Marketing Overview
Feb 13, 2024
By Ari Manor , CEO at ZOOZ

This is one in a series of articles that provide detailed and updated information about Marketing. In this specific article, which focuses on Marketing Overview, you can read about:
- What is Marketing?
- What Marketing Means?
- Why Marketing is Important
- How Marketing Helps Business
- How Marketing Works
- How Marketing Influences Consumer Behavior
- Marketing Basics
- What are the 4 Basics of Marketing?
- Marketing Principles
- Examples of Marketing
- Marketing Functions
- Types of Marketing
- How Marketing and Sales Work Together
- Marketing Ethics - Overview
- Marketing for Dummies
- Marketing for Beginners
For additional articles about Marketing, see the Topic Menu.

What is Marketing?
Marketing is a multifaceted discipline that sits at the heart of every business, serving as the bridge between a company's products or services and its customers. At its core, marketing is about understanding and meeting the needs and desires of customers, but it encompasses far more than just selling or advertising.
Firstly, marketing involves research and analysis to understand the market, including customer behaviors, preferences, and trends, as well as the competitive landscape. This foundational step ensures that marketing strategies are data-driven and targeted effectively.
Secondly, marketing is about creating value. It's not just about the product or service itself but the value proposition to the customer. This includes branding, which builds a unique identity and reputation in the market, and the customer experience, which encompasses every interaction a customer has with a business, from initial awareness to post-purchase support.
 Case Study: Spotify's Discover Weekly Feature
Case Study: Spotify's Discover Weekly Feature
- Company: Spotify, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Spotify introduced the Discover Weekly feature, a personalized playlist generated through algorithmic analysis of a user's listening history. This marketing initiative showcases Spotify’s understanding of individual music preferences, offering a unique value proposition by helping users discover new artists and tracks they're likely to enjoy. The feature is promoted across various platforms, including social media, to emphasize Spotify's commitment to personalization in the music streaming experience.
- Results/Impact: Discover Weekly quickly became a hallmark of Spotify's service, significantly enhancing user engagement and satisfaction. It has led to increased user retention rates and has been instrumental in attracting new subscribers. By effectively marketing this feature, Spotify has not only differentiated itself from competitors but also strengthened its position as a leader in personalized music streaming.
Thirdly, marketing employs a mix of strategies and channels to communicate with potential and existing customers. This includes, among many other components, the following Marketing Mix (The 4 Ps):
- Product Strategy: Developing products or services that meet the needs of the target market.
- Price Strategy: Setting prices that reflect the value provided while being competitive in the market.
- Place Strategy: Ensuring products or services are available where and when customers want them.
- Promotion Strategy: Communicating the value proposition through advertising, public relations, social media, content marketing, and more.
Fourthly, marketing is inherently dynamic, requiring continuous adaptation to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and consumer expectations. Marketers must be agile, constantly testing, learning, and refining their approaches based on measurable outcomes and feedback.
 Case Study:
Case Study:
Warby Parker's Home Try-On Program
- Company: Warby Parker, USA (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Warby Parker revolutionized the eyewear industry with its Home Try-On program, allowing customers to select five frames from their website, which are then shipped to them for free. This marketing strategy addresses the hesitation many consumers feel about buying glasses online by offering a risk-free way to try before buying. The program is heavily promoted through digital marketing channels, leveraging social proof by encouraging customers to share their experiences on social media.
- Results/Impact: The Home Try-On program has been a pivotal factor in Warby Parker's success, substantially increasing sales and customer loyalty. It has also enhanced the brand's visibility and reputation, positioning Warby Parker as a customer-centric brand. The program's success demonstrates the effectiveness of understanding and addressing customer needs in marketing.
Finally, marketing is about building relationships. It seeks to establish trust and loyalty with customers through consistent, positive experiences, engagement, and delivering on promises. This long-term perspective is essential for sustaining a business's growth and profitability.
 Case Study: Starbucks' Community Focus
Case Study: Starbucks' Community Focus
- Company: Starbucks, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Starbucks' marketing goes beyond selling coffee; it focuses on creating a 'third place' between home and work where people can relax and enjoy their coffee. This concept has been central to Starbucks' marketing strategy, emphasizing the experience over the product. They have implemented this through store design, community events, and customer loyalty programs.
- Results/Impact: This strategy has not only helped Starbucks to differentiate itself in a crowded market but has also cultivated a loyal customer base. The emphasis on experience over just coffee has led to significant brand loyalty and global expansion, making Starbucks a part of customers' daily lives.
In essence, marketing is a comprehensive approach to identifying, anticipating, and satisfying customer needs and desires profitably. It's both an art and a science, blending creativity with analytical insights to engage customers and drive business success.

What Marketing Means?
Marketing, in the broadest sense, is an essential function of business that encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at identifying, anticipating, and satisfying customer requirements profitably. It's a discipline that integrates both the art of creative strategies and the science of data-driven decisions, reflecting the dynamic interplay between businesses and their target audiences.
Key Components of Marketing:
- Market Research: The foundation of effective marketing lies in understanding your audience. This involves gathering and analyzing data on consumer needs, preferences, behaviors, and market trends. For example, using tools like Google Analytics and social media insights can reveal valuable information about your audience's online behavior and preferences. In addition, market research involved competitive analysis, benchmarking of leading providers from other industries, concept testing for products and services, and more.
- Strategic Planning: Developing a marketing strategy that aligns with business goals is crucial. This includes setting objectives, identifying target markets, and positioning the brand in a way that distinguishes it from competitors. Real-world application involves leveraging SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to inform strategy development.
- Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC): This involves using a mix of communication tools and channels—such as advertising, PR, social media, content marketing, and email marketing—to consistently convey the brand's message to the target audience. A successful example is Coca-Cola's "Share a Coke" campaign, which personalized the brand experience and leveraged social media to amplify its reach.
 Case Study: Tesla's Disruptive Marketing
Case Study: Tesla's Disruptive Marketing- Company: Tesla, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Tesla has revolutionized the automotive and energy industries with its focus on sustainable energy. Instead of traditional advertising, Tesla relies on word-of-mouth, media coverage, and Elon Musk's personal brand on social media to market its innovations. Tesla's marketing strategies include unveiling futuristic products and leveraging pre-orders to gauge and generate demand.
- Results/Impact: Tesla's marketing strategy has helped it to not only save on advertising costs but also build a strong brand presence. It has disrupted the automotive industry, positioned itself as a leader in innovation, and cultivated a passionate fan base eager for its next breakthrough.
- Customer Experience and Relationship Management: Creating a positive, engaging customer experience at every touchpoint builds loyalty and advocacy. This can include anything from personalized email marketing campaigns to responsive customer service. Companies like Amazon excel in this area by prioritizing customer satisfaction with fast shipping, easy returns, and personalized recommendations.
- Analytics and Performance Measurement: Continuous measurement and analysis of marketing activities allow businesses to understand what works and what doesn't. Using metrics such as ROI (Return on Investment), conversion rates, and customer lifetime value helps in refining strategies and optimizing performance.

Why Marketing is Important
Marketing is a crucial component of any business's success, acting as the engine that drives awareness, engagement, customer acquisition, and ultimately, revenue. Its importance cannot be over-stated, as it encompasses a wide range of activities that help businesses understand their customers, create value, and communicate effectively. Here are several reasons why marketing is so important:
- Creates Awareness: Marketing strategies such as advertising, content marketing, and social media play a pivotal role in building brand awareness. Without marketing, potential customers may never learn about a business and its products or services, regardless of their quality.
- Facilitates Engagement: Marketing engages customers through compelling storytelling, interactive content, and meaningful interactions. This engagement is critical for building relationships, fostering loyalty, and encouraging word-of-mouth promotion.
 Case Study: Slack's User-Centric Marketing
Case Study: Slack's User-Centric Marketing- Company: Slack, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Slack’s marketing strategy focuses on user experience and efficiency, positioning itself as an indispensable tool for team communication. By highlighting real user stories and the tangible benefits of using Slack, such as reduced email clutter and improved team collaboration, in their marketing materials, Slack has been able to communicate its value proposition effectively. The company utilizes a mix of content marketing, social media engagement, and targeted advertising to reach potential users.
- Results/Impact: This user-centric approach has helped Slack rapidly grow its user base and become a leader in the team communication software market. The emphasis on solving common workplace challenges and the active engagement with the user community have fostered strong brand loyalty and advocacy among its users.
- Drives Customer Decision-making: Effective marketing influences customer decisions, guiding them through the buying journey from awareness to consideration and purchase. By providing valuable information and persuasive messaging, marketing helps consumers make informed choices.
- Supports Business Growth: Marketing efforts directly contribute to business growth by attracting new customers and retaining existing ones. It's essential for launching new products, entering new markets, and achieving sales targets.
 Case Study:
Case Study:
Lego's Rebranding and Market Expansion- Company: Lego, Worldwide (since 2004)
- What Was Done: Facing a declining market in the early 2000s, Lego embarked on a strategic rebranding and expansion effort. This included diversifying its product line with themed sets (e.g., Harry Potter, Star Wars), engaging in storytelling through Lego movies and video games, and enhancing customer experience in Lego stores. Lego's marketing strategy focused on rebuilding the brand as not just a toy but a creative and educational experience for children and adults alike, utilizing traditional and digital marketing channels to reach a broader audience.
- Results/Impact: Lego’s revitalized marketing approach led to a remarkable turnaround, with the company seeing unprecedented growth in sales and becoming the world's leading toy company. The strategy not only expanded Lego's market but also reinvigorated the brand, creating a strong emotional connection with consumers across generations.
- Builds Brand Identity and Reputation: Marketing shapes a brand's identity and reputation through consistent messaging, visual identity, and customer experiences. A strong brand can differentiate a business in a crowded market, build trust, and create a loyal customer base.
 Case Study: Apple's Brand Loyalty
Case Study: Apple's Brand Loyalty- Company: Apple, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: pple has excelled in creating a strong brand through meticulous product design, innovative technology, and a clear marketing message that emphasizes user experience. Apple's marketing goes beyond advertising products; it sells an ecosystem and a lifestyle, making customers feel a part of an exclusive community.
- Results/Impact: Apple's approach has led to unparalleled brand loyalty and a massive, dedicated customer base willing to queue for hours for the latest product launch. This loyalty has not only sustained long-term growth but also made Apple one of the most valuable companies in the world.
- Provides Market Insights: Through market research, marketing helps businesses gain insights into customer needs, market trends, and competitive landscapes. These insights are invaluable for strategic planning, product development, and staying ahead of industry changes.
- Enables Customer Satisfaction and Retention: By understanding and meeting customer needs, marketing strategies enhance customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to be loyal, repeat buyers, and brand advocates.
- Optimizes ROI: Marketing strategies, especially in digital marketing, allow for the measurement and analysis of return on investment (ROI). Businesses can allocate their resources more effectively, focusing on high-performing channels and campaigns.
- Adapts to Changing Consumer Behaviors: The digital age has transformed how consumers interact with brands. Marketing keeps businesses at the forefront of these changes, leveraging digital channels and technologies to reach consumers where they are.
- Drives Innovation: Marketing encourages innovation by identifying gaps in the market and understanding consumer pain points. This leads to the development of new products or services that fulfill unmet needs, keeping businesses competitive.
In conclusion, marketing is not just an isolated business function; it's an integrated approach that impacts almost every aspect of a business. From building brand awareness to driving sales and fostering customer loyalty, marketing is essential for sustaining and growing a business in today's competitive environment.

How Marketing Helps Business
Marketing is essential for businesses as it bridges the gap between a company's offerings and consumer needs. In a concise manner, marketing boosts business success through:
- Visibility: Increases brand exposure to attract new customers.
- Engagement: Fosters a connection with the audience, enhancing customer loyalty.
- Sales Support: Directly influences purchasing decisions, boosting sales.
- Differentiation: Positions the brand uniquely in the market, standing out from competitors.
- Feedback Loop: Provides valuable insights into consumer preferences for better business decisions.
 Case Study: Peloton's Community-Building Efforts
Case Study: Peloton's Community-Building Efforts
- Company: Peloton, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Peloton transformed the home exercise experience by integrating cutting-edge technology with live streaming and on-demand fitness classes. Their marketing strategy focused on building a sense of community among users, leveraging social media platforms, and creating engaging content that highlights member success stories. Peloton's approach included interactive challenges, leaderboards, and the promotion of a supportive community atmosphere that encourages motivation and accountability.
- Results/Impact: This emphasis on community and interconnectedness has led to a rapid increase in Peloton's membership and brand loyalty. The company has successfully differentiated itself in a crowded fitness market, fostering a passionate user base willing to advocate for the brand. Peloton's marketing efforts have significantly contributed to its growth, demonstrating how creating a strong brand community can enhance customer engagement and retention.
In essence, marketing is pivotal for driving growth, building a loyal customer base, and staying competitive in a dynamic market environment.

How Marketing Works
Marketing functions through a strategic framework that combines research, planning, execution, and analysis to connect businesses with their target audiences effectively. This framework ensures that a company's products or services meet customer needs and preferences, facilitating successful exchanges that benefit both the company and its customers.
Marketing Elements
Here’s a simplified overview of how marketing works:
- Market Research: The process begins with market research to gather insights about the target market, including customer demographics, preferences, behaviors, and competitor analysis. This step is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Marketing Strategy: Based on research findings, businesses develop a marketing strategy that defines target audience segments, marketing objectives, positioning, and the marketing mix (Product, Price, Place, Promotion).
- Marketing Mix Implementation:
- Product: Ensuring the product or service meets the needs of the target market.
- Price: Setting a price that reflects the perceived value and is competitive.
- Place: Distributing the product in locations where the target customers can easily find and purchase it.
- Promotion: Communicating the value proposition through various channels (advertising, social media, email marketing, etc.) to inform, persuade, and engage the target audience.
- Customer Engagement: Engaging with customers through multiple touchpoints to build relationships, gather feedback, and foster loyalty. This includes content marketing, social media interactions, and personalized communication.
 Case Study: Dove's Real Beauty Campaign
Case Study: Dove's Real Beauty Campaign- Company: Dove, Worldwide (2004)
- What Was Done: Dove launched the "Real Beauty" campaign to redefine beauty standards marketed by the beauty industry. The campaign featured women of all shapes, sizes, and ethnicities, challenging the traditional perceptions of beauty. It included billboards, videos, and workshops, aiming to boost women's self-esteem worldwide.
- Results/Impact: The campaign not only significantly increased Dove's product sales but also sparked a global conversation about beauty standards. Dove established itself as a brand that values inner beauty and self-confidence, deepening its emotional connection with consumers.
- Performance Measurement and Analysis: Evaluating the effectiveness of marketing activities using metrics like ROI, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction. This analysis informs future marketing strategies and tactics.
- Adaptation and Continuous Improvement: Marketing is a dynamic process. Based on performance analysis and changing market conditions, businesses must adapt their strategies and tactics for continuous improvement and to stay competitive.
Marketing Business Goals
Marketing achieves various business goals as follows:
- Increases Visibility: Raises awareness of the brand and its offerings.
- Drives Sales: Encourages purchases through effective promotion and persuasion.
- Builds Brand Equity: Develops and maintains a strong brand identity and reputation.
- Enhances Customer Relationships: Engages and retains customers for long-term loyalty.
- Informs Product Development: Uses customer feedback and market trends to guide innovation and improvement.
 Case Study: Trello's Visual Marketing for Productivity
Case Study: Trello's Visual Marketing for Productivity
- Company: : Trello, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Trello, a web-based project management application, employs a marketing strategy that emphasizes the visual and intuitive nature of its software to improve team productivity. Through the use of engaging and informative content, including video tutorials, blog posts, and case studies, Trello highlights how its tool can streamline project management and collaboration. Their marketing efforts focus on demonstrating the software's flexibility and ease of use across different industries and team sizes.
- Results/Impact: Trello's clear and visually appealing marketing has played a crucial role in its user growth, attracting millions of users worldwide. By effectively communicating the benefits and versatility of its tool, Trello has not only increased its user base but also established itself as a go-to solution for teams seeking to enhance productivity and collaboration. The company's success illustrates the importance of tailored marketing strategies that resonate with the target audience's needs and preferences.
In summary, marketing is a comprehensive process that encompasses understanding customer needs, crafting strategic messages, delivering value, and fostering relationships. Its ultimate goal is to achieve business objectives by satisfying customer needs better than competitors, thereby driving sales and ensuring business growth.

How Marketing Influences Consumer Behavior
Marketing significantly influences consumer behavior by shaping perceptions, creating preferences, and ultimately driving purchasing decisions. Through a combination of strategies and tools, marketing communicates messages to consumers, engaging them and guiding their journey from awareness to purchase and beyond. Here’s how marketing influences consumer behavior:
- Awareness Creation: Marketing introduces consumers to new products and services, creating initial awareness. Through advertising, social media, and content marketing, businesses can capture the attention of potential customers, making them aware of solutions they hadn’t considered before.
 Case Study: GoPro's User-Generated Content Strategy
Case Study: GoPro's User-Generated Content Strategy- Company: GoPro, Nationwide (ongoing since early 2010s)
- What Was Done: GoPro encouraged its users to capture and share their adventures using its cameras, essentially turning customers into brand ambassadors. The company heavily featured user-generated content in its marketing campaigns, on social media, and in promotional materials, showcasing the quality and versatility of its products in real-world scenarios.
- Results/Impact: This approach not only amplified GoPro's online presence and brand awareness but also significantly boosted sales. By highlighting authentic experiences captured by everyday users, GoPro was able to demonstrate the value of its products in a relatable way, encouraging more consumers to join its community of brand advocates. The strategy effectively leveraged the power of social proof, contributing to GoPro's status as a leading name in action cameras.
- Information Provision: By providing detailed information about products or services, marketing helps consumers make informed decisions. This includes highlighting features, benefits, and differentiators from competitors, which can sway consumer preferences and choices.
- Emotional Engagement: Effective marketing often appeals to emotions, creating a connection between the consumer and the brand. Emotional engagement can significantly influence consumer preferences and loyalty, making it a powerful tool for shaping behavior.
- Brand Image and Perception: Marketing efforts build and maintain a brand's image, influencing how consumers perceive it. A positive brand image can lead to a preference for that brand’s products or services, even when presented with similar alternatives.
 Case Study: Intel’s Campaign: Humanizing Technology
Case Study: Intel’s Campaign: Humanizing Technology- Company: Intel, Santa Clara (2013)
- What Was Done: Launched the "Look Inside" campaign to highlight how Intel processors are part of individuals’ passions and achievements, featuring personal stories and the impact of technology.
- Results/Impact: Achieved increased brand awareness and perception. The campaign received multiple marketing awards, reflecting its resonance with consumers and its effectiveness in humanizing the brand.
- Social Influence: Marketing leverages social proof, testimonials, influencer partnerships, and user-generated content to influence consumer behavior. Seeing others endorse a product or service can significantly impact an individual's decision to purchase.
 Case Study: The Power of Local Sourcing
Case Study: The Power of Local Sourcing- Company: Bean Around the World Coffees, Vancouver (2018)
- What Was Done: This small chain of coffee shops focused on marketing its commitment to local sourcing and fair trade practices. They highlighted their relationships with local farmers and the community through their marketing materials.
- Results/Impact: The company saw a significant increase in customer loyalty and a boost in sales. Their commitment to local and ethical sourcing also led to positive media coverage, enhancing their reputation in the market.
- Creating Perceived Need: Through targeted marketing strategies, businesses can create a perceived need for their products or services. By highlighting problems or needs that consumers may not have been aware of, marketing can motivate them to seek out solutions, directing them towards specific brands or products.
- Encouraging Action: Call-to-actions (CTAs) in marketing are designed to prompt immediate responses from consumers, whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or following a brand on social media. Effective CTAs can significantly influence the immediacy of consumer actions.
- Loyalty and Retention: Post-purchase marketing efforts, such as email marketing, loyalty programs, and customer feedback initiatives, work to keep consumers engaged and satisfied, influencing repeat purchases and long-term loyalty.
- Gamification, for example, is a powerful tactic that encourages engagement of consumers, and is a very common approach for gaining users’ loyalty online.
- Gamification, for example, is a powerful tactic that encourages engagement of consumers, and is a very common approach for gaining users’ loyalty online.
- Shaping Consumer Expectations: Marketing sets expectations for the consumer experience. By consistently delivering on promises made through marketing, brands can positively influence consumer satisfaction and perceptions.
- Adapting to Consumer Trends: Marketing is dynamic, adapting to changing consumer trends and preferences. By staying relevant and aligned with consumer desires, marketing strategies can effectively influence consumer behavior over time.
In conclusion, marketing plays a pivotal role in influencing consumer behavior, leveraging a blend of informational, emotional, and social strategies to guide consumers through their decision-making process. Understanding these influences can help businesses craft more effective marketing strategies, driving consumer actions in favor of their products or services.

Marketing Basics
Marketing basics encompass the foundational elements and strategies that businesses use to promote their products or services, engage with their target audience, and ultimately drive sales and growth. Understanding these basics is crucial for any successful marketing effort. Here's a concise overview:
- The Marketing Mix (The 4 Ps):
- Product: What you are selling, including all of the features, advantages, and benefits that your customers can enjoy by buying what you are selling.
- Price: What your customers are willing to pay, and what your competitors charge. You must find the balance between what customers are willing to pay and what you need to charge to make a profit.
- Place: Where your products are sold, which can range from physical locations to online platforms. This also encompasses distribution channels and logistics.
- Promotion: The activities you undertake to make your customers aware of your products or services. This includes advertising, sales tactics, promotions, and direct marketing.
- Market Research: Understanding your market and customers through research is crucial. This involves gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, including potential customers and competitors. It's foundational for making informed marketing decisions.
- Target Audience: Identifying and understanding your target audience is essential. This includes knowing their demographics, behaviors, preferences, and needs. Tailoring your marketing strategies to meet the specific demands of your target audience can significantly increase the effectiveness of your marketing.
- Branding: Developing a strong brand identity that resonates with your target audience is key. Branding goes beyond just a logo or tagline; it encompasses the entire customer experience, from the product design to the post-purchase service. A strong brand creates loyalty and value.
 Case Study:
Case Study:
Old Spice, Revitalizing a Classic Brand- Company: Old Spice, Nationwide (2010)
- What Was Done: Rebranded with a new campaign aimed at a younger demographic, leveraging humor and virality to reshape and update the brand's image.
- Results/Impact: Saw a 107% increase in body wash sales and gained extensive online engagement, resulting in a significant brand refresh and greater appeal to a new generation of consumers.
- Digital Marketing: In today's digital age, marketing increasingly relies on digital channels. This includes content marketing, email marketing, social media, SEO (Search Engine Optimization), and online advertising. Digital marketing allows for targeted campaigns and analytics to measure success.
 Case Study: Dollar Shave Club, Crafting a Niche in a Crowded Market
Case Study: Dollar Shave Club, Crafting a Niche in a Crowded Market- Company: Dollar Shave Club, Nationwide (2012)
- What Was Done: Introduced a subscription-based razor service with a humorous and disruptive launch video, positioning themselves as a convenient and cost-effective option.
- Results/Impact: The launch video went viral, leading to over 12,000 orders within two days. The company’s substantial growth culminated in a $1 billion acquisition by Unilever in 2016.
- Content Marketing: Creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience. Content marketing is aimed at driving profitable customer action.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Strategies and technologies used by companies to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. The goal is to improve customer service relationships and assist in customer retention and sales growth.
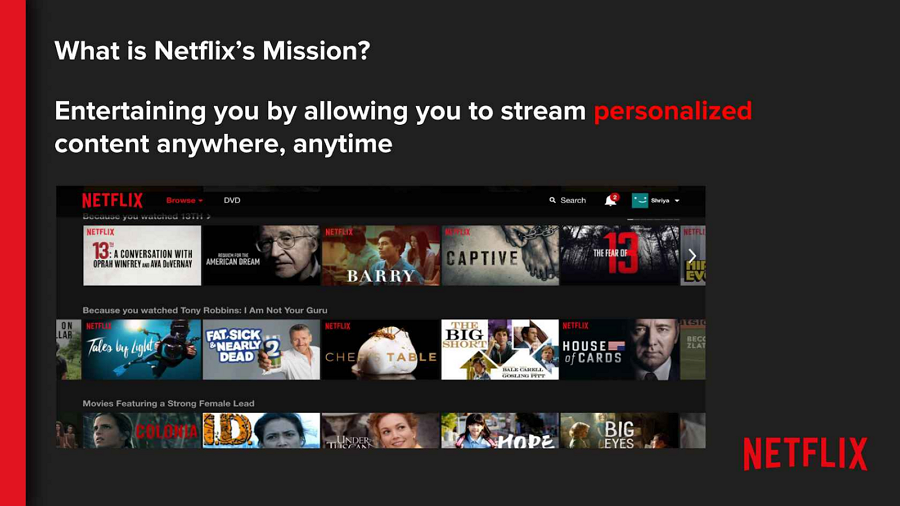 Case Study: Netflix's Personalized Marketing
Case Study: Netflix's Personalized Marketing- Company: Netflix, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Netflix utilizes big data and analytics to personalize its marketing efforts. By analyzing viewer habits, preferences, and behaviors, Netflix creates targeted marketing campaigns and recommendations for its users. This strategy includes personalized emails, tailored show recommendations, and even custom thumbnails for each user.
- Results/Impact: This personalized approach has led to increased viewer engagement, higher subscription retention rates, and the rapid growth of Netflix's user base. By making content discovery more personalized and relevant, Netflix has not only enhanced user satisfaction but also set a new standard for content delivery and marketing in the streaming industry.
- Analytics and Metrics: Measuring and analyzing performance is essential for understanding the effectiveness of marketing strategies and making data-driven decisions. Key metrics include conversion rates, ROI (Return on Investment), customer acquisition costs, and customer lifetime value.
- Adaptability: The marketing landscape is constantly changing, influenced by technological advancements, cultural shifts, and consumer behavior trends. Being adaptable and open to change is crucial for staying relevant and competitive.
Understanding these marketing basics provides a solid foundation for developing and implementing effective marketing strategies. Whether you're a small business owner, a marketing professional, or someone interested in entering the field, grasping these fundamentals is the first step towards marketing success.

What are the 4 Basics of Marketing?
The four basics of marketing, often referred to as the "4 Ps of Marketing," are a foundational model for businesses aiming to effectively reach and engage their target audience. This concept was first introduced by Jerome E. McCarthy in the 1960s and has since been a cornerstone of marketing theory and practice. Here’s a breakdown:
- Product: This refers to what you are selling, including all physical products, services, or digital goods. It's not just about the item itself but also about solving a problem or fulfilling a need for the customer. Successful products are those that meet a specific customer demand or offer a unique benefit, supported by unique features.
- Price: Price is what the customer pays for the product. It's a reflection of the perceived value of the product, influenced by production costs, competition, market demand, and customers' willingness to pay (price sensitivity). Pricing strategies can significantly impact sales, market share, and profitability.
- Place: Also known as distribution, place involves making the product available to the customer at the right time, location, and in the right quantity. It includes decisions about distribution channels (online, retail, direct sales, etc.) and logistics. The goal is to maximize convenience for the customer, thereby increasing the likelihood of purchase.
- Promotion: Promotion encompasses all the ways a business communicates about its product to its target audience, including advertising, sales promotions (including discounts, bundles and giveaways), public relations, and social media marketing. The aim is to inform, persuade, and remind potential and existing customers about the product, its benefits, and any special offers.
 Case Study: Burt's Bees Product Positioning and Eco-Friendly Marketing
Case Study: Burt's Bees Product Positioning and Eco-Friendly Marketing
- Company: Burt's Bees, USA (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Burt's Bees demonstrates the 4 Ps through its natural personal care products, pricing strategy that reflects its quality and ethical sourcing, widespread availability in both online and physical stores, and promotion of its sustainability efforts.
- Results/Impact: This strategy has enabled Burt's Bees to stand out in the crowded beauty market, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and growing its business sustainably. The brand has become synonymous with natural ingredients and environmental responsibility.
These four basics work together to create a comprehensive marketing strategy. Understanding and effectively managing the 4 Ps allows marketers to position their product attractively in the marketplace, meeting customer needs and driving sales. Therefore, when devising a marketing strategy, it is crucial to tailor the products, pricing, placement, and promotions to align with the brand's (actual or desired) differentiation and positioning in the market.
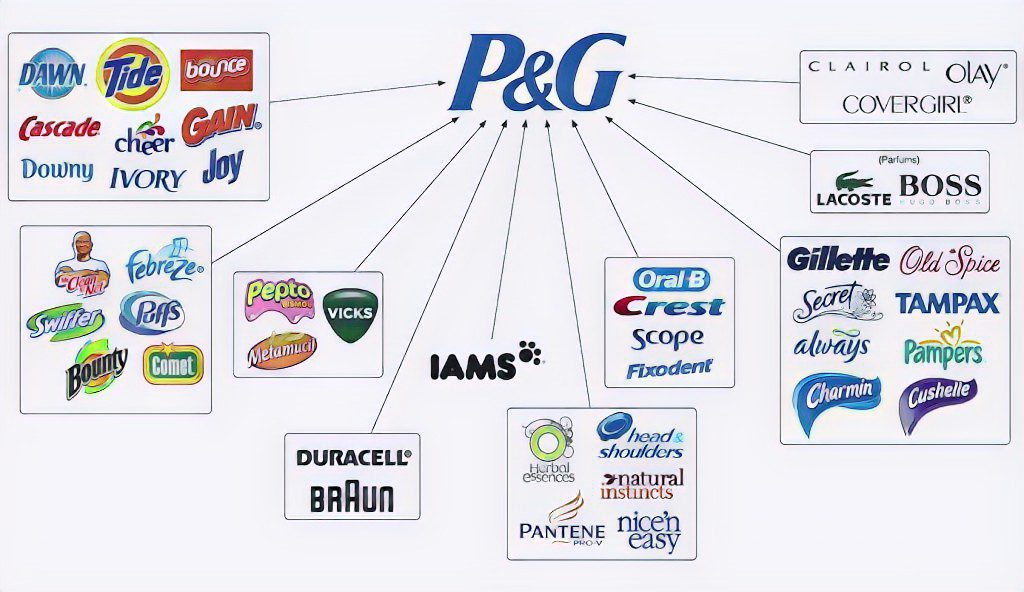 Case Study: P&G's Product Innovation and Market Segmentation
Case Study: P&G's Product Innovation and Market Segmentation
- Company: Procter & Gamble (P&G), Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: P&G exemplifies the 4 Ps of marketing—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—through its extensive product portfolio, innovative product development, strategic pricing models, widespread distribution channels, and targeted advertising campaigns. P&G continuously analyzes market trends and consumer needs to introduce or reformulate products that meet specific customer segments.
- Results/Impact: By adeptly applying the 4 Ps of marketing, P&G has maintained its position as a leader in the global consumer goods industry. This approach has enabled P&G to build strong brand equity, foster customer loyalty, and achieve sustainable growth across its diverse range of brands and products.
Over time, some have suggested extensions to the original 4 Ps, incorporating elements like People, Process, and Physical evidence (expanding it to 7 Ps in the service marketing mix) to acknowledge the importance of human interaction, customer service, and the physical environment in the marketing strategy. However, the original 4 Ps remain the fundamental pillars on which marketing strategies are built.

Marketing Principles
Marketing principles are foundational guidelines that underpin effective marketing strategies and practices. These principles guide businesses in creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
Here are key marketing principles:
- Customer Orientation: The customer should be at the heart of all marketing efforts. Understanding customer needs, preferences, and behaviors is crucial for creating products and services that meet their expectations. This involves ongoing market research and customer feedback mechanisms to stay aligned with customer demands.
 Case Study: Amazon's Use of AI in Marketing
Case Study: Amazon's Use of AI in Marketing- Company: Amazon, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Amazon employs artificial intelligence to enhance its marketing strategies. This includes personalized recommendations for customers based on their browsing and purchasing history, which is displayed on their homepage and through targeted email campaigns.
- Results/Impact: This AI-driven personalization has significantly increased customer engagement and sales, making Amazon a leader in personalized marketing. It has also improved customer satisfaction by making product discovery more relevant and efficient.
- Value Creation and Delivery: Marketing is about creating value that customers appreciate. This involves not only developing valuable products or services but also ensuring that the way they are delivered enhances their value. The entire process, from product development to delivery, should focus on maximizing customer value and satisfaction.
 Case Study: The Dieline, Community-Driven Marketing
Case Study: The Dieline, Community-Driven Marketing- Company: The Dieline, Online (2015)
- What Was Done: As a small but influential packaging design website, The Dieline created a community around packaging design excellence, integrating user submissions and featuring community-driven content.
- Results/Impact: By adhering to the marketing principle of engaging customers as part of the brand story, The Dieline grew to become the go-to resource in its niche, expanding its readership and increasing its influence in the design community.
- Integrated Marketing Communications: A consistent and cohesive message across all marketing channels strengthens brand recognition and customer trust. Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) ensures that all forms of communications and messages are carefully linked together, from traditional advertising to digital marketing and social media.
 Case Study: Bella Boutique's Localized Marketing Effort
Case Study: Bella Boutique's Localized Marketing Effort- Company: Bella Boutique, Savannah, GA, (2020)
- What Was Done: Bella Boutique, a small fashion boutique, utilized a combination of local SEO, social media marketing focusing on Instagram and Facebook, and community events to engage the local market. Their strategy was designed to increase foot traffic and drive online sales by showcasing their unique offerings and connecting with the local community.
- Results/Impact: This localized multi-channel approach resulted in a 60% increase in in-store foot traffic and a 45% rise in online sales over the year, proving that small businesses can achieve substantial growth by effectively leveraging a mix of marketing channels tailored to their audience.
- Branding and Positioning: Establishing a strong brand identity and clear market positioning is essential for differentiation. Branding goes beyond a logo or slogan; it encompasses the entire customer experience with the product or service. Effective positioning highlights the unique benefits and features that set a product apart from competitors.
- Relationship Marketing: Building and maintaining long-term relationships with customers is key to sustained business success. This principle focuses on customer retention through loyalty programs, personalized communication, and exceptional customer service, recognizing the long-term value of customer relationships over transactional exchanges.
 Case Study: Bloom & Wild's Personalized Email Campaigns
Case Study: Bloom & Wild's Personalized Email Campaigns- Company: Bloom & Wild, UK (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Bloom & Wild, a small online flower delivery service, uses customer data to send personalized email marketing campaigns. They consider previous purchases and dates important to the customer, such as anniversaries, to suggest relevant gifts.
- Results/Impact: This personalized approach has led to higher opening rates, increased repeat purchases, and a strong customer loyalty. Bloom & Wild has seen significant growth in its customer base and revenue through its focus on personalized customer experiences.
- Marketing Mix: The 4 Ps—Product, Price, Place, Promotion—serve as the primary pillars of marketing strategy. Balancing these elements to meet the needs of the target market is crucial for effective marketing:
- Product: What you are selling must solve a problem or fulfill a need.
- Price: Must reflect the perceived value and be competitive.
- Place: How and where customers can purchase the product.
- Promotion: How you communicate the product's value to the target audience, and encourage purchases.
- Consumer Psychology Understanding: Understanding the psychological factors that influence consumer behavior, such as motivations, perceptions, attitudes, and beliefs, enables marketers to design more effective campaigns and product offerings.
- In-depth Interviews, for example, can be used to uncover consumers’ sub-conscious beliefs and concerns
- In-depth Interviews, for example, can be used to uncover consumers’ sub-conscious beliefs and concerns
- Adaptability and Responsiveness: The marketing environment is dynamic, influenced by changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and competitive landscapes. Successful marketing requires adaptability and responsiveness to these changes.
- Ethical Marketing: Ethical considerations and social responsibility should guide marketing practices. Honest communication, respect for customer privacy, and ethical behavior build trust and enhance brand reputation.
 Case Study: Patagonia, Empowering Through Education
Case Study: Patagonia, Empowering Through Education- Company: Patagonia, Ventura (2013)
- What Was Done: Launched the "Worn Wear" campaign that encourages customers to buy fewer items, repair their gear, and reduce their environmental footprint. This campaign was based on the marketing principle of corporate social responsibility.
- Results/Impact: Patagonia experienced a boost in customer loyalty and brand differentiation. The campaign helped to solidify the company’s reputation as an environmentally conscious brand and actually increased sales by reinforcing trust and aligning with customer values.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Utilizing data analytics for decision making allows businesses to tailor their marketing strategies based on actual customer behavior and market trends, leading to more effective and efficient marketing efforts.
Understanding and applying these fundamental marketing principles can help businesses develop strategies that effectively engage customers, build brand loyalty, and drive growth.

Examples of Marketing
Examples of marketing span a broad range of activities and strategies businesses use to promote their products or services, engage with their target audience, and ultimately drive sales.
Here are several examples illustrating various aspects of marketing in action:
- Social Media Marketing: A fashion brand launches a new line of eco-friendly clothing and uses Instagram to showcase the collection through high-quality images, influencer collaborations, and interactive stories to engage with their environmentally conscious audience.
 Case Study: The Grind Coffee Company's Instagram Engagement
Case Study: The Grind Coffee Company's Instagram Engagement- Company: The Grind Coffee Company, Johannesburg (ongoing)
- What Was Done: The Grind Coffee Company leverages Instagram to engage customers by posting high-quality images of their coffee and café, hosting giveaways, and featuring customers' photos.
- Results/Impact: Their approach has built a strong local community around the brand, increased foot traffic, and enhanced customer loyalty. Their effective use of social media marketing has also attracted tourists looking for the renowned coffee experience.
- Content Marketing: A software company creates a series of blog posts, webinars, and downloadable guides offering valuable insights on how to solve common industry problems using their tools, positioning themselves as thought leaders in their sector.
- Email Marketing: An online retailer sends personalized email newsletters to its customers featuring special discounts, product recommendations based on past purchases, and exclusive previews of upcoming products to encourage repeat business.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): A local bakery optimizes its website content with relevant keywords, improves site speed, and ensures mobile-friendliness to rank higher in search engine results for searches related to "best bakery near me" or "homemade bread."
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: A financial services firm runs targeted PPC ads on Google and LinkedIn to reach individuals searching for investment advice, directing them to a landing page offering a free investment planning consultation.
- Influencer Marketing: A beauty brand partners with several high-profile beauty influencers on YouTube and TikTok to create content using their products, reaching millions of followers and driving brand awareness and sales.
- Public Relations (PR): A tech startup launching a groundbreaking app organizes a virtual press conference and sends press releases to technology news outlets, generating media coverage and buzz ahead of the launch.
- Event Marketing: A sports equipment company sponsors a well-known marathon event, setting up booths where participants can try out and purchase their latest running gear, enhancing brand visibility and engagement.
 Case Study: Red Bull's Extreme Sports Sponsorship
Case Study: Red Bull's Extreme Sports Sponsorship- Company: Red Bull, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Red Bull has taken a unique approach to marketing by associating its brand with extreme sports and adrenaline-fueled activities. This strategy involves sponsoring athletes, hosting events (like the Red Bull Stratos space diving project), and producing content that highlights extraordinary human achievements.
- Results/Impact: Red Bull's marketing strategy has successfully built a brand image that transcends being just an energy drink. It has become synonymous with extreme sports and adventure, significantly boosting its global presence and consumer engagement. This approach has not only differentiated Red Bull from its competitors but also created a strong, loyal community around the brand.
- Direct Mail Marketing: A real estate agency sends out high-quality, personalized brochures to residents in targeted neighborhoods, showcasing available properties and testimonials from satisfied clients.
- Guerrilla Marketing: a new energy drink brand creates a high-energy flash mob in a busy city center, capturing the event on video and sharing it across social media platforms for viral impact.
These examples highlight the diversity of marketing strategies available to businesses today, each leveraging different channels and tactics to achieve specific marketing objectives. From digital campaigns to traditional methods, effective marketing involves a mix of approaches tailored to the business's goals and the preferences of its target audience.

Marketing Functions
Marketing functions encompass a wide range of activities and processes that aim to maximize a company's reach, impact, and engagement with its target audience, ultimately driving sales and fostering brand loyalty. These functions are fundamental to the success of a business's marketing strategy.
Here are several key marketing functions:
- Market Research: Gathering and analyzing data about the market, competition, and consumer behaviors to inform strategic decisions. This includes surveys, focus groups, and analysis of consumer data to understand market needs and trends.
- Product Development and Management: Creating new products or improving existing ones based on market research, customer feedback, and technological advancements. This involves concept testing, design, development, and lifecycle management.
- Pricing Strategy: Determining pricing models that reflect the value of the product or service to the customer, competitive pricing, and company objectives. Pricing strategies must consider costs, market demand, and perceived value.
 Case Study: Mailchimp's Freemium Model
Case Study: Mailchimp's Freemium Model- Company: Mailchimp, Online (2009)
- What Was Done: Mailchimp adopted a freemium model, offering a free email marketing service with the option to upgrade for advanced features. They focused on ease-of-use and education, providing extensive resources for those new to email marketing.
- Results/Impact: he freemium model dramatically expanded Mailchimp’s user base, with the company seeing revenue growth from $280 million in 2015 to $700 million in 2019. It illustrated the effectiveness of a product-led growth strategy in market penetration and customer acquisition.
- Distribution and Logistics: Managing how products are delivered to consumers, including choosing distribution channels (retail, online, direct sales) and managing supply chain logistics to ensure products are available where and when consumers want them.
 Case Study: Zara's Fast Fashion Model
Case Study: Zara's Fast Fashion Model- Company: Zara, Worldwide (ongoing)
- What Was Done: Zara’s marketing is largely driven by its fast fashion business model, which focuses on rapid production cycles and frequent releases of new items to keep up with the latest trends. The company minimizes advertising spend and instead invests in store location and layout, creating a constantly changing environment that encourages regular customer visits.
- Results/Impact: This strategy has allowed Zara to grow into one of the world’s largest fashion retailers, with a strong global presence and high turnover rates for its products. The brand has mastered the art of responsiveness to fashion trends, maintaining customer interest and ensuring that stores always offer something new and exciting. This approach has not only solidified Zara’s market position but also redefined consumer expectations within the fashion industry.
- Promotion and Advertising: Communicating with target audiences about the brand, products, or services through various channels, including advertising, public relations, social media, and content marketing, to build brand awareness and stimulate demand.
- Sales Management: Directly facilitating the purchase of products or services. This includes sales strategy, customer interaction, negotiations, and closing deals. Effective sales management is crucial for converting prospects into customers.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Building and maintaining relationships with customers to enhance loyalty and retention. This involves using data to personalize interactions, address customer needs, and provide exceptional service.
- Branding and Brand Management: Developing and maintaining a brand's identity, values, and promise to the consumer. This includes managing the visual identity, brand messaging, and overall perception in the market.
 Case Study: Nike's Just Do It Campaign
Case Study: Nike's Just Do It Campaign- Company: Nike, Worldwide (1988)
- What Was Done: Nike launched the "Just Do It" campaign, aimed at inspiring athletes and non-athletes alike to push beyond their limits. The campaign featured advertisements with high-profile athletes and everyday people achieving personal bests, reinforcing Nike’s brand as a motivator for athletic achievement.
- Results/Impact: The campaign catapulted Nike from a company known primarily for its running shoes to a global sports and lifestyle brand. Sales skyrocketed from $877 million in 1988 to over $9.2 billion by 1998. "Just Do It" became one of the most recognizable and successful marketing slogans in history, significantly enhancing Nike's market share and brand loyalty.
- Digital Marketing: Leveraging online platforms and technologies to reach consumers, including SEO, email marketing, social media, and online advertising. Digital marketing is essential for engaging with the modern, connected consumer.
- Analytics and Reporting: Measuring and analyzing marketing performance to understand ROI, effectiveness of campaigns, and consumer engagement. This data-driven function informs future marketing strategies and adjustments.
These functions work together to create a cohesive and comprehensive marketing strategy that aligns with business objectives, meets customer needs, and adapts to the dynamic market environment. Effective management of these functions enables businesses to build strong brands, develop loyal customer bases, and achieve sustainable growth.

Types of Marketing
The marketing landscape is diverse, encompassing various strategies and channels through which businesses connect with their target audiences. Each type of marketing serves different purposes and leverages unique platforms or methodologies to engage customers and drive business objectives.
Here are several key types of marketing:
- Digital Marketing: Utilizes online channels to reach consumers, including social media, email, SEO (Search Engine Optimization), and online advertising. Digital marketing is crucial for reaching internet-savvy consumers and offers precise targeting and analytics.
 Case Study: Airbnb, Storytelling in Service Marketing
Case Study: Airbnb, Storytelling in Service Marketing- Company: Airbnb, San Francisco (2014)
- What Was Done: Airbnb's "Belong Anywhere" campaign utilized storytelling by featuring real hosts and travelers and their experiences. This service marketing strategy showcased the unique stays and personal connections made through Airbnb.
- Results/Impact: Airbnb saw significant growth in listings and bookings, with a notable increase in brand awareness. The campaign helped position Airbnb not just as a service, but as a platform for unique travel experiences.
- Content Marketing: Focuses on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience. This type of marketing is aimed at driving profitable customer action through articles, videos, podcasts, and infographics.
 Case Study:
Case Study:
Casper's Sleep-Related Content Strategy- Company: Casper, Online (2014)
- What Was Done: Casper, an online mattress retailer, created an entire content marketing strategy around sleep culture. They launched an online magazine called 'Van Winkle’s' and a digital sleep channel, broadening the conversation around sleep and wellness.
- Results/Impact: Casper's content marketing efforts effectively established the brand as a thought leader in the sleep space, contributing to a meteoric rise in brand awareness and sales. Casper reported revenues of $100 million within two years of its launch, underlining the power of content marketing in building brand authority.
- Social Media Marketing: Leverages platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn to engage with audiences, build brand awareness, and promote products or services. It’s effective for two-way communication and building community around a brand.
 Case Study: Glossier, Niche Product Marketing
Case Study: Glossier, Niche Product Marketing- Company: Glossier, Online (2014)
- What Was Done: Started as a beauty blog, Glossier launched a line of skincare and makeup products targeted at millennials. By focusing on a niche market and using direct-to-consumer marketing, Glossier cultivated a strong brand community.
- Results/Impact: The direct-to-consumer approach resulted in rapid growth, with Glossier reaching cult status among beauty enthusiasts and a $1.2 billion valuation by 2019. Its focused product marketing fostered a loyal customer base and impressive social media presence.
- Influencer Marketing: Involves partnering with influencers or thought leaders to tap into their audiences. This type of marketing is powerful for reaching specific niches and leveraging the trust influencers have built with their followers.
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM): Includes both SEO (to improve organic search results) and paid search advertising like Google Ads. SEM is essential for increasing visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) and driving targeted traffic to websites.
- Email Marketing: Uses email to communicate with potential and existing customers. Email marketing can nurture leads, promote special offers, and maintain customer relationships through personalized messages.
- Affiliate Marketing: Involves earning a commission for marketing another person's or company’s products. It’s a performance-based type of marketing where affiliates earn through leads or sales generated from their efforts.
- Direct Marketing: Directly communicates with targeted customers through mail, telephone, or direct email to generate a response or transaction. This includes promotional letters, catalogs, and telemarketing.
- Guerrilla Marketing: Utilizes unconventional and creative strategies to captivate attention and create a memorable impression of the brand. It’s often low-cost and relies on surprise or creativity to reach audiences.
- Public Relations (PR): Focuses on managing the public perception of a business or brand. PR strategies include press releases, public events, and media relations to earn positive coverage and manage reputation.
- Event Marketing: Involves promoting a brand, product, or service through in-person or virtual events. This can include trade shows, product launches, webinars, and workshops.
- Experiential Marketing: Creates immersive experiences for consumers to directly engage with a brand. This hands-on approach is designed to create lasting emotional connections and often involves interactive installations or events.
 Case Study:
Case Study:
Coca-Cola's Share a Coke Campaign- Company: Coca-Cola, Worldwide (2011)
- What Was Done: Coca-Cola replaced its iconic logo on bottles with 250 of the most popular names in each country it operated in. The campaign encouraged sharing by inviting customers to find a bottle with their name or that of a friend or family member.
- Results/Impact: This personalized marketing campaign boosted Coke’s U.S. sales by more than 2% and increased customer engagement across social media platforms. It tapped into the personalization trend, leading to a global marketing success and rejuvenating the brand.
Each of these marketing types can be adapted to fit different business models, target audiences, and objectives. The choice of marketing type(s) depends on the specific goals of the marketing strategy, the nature of the products or services, and the preferences of the target audience.

How Marketing and Sales Work Together
Marketing and sales are closely interconnected functions within a business, working together to drive revenue and business growth. While marketing focuses on generating interest and attracting potential customers, sales aim to convert that interest into purchases.
Here’s how marketing and sales teams collaborate effectively in various business aspects:
- Lead Generation: Marketing’s role is to create awareness and generate leads through various strategies like content marketing, digital advertising, and social media campaigns. Sales teams then take these leads and work on converting them into customers.
- Lead Nurturing: Marketing continues to nurture leads that are not yet ready to buy through email marketing, retargeting, and personalized content. This helps keep potential customers engaged until they are ready for a sales conversation.
- Brand and Product Awareness: Marketing builds brand and product awareness, creating a positive perception that sales teams can leverage during direct interactions with prospects. This background awareness makes the sales process smoother.
- For example, see this ad created by adman David Ogilvy in 1958, and still very relevant:

- For example, see this ad created by adman David Ogilvy in 1958, and still very relevant:
- Sharing Insights and Feedback: Sales teams provide valuable insights to the marketing department about customer needs, preferences, and objections encountered during sales conversations. Marketing can use this feedback to adjust strategies and materials to better address target audience concerns.
- Aligning Messages and Promotions: Consistency in messaging and promotions across marketing and sales ensures a unified brand experience for the customer. Marketing creates promotional materials and sales messages, which sales teams then use to communicate effectively with prospects.
- Sales Enablement: Marketing supports sales teams by providing them with sales enablement materials, such as brochures, presentations, case studies, and product demos, which help convincing prospects to make a purchase.
 Case Study: HubSpot's Content-Sales Alignment
Case Study: HubSpot's Content-Sales Alignment- Company: HubSpot, Cambridge (2016)
- What Was Done: HubSpot's marketing team created a suite of rich, educational content tailored to the buyer’s journey, aimed at addressing common questions and challenges faced by potential customers. This content served to generate leads while simultaneously equipping the sales team with resources to assist prospects through the sales funnel more effectively.
- Results/Impact: The initiative resulted in a 17% rise in average deal size and a 20% decrease in the length of the sales cycle, demonstrating the efficacy of integrating informative content with a streamlined sales process.
- Targeting and Segmentation: Marketing uses market research to identify and segment the target audience, focusing on those most likely to buy. Sales can then prioritize their efforts on these segments to increase conversion rates.
 Case Study: Salesforce's CRM Synergy
Case Study: Salesforce's CRM Synergy- Company: Salesforce, San Francisco (2018)
- What Was Done: To achieve a synergistic relationship between marketing and sales, Salesforce refined its CRM platform's analytics to track customer interactions and engagement through various marketing channels. The insights gained from this data were leveraged to equip the sales team with detailed customer profiles and behavior predictions, enabling personalized sales approaches.
- Results/Impact: This strategic alignment of departments led to a 38% jump in sales productivity and a 32% increase in the sales win rate. By providing sales teams with high-quality leads and a deep understanding of customer needs, Salesforce accelerated its revenue growth and reinforced its leadership in the CRM market.
- Event Coordination: Marketing often organizes events (e.g., trade shows, webinars) that can generate high-quality leads for the sales team. Sales can also provide insights on which events are likely to attract their ideal customers.
- Customer Retention: After the sale, marketing works on retaining customers through loyalty programs, customer feedback initiatives, and regular communication. Sales provide insights into customer satisfaction and upsell opportunities.
- Collaborative Goals and Metrics: Both departments work towards common goals, such as revenue targets and customer acquisition costs, and share metrics to track progress. This alignment ensures that both teams are focused on the business’s overall success.
When marketing and sales are aligned and work together seamlessly, businesses can more effectively move prospects through the sales funnel, from awareness to purchase, and beyond to loyalty and advocacy. This collaboration not only improves the efficiency of both teams but also enhances the customer experience, leading to higher customer satisfaction and increased revenue.

Marketing Ethics - Overview
Marketing ethics refers to the moral principles and standards that guide behavior within the marketing profession. Ethical marketing practices are crucial for building trust with customers, maintaining a positive public image, and ensuring long-term business success.
Here’s an overview of key aspects of marketing ethics:
- Honesty and Transparency: Ethical marketing demands honesty in all communications. This means accurately representing products or services without misleading or deceiving customers. Transparency about product features, pricing, and return policies is essential.
 Case Study: Everlane's Radical Marketing Transparency
Case Study: Everlane's Radical Marketing Transparency- Company: Everlane, Online (2010)
- What Was Done: Everlane embraced radical transparency in its marketing campaigns by sharing detailed information about product pricing, manufacturing processes, and factory working conditions. This openness was intended not just to educate consumers but to also create a brand built on the values of honesty and ethical consumerism.
- Results/Impact: The transparency strategy developed by Everlane fostered a strong, trusting relationship with customers, contributing to a loyal customer base and impressive sales growth. Everlane's marketing efforts have distinguished the brand as an ethical leader in the apparel industry.
- Privacy and Data Protection: With the rise of digital marketing, protecting consumer privacy and handling data responsibly have become paramount. Ethical practices include obtaining consent for data collection, ensuring data security, and respecting customer preferences regarding how their information is used and shared.
- Fairness and Equity: Marketing efforts should be fair, avoiding exploitation or manipulation of vulnerable groups. This includes equitable treatment of customers, avoiding discrimination, and ensuring products and services are accessible to all segments of society.
- Social Responsibility: Ethical marketers consider the broader impact of their actions on society and the environment. This involves promoting sustainable practices, engaging in corporate social responsibility initiatives, and avoiding marketing that perpetuates harmful stereotypes or contributes to societal issues.
 Case Study: The Body Shop's Ethical Marketing Leadership
Case Study: The Body Shop's Ethical Marketing Leadership- Company: The Body Shop, London (1997)
- What Was Done: The Body Shop engaged in a series of groundbreaking marketing campaigns that highlighted their commitment to social and environmental causes. This included their steadfast policy against animal testing, promotion of self-esteem among consumers, and advocacy for natural ingredient use, all communicated through honest and positive messaging.
- Results/Impact: These ethical marketing practices reinforced The Body Shop’s brand identity as a leader in corporate social responsibility, leading to increased customer loyalty and enhanced brand equity, showing that marketing with a conscience can also be a powerful driver of business success.
- Respect for Stakeholders: Ethical marketing practices respect the interests of all stakeholders, including customers, employees, shareholders, suppliers and the wider community. This means engaging in practices that are not only legally compliant but also morally sound.
- Avoiding False or Misleading Advertising: Advertisements should not contain false claims or exaggerate the benefits of products or services. Ethical marketing requires that all claims can be substantiated, and that advertising is clear and truthful.
- Competitor Respect: Ethical marketing also involves fair competition. This includes avoiding slander or misleading statements about competitors and respecting intellectual property and trade secrets.
- Product Safety and Quality: Ensuring products are safe and meet quality standards is a fundamental ethical responsibility. This includes being proactive in recalling defective products and being transparent about potential risks.
- Sustainability: Marketing practices should promote sustainability, encouraging the use of eco-friendly products and practices that reduce environmental impact.
- Consumer Education: Ethically responsible marketers provide consumers with the information they need to make informed choices, including education on the use, maintenance, and disposal of products.
Marketing ethics not only guide businesses in conducting their marketing efforts responsibly but also serve as a foundation for building trust and loyalty with customers, employees, investors and suppliers. By adhering to ethical principles, companies can navigate complex moral challenges, contribute positively to society, and achieve sustainable.

Marketing for Dummies
Marketing For Dummies is part of the popular "For Dummies" series, known for making complex subjects accessible to beginners. This book serves as a comprehensive guide for those new to marketing or looking to refresh their knowledge. Authored by Alexander Hiam, the book covers a wide range of essential marketing concepts and practices in a reader-friendly format.
Key Features of the Book
- Foundational Marketing Concepts: It starts with the basics, explaining what marketing is and why it's essential for businesses of all sizes. It demystifies marketing jargon and introduces the fundamental principles in an easy-to-understand manner.
- The Marketing Mix: The book dives into the 4 Ps of marketing—Product, Price, Place, Promotion—offering practical advice on how to develop and implement strategies around them.
- Digital Marketing: Recognizing the importance of the digital landscape, it provides insights into digital marketing strategies, including social media marketing, email marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO).
- Practical Strategies: Beyond theory, the book offers actionable strategies for conducting market research, identifying target audiences, developing a marketing plan, and executing marketing campaigns.
- Real-World Examples: To help readers better understand the concepts, it includes real-world examples and case studies that illustrate effective marketing in action.
- Latest Editions: The book has been updated in its latest editions to reflect new marketing trends, technologies, and practices, making it relevant for today's marketers.

Why is it Useful?
Marketing For Dummies is valuable for anyone looking to gain a solid grounding in marketing without getting overwhelmed by complexity. It's particularly beneficial for small business owners, marketing students, and professionals in other fields who need to understand marketing's role in business success. The book's straightforward explanations, combined with practical tips and examples, make it an excellent starting point for developing effective marketing strategies.
Where to order this book
- At the time of writing this artilce, this is the most updated version at Amazon:
Marketing for Dummies – Sixth Edition - For the most current insights and strategies, readers should look for the latest edition of Marketing for Dummies by Alexander Hiam, ensuring they have access to the most up-to-date information in the ever-evolving field of marketing.

Marketing for Beginners
Marketing is a vital aspect of any business, serving as the bridge between a product or service and its potential customers. For beginners, understanding the fundamentals of marketing is essential for building effective strategies that can elevate a brand, attract and retain customers, and drive sales.
Here’s a foundational guide to marketing for beginners:
- Understanding the Basics:
- Marketing Definition: At its core, marketing is about communicating the value of a product or service to customers, for the purpose of selling that product or service.
- Marketing vs. Sales: Marketing focuses on attracting potential customers to your product or service, while sales concentrate on converting those potential customers into actual buyers.
- The Marketing Mix (The 4 Ps):
- Product: What you’re selling. It could be a physical item, a service, or even a digital good. It's crucial to understand what makes your product unique and how it meets customers' needs.
- Price: How much does your product cost? Pricing strategies are essential for positioning your product in the market and should reflect the value it provides to customers.
- Place: Where and how your product is sold. This could range from online platforms to physical stores, depending on where your target market is most likely to make a purchase.
- Promotion: The strategies used to promote your product. This includes advertising, social media, email marketing, and any other method used to raise awareness about your product.
 Case Study: Canva’s Design Simplification
Case Study: Canva’s Design Simplification- Company: Company: Canva, Online (2012)
- What Was Done: Canva made sophisticated design accessible to beginners by providing a drag-and-drop interface with thousands of templates. Their marketing emphasized the ease with which users could create professional-level designs without prior experience.
- Results/Impact: Canva's user-friendly approach disrupted the design software industry, attracting millions of users and reaching a $6 billion valuation by 2020. Its success highlighted the demand for tools that simplify complex processes for beginners, driving widespread adoption.
- Market Research: Conducting market research is critical for understanding your target audience, including their needs, preferences, and behaviors. This can involve surveys, interviews, and analysis of market trends.
- Target Audience: Identifying and understanding your target audience is key. This includes knowing their demographics (age, gender, income level, etc.), as well as psychographics (lifestyle, values, interests).
- Digital Marketing: An increasingly key area, digital marketing involves using online channels to reach your audience. Key components include SEO (Search Engine Optimization), content marketing, social media marketing, and PPC (Pay-Per-Click advertising).
- Branding: Branding is about creating a unique identity and image for your product or service. This encompasses your logo, color scheme, messaging, and the overall customer experience with your brand. Branding can also be linked to additional senses, like smell (e.g. – a calming lavender scent at a spa), sound (e.g. - AT&T chimes), and taste (e.g. – the extreme bitterness of Guinness beer).
- Measuring Success: Understanding how to measure the success of your marketing efforts is crucial. This can involve tracking sales, website traffic, engagement rates on social media, and other relevant metrics.
- Ethics and Social Responsibility: Ethical marketing practices are essential for building trust with your audience. This includes being honest in your advertising, respecting customer privacy, and engaging in socially responsible activities.
For beginners, mastering these foundational elements of marketing is the first step towards developing strategies that effectively communicate the value of your products or services to your target audience. Remember, marketing is a dynamic and ever-evolving field, so continual learning and adaptation are key to staying relevant and successful.
Marketing Strategy and Consulting
Interested in getting help with your marketing efforts and marketing strategy?
Contact us: info@zooz.co.il ,+972-9-958-5085
Marketing Articles
- Marketing Overview
- Marketing Goals
- Marketing Metrics
- Marketing Types
- Marketing Channels
- Demographic Marketing
- Marketing Business Models
- Industry-Specific Marketing
- Professional Services Marketing
- Marketing Strategy
- Market Research
- Marketing Communications (MarCom)
- Marketing Execution
- Makreting Careers
- Marketing Education
- Marketing Glossary (200 terms)
- Marketing Versus Other Disciplines
- Marketing Agencies and Outsourcing





