or managing projects efficiently, these teams are the driving force behind an organization's ability to innovate and stay competitive in the ever-evolving business landscape. Through strategic collaboration, continuous learning, and adaptation, Innovation Teams not only contribute to the immediate success of their projects but also lay the groundwork for long-term strategic growth and transformation.

Innovation Jobs
The innovation landscape has created a diverse range of job opportunities focused on driving and managing change across various industries. Innovation jobs are characterized by roles that demand creativity, strategic thinking, and a passion for breaking new ground.
Common Innovation Positions
- Innovation Manager: Leads and manages the company's innovation efforts, overseeing the development of new products or services and fostering a culture of innovation within the organization.
- Product Developer: Works on the creation and development of new products, from conceptualization to launch, ensuring they meet market needs and consumer preferences.
- R&D Scientist/Engineer: Engages in research and development activities to discover new technologies or refine existing ones, contributing to the company's innovative capabilities.
- UX/UI Designer: Focuses on designing user experiences and interfaces that are intuitive and innovative, enhancing user engagement with products or services.
- Data Scientist: Utilizes big data and analytics to uncover insights that can lead to innovative solutions and strategies for the company.
- Innovation Consultant: Advises organizations on creating and implementing innovation strategies, helping them stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
- Chief Innovation Officer (CINO): A senior-level role responsible for setting the organization's innovation agenda and ensuring alignment with overall business objectives.
Innovation jobs are not confined to tech companies; they are increasingly common in traditional sectors such as healthcare, finance, education, and government, reflecting the universal importance of innovation across all areas of the economy.

Innovation Jobs Near Me
Finding innovation-related jobs in your area can be an exciting opportunity to engage in creative and transformative work. Here are some tips and resources to help you locate innovation jobs nearby.
- Online Job Portals: Websites like Indeed, LinkedIn, Glassdoor, and Monster allow you to search for jobs by keyword and location. Use terms like "innovation," "product development," or specific titles such as "Innovation Manager" to find relevant listings.
- Company Websites: Many companies post job openings on their own websites. Identify organizations known for their innovative culture or those with dedicated innovation departments and check their careers page regularly.
- Networking: Attend industry meetups, conferences, and seminars related to innovation. Networking with professionals in the field can provide insider information on job openings and referrals.
- Innovation Hubs and Incubators: Innovation hubs, incubators, and accelerators often host companies and startups focused on innovation. They may have job boards or connections to companies looking for innovative talent.
- Recruitment Agencies: Some agencies specialize in placing candidates in creative, tech, and innovation roles. Registering with these agencies can provide access to unadvertised opportunities.
- Social Media: Follow companies, innovation leaders, and industry groups on social media platforms. They often share job openings, insights, and updates on new projects that could lead to job opportunities.
Remember, innovation jobs aren't limited to tech startups; they're found across all sectors. Tailoring your search to your interests and industry can help you find a role that's right for you.

Innovation to Transform Education Training
Innovation plays a critical role in transforming organizational education and training, making learning more accessible, engaging, and effective. Here are keyways innovation is reshaping the educational landscape:
- E-Learning Platforms: Online learning platforms offer flexible, self-paced learning opportunities that can be tailored to individual needs, breaking geographical barriers to education.
- Gamification: Incorporating game design elements into education increases engagement and motivation, making learning more interactive and enjoyable.
- Adaptive Learning Technologies: These technologies adjust the content and pace of learning based on the learner's performance, providing personalized learning experiences.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR can simulate real-world environments for immersive learning experiences, particularly useful in fields requiring hands-on training.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education: AI can automate administrative tasks for educators, provide tutoring and support for students, and offer insights into learning patterns to improve educational outcomes.
- Blockchain for Education: Blockchain technology can securely store educational records, making it easier to verify qualifications and share credentials between institutions.
- Collaborative Learning Tools: Tools like online forums, video conferencing, and shared digital workspaces facilitate collaboration among students and teachers, regardless of location.
Innovations in education and training are not only improving the delivery of organizational education but also preparing learners for a future where adaptability and lifelong learning are key.

Innovation Job Titles
The landscape of innovation within organizations has evolved dramatically, leading to the emergence of new roles and job titles that reflect the growing importance of creativity, strategic thinking, and technological advancement. These titles not only signify the bearer's responsibility in driving innovation but also highlight the diverse approaches companies are taking to stay competitive in an ever-changing market.
Here's a look at some of the innovation job titles that have become more prevalent in today's corporate structure:
- Chief Innovation Officer (CInO): A senior executive role responsible for defining and leading the company's innovation strategy. This person works across departments to foster a culture of innovation and ensures that the company remains at the forefront of industry advancements.
- Innovation Manager: Oversees the innovation process within the organization, from ideation to execution. They are responsible for managing innovation projects, facilitating collaboration among teams, and measuring the outcomes of innovation efforts.
- Product Innovation Manager: Focuses specifically on the development of new products or enhancements to existing products. This role involves market research, product design, and coordination with engineering and marketing teams.
- Innovation Strategist: Works on developing and implementing strategies that promote innovation within the organization. They analyze market trends, identify opportunities for growth, and recommend strategic directions.
- Resident Entrepreneur: Embedded within the company, this role acts as an internal entrepreneur, leveraging deep industry insights and entrepreneurial skills to develop new business models, products, or services from within the organization. They are tasked with driving innovation by thinking and acting like an external startup founder, while having access to the company's resources and networks.
- Innovation Evangelist: This role is responsible for promoting and advocating for a culture of innovation within the organization and to external stakeholders. Innovation Evangelists work to inspire employees, share success stories, and communicate the value of innovation through various platforms and channels. They play a key role in building enthusiasm and support for innovative initiatives across the company.
- Innovation Consultant: An external or internal consultant who advises on processes, strategies, and cultures that encourage innovation. They often conduct workshops, training sessions, and provide guidance on best practices in innovation management.
- Director of Innovation: Similar to the Chief Innovation Officer but typically in smaller organizations or specific departments, this role involves leading the innovation agenda and integrating innovative practices throughout the organization.
- Innovation Analyst: Responsible for researching and analyzing data to identify trends, insights, and opportunities for innovation. They support decision-making by providing evidence-based recommendations.
- Innovation Engineer: Focuses on the technical development of innovative products or solutions. This role requires a strong background in engineering and technology, combined with creative problem-solving skills.
- Design Thinker: Specializes in applying design thinking methodology to solve complex problems and drive innovation. They facilitate workshops and collaborate with teams to develop user-centric solutions.
- Digital Innovation Lead: Concentrates on leveraging digital technologies to create new or improved processes, products, or services. They stay abreast of technological trends and lead digital transformation initiatives.
- Sustainability Innovation Specialist: Dedicated to developing innovations that contribute to environmental sustainability and social responsibility. They work on creating sustainable business models and eco-friendly product innovations.
The creation of these roles within organizations underscores the recognition that innovation is not a one-time project but a continuous, strategic imperative that requires dedicated leadership and specialized skills. As businesses continue to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by digital transformation, global competition, and changing consumer behaviors, the demand for professionals with innovation expertise is set to rise. These roles play a critical part in ensuring that companies not only adapt to the present but are also well-positioned to shape the future.

Innovation Officer
The role of an Innovation Officer, often titled Chief Innovation Officer (CInO) or simply Innovation Officer, is pivotal in steering an organization's innovation strategy and embedding a culture of innovation across all levels. This executive position is tasked with identifying new opportunities for growth, driving the development of innovative products and services, and ensuring that the organization remains competitive in a rapidly changing business environment.
Key Responsibilities of an Innovation Officer
- Strategic Leadership: Developing and implementing a comprehensive innovation strategy that aligns with the organization's overall business goals. This includes setting clear objectives for innovation activities and ensuring they contribute to long-term growth.
- Cultural Change Agent: Fostering a culture of innovation within the organization by promoting open communication, collaboration, and risk-taking. The Innovation Officer works to break down silos and encourage cross-functional teams to innovate together.
- Market Insight and Trends Analysis: Keeping abreast of industry trends, emerging technologies, and market shifts to identify opportunities for innovation. This requires a deep understanding of the competitive landscape and the ability to anticipate future challenges and opportunities.
- Collaboration and Partnership: Building relationships with external partners, such as startups, research institutions, and other organizations, to co-develop innovative solutions and bring fresh perspectives into the organization.
- Portfolio Management: Overseeing the innovation project portfolio, ensuring a balanced mix of incremental and radical innovation initiatives. This involves prioritizing projects, allocating resources effectively, and managing the risk associated with innovation investments.
- Measurement and Evaluation: Establishing metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of innovation activities on the organization's performance. The Innovation Officer is responsible for tracking progress, evaluating the success of innovation projects, and making data-driven decisions to adjust the innovation strategy as needed.
Impact of the Innovation Officer Role
The presence of an Innovation Officer significantly impacts an organization's ability to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape. By championing innovation at the executive level, they ensure that it is not viewed as a peripheral activity but as a central, strategic function integral to the organization's success. The Innovation Officer plays a crucial role in transforming ideas into tangible outcomes that drive growth, enhance competitiveness, and foster a forward-thinking organizational culture.
In summary, the Innovation Officer is a strategic visionary and a catalyst for change, guiding the organization through the intricacies of innovation management and ensuring that innovation remains at the heart of the organization's strategy and operations.

Innovation Leader
Innovation leadership is a critical aspect of driving forward progress and change within organizations. An effective innovation leader not only fosters a culture of creativity and experimentation but also provides strategic direction and resources to support innovative initiatives.
Following is a closer look at the role of innovation leaders and what sets them apart.
Visionary Guidance
- An innovation leader sets a clear vision for the organization's innovation goals and priorities, aligning them with the overall business strategy.
- For example, Sara Blakely, the founder of Spanx, demonstrated innovation leadership by identified a gap in the market for comfortable, flattering undergarments that were invisible under clothing, and envisioning and creating a revolutionary product , which `transformed the fashion industry with her innovative approach to shapewear. Her use of breathable, lightweight fabrics and seamless designs that eliminated visible lines transformed the industry's approach to undergarments, making Spanx a pioneering brand in fashion innovation.
Encouraging Creativity
- Innovation leaders cultivate a supportive environment where employees feel empowered to explore new ideas and take calculated risks.
- Take Pixar's Ed Catmull, for instance, who fostered a culture of creativity and collaboration, leading to groundbreaking animated films like "Toy Story" and "Finding Nemo."
Championing Experimentation
- They encourage experimentation and provide resources for research and development, allowing for the exploration of innovative solutions.
- At Google's X Lab, led by Astro Teller, moonshot projects like Google Glass and Project Loon were pursued, pushing the boundaries of innovation through ambitious experimentation.
Embracing Diversity
- Effective innovation leaders value diversity of thought and encourage diverse perspectives to drive innovation.
- IBM's Ginni Rometty promoted diversity and inclusion within the company, fostering innovation by leveraging the unique strengths and perspectives of employees from different backgrounds.
Adapting to Change
- They adapt to change and navigate uncertainty with resilience, continuously seeking new opportunities for innovation.
- Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, embraced a growth mindset and led the company's transformation by shifting its focus towards cloud computing and AI-driven innovations.
In conclusion, innovation leaders play a pivotal role in shaping the future of organizations by fostering a culture of innovation, empowering teams to push boundaries, and driving strategic initiatives that lead to impactful outcomes. By embodying visionary leadership qualities and embracing the principles of creativity and experimentation, they pave the way for transformative innovation and sustainable growth.

Innovation Training
Innovation training is a transformative journey that equips individuals and organizations with the methodologies, tools, and mindset needed to excel in today's dynamic business environment. Recognizing the critical role of innovation in sustaining competitiveness and driving growth, our approach integrates decades of insights into a structured program designed to unleash the creative potential and strategic thinking of participants. This comprehensive training regimen, developed from extensive experience in fostering innovation across diverse sectors, is structured as follows:
Foundation Building
Establishing a baseline for innovation knowledge:
- Introduction to the principles of innovation, including definitions, importance, and types of innovation.
- Overview of the innovation lifecycle, from ideation to implementation and diffusion.
- Understanding the role of innovation within the broader business strategy and objectives.
Mindset and Culture
Cultivating an environment conducive to innovation:
- Techniques for fostering a culture of innovation, including leadership practices, communication strategies, and reward systems.
- Training on developing a growth mindset among employees, emphasizing resilience, openness to change, and the value of feedback and learning from failures.
- Workshops on creative thinking and problem-solving, utilizing approaches like Design Thinking and the Lean Startup methodology.
Case Study: Pixar Animation Studios
- Company: Pixar Animation Studios, Emeryville, California, USA

- Overview: Pixar's "Pixar University" is a comprehensive training program offering employees across all departments the opportunity to attend classes on storytelling, animation, fine arts, and more, aiming to foster continuous learning and creativity.
- Unique Features: With over 14 different courses offered weekly, employees are encouraged to explore areas outside their expertise, fostering a culture of creativity and interdisciplinary collaboration.
- Results/Impact: The initiative has been pivotal in maintaining Pixar’s reputation for creativity and innovation. Employees bring fresh perspectives to their projects, contributing to the studio's string of successful films. The program has helped sustain a vibrant corporate culture where innovation thrives, illustrating the value of investing in employee development.
Process and Implementation
Practical tools for managing the innovation process:
- Detailed training on ideation techniques such as SIT, SCAMPER, mind mapping, and other creativity tools.
- Guidance on prototyping and testing concepts with minimal viable products (MVPs) to gather insights and refine solutions.
- Strategies for effective project management in innovation, including agile and scrum methodologies, to enhance flexibility and responsiveness.
Case Study: Zapier
- Company: Zapier, Remote/Online (Headquartered in San Francisco, California, USA)

- Overview: Zapier, a web application integration company, promotes a unique culture of self-directed learning by offering each employee an annual stipend for books, courses, and conferences, encouraging personal and professional growth in any area of interest.
- Unique Features: The company’s fully remote workforce participates in virtual hackathons and knowledge-sharing sessions, with a strong emphasis on experimentation and learning from failure. The learning stipend supports employees in exploring new technologies and methodologies.
- Results/Impact: Zapier’s approach has led to a highly adaptable and innovative team capable of rapid problem-solving and continuous improvement. The investment in employee learning has not only enhanced job satisfaction but also contributed to the company’s growth and success in automating workflows for businesses worldwide. This model showcases the effectiveness of empowering employees to lead their innovation journeys, even in small, remote teams.
Measurement and Improvement
Evaluating innovation efforts and fostering continuous growth:
- Establishing metrics and KPIs to track the effectiveness of innovation initiatives and their impact on organizational goals.
- Continuous improvement processes to refine innovation strategies based on performance data and feedback loops.
- Leveraging technology and data analytics to support decision-making and uncover new opportunities for innovation.
Embarking on an innovation training program is not just about acquiring new skills; it's about transforming the way organizations think about and approach challenges and opportunities. Through this structured and comprehensive training, individuals and teams learn to navigate the complexities of the innovation process with confidence, creativity, and strategic insight.
The ultimate goal is to embed innovation into the DNA of the organization, ensuring it remains agile, forward-thinking, and poised for success in an ever-evolving marketplace. This journey towards systematic innovation is a commitment to continual learning, adaptation, and growth, enabling organizations to not only survive but thrive in the face of change.

Innovation Workshops
Innovation workshops are immersive, interactive sessions designed to unlock the creative potential within teams and organizations, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration. These workshops are crucial in today's fast-paced business environment, where the ability to innovate quickly and effectively sets companies apart from their competition. By bringing together diverse groups of people, innovation workshops facilitate the exchange of ideas, challenge conventional thinking, and encourage participants to explore new solutions to complex problems.
Core Elements of Effective Innovation Workshops
- Diverse Participation: Ensuring a mix of participants from various functions and levels within the organization to bring different perspectives and expertise to the table.
- Facilitated Ideation Sessions: Guided brainstorming and ideation exercises, using methods like SIT, Design Thinking, SCAMPER, and Six Thinking Hats to generate a wide array of ideas.
- Problem-Solving Challenges: Focusing on specific business challenges or opportunities, these sessions leverage creative problem-solving techniques to explore potential solutions.
- Prototyping and Testing: Encouraging rapid development of prototypes for selected ideas, followed by testing and feedback loops to refine the concepts.
- Collaborative Environment: Creating a safe and open space where participants feel comfortable sharing ideas and providing constructive feedback without fear of judgment.
- Expert Facilitation: Led by experienced facilitators who can guide discussions, stimulate creativity, and keep the group focused on the workshop objectives.
- Actionable Outcomes: Concluding with clear next steps, assigning responsibilities, and setting timelines for implementing the ideas generated during the workshop.
Types of Innovation Workshops
Innovation workshops can vary significantly in their focus, format, and audience, each designed to cater to specific needs and objectives within the innovation ecosystem. Understanding the different types of workshops available can help organizations choose the most suitable approach to foster innovation effectively.
Here's a breakdown of various types of innovation workshops:
1. Theoretical vs. Practical Workshops
- Theoretical Workshops: Focus on the conceptual and foundational aspects of innovation, including theories, models, and frameworks. Ideal for building a common understanding of innovation principles.
- Practical Workshops: Emphasize hands-on activities, real-world applications, and developing practical skills. Participants work on actual projects or challenges, applying what they learn in real-time.
2. Think Tank vs. Mass Training
- Think Tank Workshops: Small, focused groups tackling specific strategic challenges or exploring new innovation opportunities. Aimed at generating high-level insights and strategic directions.
- Mass Training Workshops: Aimed at a larger audience to instill a basic level of innovation knowledge and skills across the organization. These sessions are more about spreading a culture of innovation than deep strategic thinking.
3. Workshops according to Innovation Type
- Strategic Innovation Workshops: Concentrate on aligning innovation efforts with the organization's strategic goals, such as entering new markets or developing new business models.
- Problem Solving Workshops: Focus on identifying solutions to specific, often technical, problems blocking innovation projects.
- New Product Development (NPD) Workshops: Dedicated to generating, developing, and testing ideas for new products or services.
- Cross-Functional Integration Workshops: Aimed at breaking down silos within an organization by bringing together employees from different departments to collaborate on innovation initiatives. These workshops can foster a more integrated approach to innovation.
- Customer-Centric Innovation Workshops: Focus on understanding and empathizing with customer needs and experiences to drive innovation. Techniques like customer journey mapping and persona development are often used.
- Technology Exploration Workshops: Dedicated to exploring emerging technologies and their potential applications within the organization. These workshops can help in identifying opportunities for technological innovation.
- Sustainability Innovation Workshops: Focus on developing innovations that contribute to environmental sustainability and social responsibility. These workshops align innovation efforts with sustainability goals.
4. Internal Training vs. Multi-Organizations
- Internal Training Workshops: Conducted within an organization, tailored to its unique culture, challenges, and innovation objectives. These workshops foster internal collaboration and alignment.
- Multi-Organizations Workshops: Involve participants from different organizations, industries, or sectors. These workshops offer the advantage of cross-pollination of ideas and networking opportunities.
Innovation Workshops Near You
Here are recommended resources for finding Innovation workshops in your area:
- Eventbrite: This platform hosts a wide range of events, including workshops. You can search for "innovation workshops" and filter by location to find events near you. Visit: Eventbrite
- Meetup: Meetup is great for finding groups and events based on specific interests. Look for innovation or entrepreneurship groups in your area, which often host workshops and networking events. Visit: Meetup
- Local Universities and Colleges: Many higher education institutions offer workshops and seminars open to the public or their community. Check the websites of nearby universities for their entrepreneurship or innovation centers.
- Innovation Hubs and Co-working Spaces: These spaces frequently host workshops and events aimed at the local startup and innovation community. Search for co-working spaces and innovation hubs in your city and check their event calendars.
- Professional Organizations and Chambers of Commerce: Organizations related to business and technology often organize workshops and seminars on innovation. Your local chamber of commerce may also have information on upcoming business workshops.
- Social Media and Online Forums: Platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter can be useful for finding events in your professional network. Join innovation and entrepreneurship-related groups or follow pages that share events.
- Libraries and Community Centers: Don't overlook local libraries and community centers, which sometimes host workshops on a variety of topics, including technology and business innovation.
Six Outstanding Innovation workshops, Around the World
1. LEGO® Serious Play® Workshops
- Location: Global
- Overview: LEGO® Serious Play® is a facilitated thinking, communication, and problem-solving technique for organizations, using LEGO® bricks. Workshops are designed to enhance innovation and business performance based on the belief that everyone can contribute to the discussion, decisions, and outcome.
- Unique Features: The method encourages participants to express their thoughts through model-building, which fosters creative thinking and problem-solving in a non-traditional, engaging manner.
- Results/Impact: Numerous organizations worldwide have reported breakthroughs in team cohesion, strategy development, and innovation project planning after participating in LEGO® Serious Play® workshops, highlighting its effectiveness in unlocking creativity and strategic thinking.
2. NASA's Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) Program
- Location: USA
- Overview: The NIAC program supports early-stage studies of innovative concepts that could significantly impact NASA's mission. Workshops bring together scientists, engineers, and educators to explore visionary ideas through a rigorous peer review process.
- Unique Features: The program encourages proposals that are not just out-of-the-box but out-of-this-world, literally, fostering a unique blend of scientific innovation and speculative imagination.
- Results/Impact: NIAC has been instrumental in exploring futuristic concepts, such as asteroid mining and deep space habitats, demonstrating the value of investing in high-risk, high-reward research that could redefine space exploration.
3. Future London Academy's Design Thinking & Innovation Week
- Location: London, UK
- Overview: This immersive program for creative entrepreneurs, designers, and business leaders focuses on exploring design thinking and innovation in the heart of London, one of the world's design capitals.
- Unique Features: Participants engage in workshops, talks, and studio visits to learn about breakthrough design strategies directly from leading innovators and creative directors of renowned companies like Google, Facebook, and Pentagram.
- Results/Impact: Attendees leave with a comprehensive understanding of how cutting-edge design thinking can be applied to solve complex challenges, along with actionable insights and strategies to drive innovation within their organizations or practices.
4. Singularity University's Global Solutions Program
- Location: Silicon Valley, CA, USA
- Overview: Singularity University offers an intensive program that brings together leaders, entrepreneurs, and technologists from around the world to develop solutions to global grand challenges using exponential technologies.
- Unique Features: The program emphasizes disruptive thinking and the application of advanced technologies like AI, nanotechnology, and biotechnology to address critical global issues.
- Results/Impact: Graduates of the program have launched successful startups and initiatives that tackle problems in health, environmental sustainability, and education, showcasing the power of technology and innovative thinking to create positive global impact.
5. IDEO's Design Thinking Workshops
- Location: Global
- Overview: IDEO, a global design and innovation company, offers workshops that teach its renowned design thinking methodology, aimed at fostering creativity, empathy, and innovation in problem-solving.
- Unique Features: Workshops are highly interactive, involving rapid prototyping and user-centered design exercises that encourage participants to think and act creatively.
- Results/Impact: Organizations that have participated in IDEO's workshops report significant improvements in their approach to innovation, with enhanced ability to generate user-centric solutions and foster a culture of creativity and collaboration.
6. Systematic Innovation WorkshopsTM by ZOOZ
- Location: Global
- Overview: Our flagship workshops, focusing on strategic innovation, product and service innovation, or technological problem-solving. Designed for internal think tanks, and applied in developing real solutions.
- Unique Features: Systematic and highly practical workshops. For each step in the innovation process, we use highly effective principles, frameworks, and thinking tools. These are first demonstrated and then applied to real company issues to create feasible solutions for the organization.
- Results/Impact: Hundreds of organizations around the world have participated in Systematic Innovation™ Workshops, resulting in thousands of inventions, new products, and new services, as well as successful strategies and technological solutions. Additionally, organizations undergoing these workshops have assimilated innovation management processes that keep them continuously ahead of the competition.
- For further details: Read here, or contact us.
Innovation workshops are not just about generating ideas; they're about fostering a mindset of continuous improvement and adaptability. Through these sessions, participants learn to embrace change, think differently, and approach problems with a fresh perspective.
The skills and techniques learned in innovation workshops have far-reaching benefits, enhancing team collaboration, driving organizational growth, and building a resilient culture capable of navigating the complexities of the modern business landscape. As such, innovation workshops are an invaluable tool in the arsenal of any organization striving to maintain a competitive edge and foster a culture of continuous innovation.
Systematic innovation
Interested in getting help with systematic innovation processes and developing new products and services?
Contact us: info@zooz.co.il ,+972-9-958-5085
Innovation Articles
- Innovation overview
- Innovation management
- Innovation methods
- Innovation tools
- Innovation and creativity
- Innovation and other disciplines
- Innovation in organizations
- Innovation career
- Innovation importance
- Innovation goals
- Innovation values
- Inspiration for innovation
- Innovation education
- Product innovation
- Service innovation
- Technological innovation
- Innovation examples
- Innovations across various industries
- Innovation glossary (200 terms)





