Innovation Education
Mar 01, 2024
By Ari Manor , CEO at ZOOZ

This is one in a series of articles that provide detailed and updated information about Innovation. In this specific article, which focuses on Innovation Education, you can read about:
- Can Innovation Be Learned
- Can Innovation Be Taught
- Innovation Education
- Innovation Studies
- Innovation Books
- Innovation Journals
- Innovation Board Game
- Innovation Museum
- Innovation Park
- Innovation Programs
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship Minor
- Innovation Fellowship
- Innovation Academy
- Innovation Campus
For additional articles about Innovation, see the Topic Menu.

Can Innovation Be Learned
The pursuit of innovation is often seen as an elusive trait, reserved for the naturally creative or the entrepreneurial spirit. However, this perception is shifting as we understand that innovation can indeed be learned. Individuals and organizations alike are increasingly recognizing that innovation is not just a spark of genius but a skill that can be cultivated and nurtured.
Here are key points on how innovation can be learned:
- Understanding the Innovation Process: Learning about the different stages of innovation, from ideation to execution, is fundamental. One must understand that innovation is not a single event but a process that can be managed and improved upon.
- Developing a Growth Mindset: Central to learning innovation is adopting a growth mindset, as coined by psychologist Carol Dweck. This mindset embraces challenges, persists in the face of setbacks, sees effort as the path to mastery, learns from criticism, and finds lessons and inspiration in the success of others.
- Cross-Disciplinary Learning: Innovation often occurs at the intersection of different fields. By learning across various domains, individuals can combine disparate ideas to create something new and valuable.
- Collaborative Techniques: Innovation is rarely an individual effort. Learning collaborative techniques and how to work effectively in teams is essential. This includes understanding group dynamics, conflict resolution, and co-creation methods.
- Familiarity with Tools and Techniques: Various tools and techniques can facilitate the innovation process, such as design thinking, lean startup methodology, and agile development. Gaining proficiency in these can significantly bolster one's capacity to innovate.
- Exposure to Real-World Problems: Engaging with real-world problems can stimulate innovative thinking. By applying knowledge to practical challenges, learners can develop a deeper understanding of the nuances of innovating effectively.
 Case Study: EduInnovate
Case Study: EduInnovate- Company: EduInnovate (Launched in 2018)
- What Was Done: EduInnovate developed a unique educational model that connects students with local SMEs to work on real-world business challenges. This approach allows students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical problems, leading to the creation of innovative solutions such as a low-cost water purification system for rural communities.
- Results/Impact: The program not only enhanced students' problem-solving and critical thinking skills but also provided tangible benefits to local businesses and communities. The water purification system, in particular, was adopted by several NGOs, demonstrating the model's potential to drive social change and support sustainable development in underserved areas.
In conclusion, while certain individuals may have an innate proclivity for innovation, it is a skill that can be learned and honed. Through structured learning, practical experience, and a supportive environment that encourages experimentation and risk-taking, individuals can significantly enhance their innovative capabilities.

Can Innovation Be Taught
Innovation, once thought to be an inherent trait, is increasingly recognized as a teachable skill. Educational institutions and corporate training programs are incorporating curricula designed to foster skills, methodologies, and mindsets that encourage innovative thinking and problem-solving. The question is no longer whether innovation can be taught, but rather how it can be taught effectively.
Here are some strategies and concepts that are central to teaching innovation:
- Curriculum Design: Innovative thinking can be incorporated into educational programs through a curriculum that encourages creativity, problem-solving, and the application of knowledge to new scenarios. This might include case studies, project-based learning, and hands-on experiences that mimic real-world challenges.
- Encouraging Curiosity and Questioning: Teachers and trainers can cultivate a culture of curiosity by encouraging students to ask questions and explore multiple solutions to problems. This helps to develop critical thinking skills and the ability to approach problems from various angles.
- Fostering a Safe Environment for Experimentation: Innovation involves trial and error. Creating a learning environment where failure is seen as a step towards success is crucial for students to take risks and experiment with new ideas.
- Teaching Methods and Tools: Educators can introduce specific methods and tools that are known to facilitate innovation. This includes design thinking, brainstorming techniques, and prototyping. For example, the use of SCAMPER (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse) as a brainstorming tool has proven effective in helping students think beyond conventional solutions.
- Design Thinking: Introduce the principles of design thinking, which empathize with users, define pain points, ideate solutions, prototype, and test. This iterative process encourages a user-centric approach to innovation
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Innovation is often the result of interdisciplinary thinking. Teaching students to integrate knowledge from different fields can lead to breakthrough ideas. This is exemplified by the work of a small tech firm, CrossPollinate Tech, which has developed an innovative water-saving device by combining expertise in behavioral science, engineering, and design.
- Role Models and Case Studies: Using case studies of lesser-known innovators and entrepreneurs can provide relatable role models for students. This exposes them to a range of pathways to innovation beyond the well-trodden stories of famous figures.
Case Study: Greentech Innovators
- Company: Greentech Innovators (Launched in 2019)

- What Was Done: Greentech Innovators created an educational program for high school students focusing on sustainable technology. The curriculum included hands-on workshops where students designed solar-powered devices and systems for local community use.
- Results/Impact: The program fostered a strong understanding of sustainable technologies among students, with several going on to pursue careers in the green tech sector. One group of students developed a solar-powered irrigation system that was implemented in a community garden, leading to a 20% increase in crop yield and a significant reduction in water waste.
In essence, teaching innovation is about equipping individuals with the mindset and toolkit to approach problems creatively and turn ideas into reality. By emphasizing experiential learning, critical thinking, structured tools, and interdisciplinary collaboration, educators and trainers can nurture the innovators of tomorrow.

Innovation Education
The domain of innovation education encompasses a diverse array of approaches and practices aimed at preparing students to contribute to a dynamic and ever-evolving marketplace. Here's an exploration of what constitutes effective innovation education:
- Curricular Integration: Innovation is embedded into curricula across subjects, not taught as a standalone subject. This ensures that innovative thinking is reinforced regardless of the discipline.
- Problem-Based Learning (PBL): PBL challenges students to learn through the experience of solving open-ended problems, fostering an innovative mindset.
- Entrepreneurial Focus: Courses often include entrepreneurial skills, such as opportunity recognition, risk-taking, and resourcefulness, essential for innovation.
- Technology Infusion: Keeping abreast of the latest technology is crucial, as it plays a significant role in driving innovation. Education programs incorporate technology both as a tool for learning and a subject of study.
- Global Perspective: Understanding global challenges and markets is crucial, and innovation education often includes international case studies and collaboration with students and institutions abroad.
- Experiential Learning: Students engage in internships, field projects, and collaborations with industries to apply their learning in real-world contexts.
Case Study: OceanTech Community College
- Company: OceanTech Community College, Ivany Campus, Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, Canada (since 2021)

- What Was Done: OceanTech introduced a curriculum that combines marine biology, environmental science, and technology. Students participate in projects such as designing devices to clean ocean plastics or developing sustainable aquaculture systems.
- Results/Impact: The program produced several patented innovations, including a biodegradable netting material that reduces wildlife entanglement. Students' innovations have attracted interest from environmental organizations and spurred new startups focused on marine conservation technologies.
- Company: OceanTech Community College, Ivany Campus, Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, Canada (since 2021)
Through such education, students are not only equipped with knowledge but also with the mindset and skills needed to approach problems innovatively and to develop solutions that can have a real impact on the world.

Innovation Studies
Innovation studies is a multidisciplinary field that examines how new ideas, products, and practices are created, developed, and utilized. It often incorporates aspects of economics, sociology, business, and engineering, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of how innovation occurs in various contexts.
Here's what typically constitutes a program in innovation studies:
- Historical Context: Understanding the historical impact of innovation on society and economies, including the study of significant breakthroughs and their subsequent effects.
- Innovation Theories: Exploring various theories of innovation, such as disruptive innovation, incremental innovation, and open innovation.
- Policy and Regulation: Examining how government policies and regulations can foster or hinder innovation, and studying the role of intellectual property rights.
- Organizational Innovation: Learning how organizations cultivate an environment that encourages innovation, including studying corporate structures, cultures, and processes.
- Technological Advancements: Keeping up with the latest technological trends and their role in driving innovation across different sectors.
- Social Innovation: Looking at how innovation can address social challenges and contribute to social change, emphasizing ethics and responsible innovation.
 Case Study: UrbanTech Innovations
Case Study: UrbanTech Innovations- Company: UrbanTech Innovations (Research commenced in 2020)
- What Was Done: UrbanTech Innovations conducted a study on the integration of smart technologies in urban planning. The research focused on how cities can innovate to become more sustainable and efficient through the use of smart grids, IoT devices, and AI analytics.
- Results/Impact: The research led to the development of a smart traffic light system that adapts to real-time traffic conditions, reducing congestion and emissions in urban areas. The study also influenced policy recommendations for several cities looking to upgrade their infrastructure to be more responsive to citizens' needs.
Innovation studies programs aim to equip students with the analytical tools and critical thinking skills required to understand and drive innovation. The interdisciplinary approach of such programs ensures that graduates can navigate complex problems and are prepared to contribute to innovation in a variety of roles and industries.

Innovation Books
Innovation books are more than just compilations of ideas; they are the repositories of collective wisdom that have the power to ignite the spark of creativity and drive in individuals and organizations alike. These volumes offer a rich tapestry of knowledge, drawing from the experiences of past innovators, the latest in academic research, and the foresight of thought leaders. They serve not only as guides but also as companions in the solitary moments of contemplation that often precede great leaps of innovation.
Following are diverse categories of Innovation literature, with 5 recommended books to read in each of these categories.
Biographies of Pioneers
These narratives provide a window into the lives of those who have broken the mold, offering not only inspiration but practical wisdom gleaned from their successes and failures.
- "Steve Jobs" by Walter Isaacson: A comprehensive biography of Apple’s co-founder, offering insights into his innovative mind and the impact of his work on technology and society.
- "The Wright Brothers" by David McCullough: Chronicles the lives of the Wright brothers and their unwavering pursuit of manned flight, highlighting their innovative spirit.
- "Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic Future" by Ashlee Vance: Explores the life of Elon Musk, the entrepreneur behind SpaceX, Tesla, and SolarCity, and his contributions to modern technology.
- "Benjamin Franklin: An American Life" by Walter Isaacson: Provides a glimpse into the life of Benjamin Franklin, a pioneer in various fields including science, innovation, and politics.
- "Leonardo da Vinci" by Walter Isaacson: Delves into the life of Leonardo da Vinci, showcasing his extraordinary creativity and innovation across art, science, and technology
Frameworks for Innovation
Books that lay out systematic approaches to innovation, such as the Lean Startup methodology, help demystify the process and provide readers with actionable steps to bring their ideas to life.
- "The Lean Startup" by Eric Ries: Introduces a methodology for developing businesses and products that emphasizes innovation, flexible product development, and customer feedback.
- "Innovator's Dilemma" by Clayton M. Christensen: Discusses how successful, outstanding companies can do everything "right" and still lose their market leadership due to new, disruptive technologies.
- "Blue Ocean Strategy" by W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne: Offers a strategic framework for creating uncontested market space and making the competition irrelevant.
- "Crossing the Chasm" by Geoffrey A. Moore: Focuses on the challenges startup companies face transitioning from early adopting to mainstream customers.
- "Running Lean" by Ash Maurya: A practical guide to applying lean startup principles to product development, offering tools and techniques for rapid, iterative learning.
Cultural Change
Titles that focus on how to cultivate a culture of innovation within an organization, stressing the importance of leadership, communication, and an environment that encourages experimentation.
- "Creativity, Inc." by Ed Catmull: Provides insights into building a creative culture, drawn from the author’s experience at Pixar Animation and Walt Disney Animation Studios.
- "The Culture Code" by Daniel Coyle: Explores the secrets of highly successful groups and how they cultivate cultures of deep creativity and innovation.
- "Drive" by Daniel H. Pink: Investigates what motivates us and how leaders can foster a culture of motivation and innovation.
- "Leading Change" by John P. Kotter: A roadmap for leading change in an organization with a focus on creating a culture receptive to innovation.
- "The Innovator’s DNA" by Jeff Dyer, Hal Gregersen, and Clayton M. Christensen: Identifies the behaviors of the world’s best innovators and how they foster cultures that encourage innovation.
Industry Disruption
Some authors dissect cases of industry disruption, explaining how new players upend established markets by doing things differently and what can be learned from these shake-ups.
- "The Innovator’s Solution" by Clayton M. Christensen and Michael E. Raynor: Expands on the ideas of "The Innovator's Dilemma", offering strategies for becoming a disruptive innovator.
- "Zero to One" by Peter Thiel: Discusses how to build companies that create new things, going from zero to one, as opposed to companies that iterate on existing innovations.
- "The Upstarts" by Brad Stone: Tells the story of Airbnb and Uber, two companies that redefined their industries and sparked widespread disruption.
- "Platform Revolution" by Geoffrey G. Parker, Marshall W. Van Alstyne, and Sangeet Paul Choudary: Examines how platform-based businesses like Amazon, Airbnb, and Uber have disrupted industries across the globe.
- "Disrupt Yourself" by Whitney Johnson: Focuses on personal disruption and how individuals can harness the power of disruption for their own growth, applicable to entrepreneurs and professionals alike.
Ideation Techniques
From brainstorming to mind-mapping, books that focus on ideation techniques give readers a toolbox for generating new ideas and strategies for refining them.
- "Thinkertoys" by Michael Michalko: A handbook of creative-thinking techniques for developing ideas in business and in life.
- "The Art of Innovation" by Tom Kelley: Offers strategies for fostering a culture of innovation and creativity, drawing from the experiences of IDEO, one of the world's leading design firms.
- "Creative Confidence" by Tom Kelley and David Kelley: Unveils the principles and strategies IDEO uses to foster innovative thinking and creativity throughout organizations.
- "The Creative Habit" by Twyla Tharp: Provides insights and exercises to help anyone achieve greater creativity and innovation in their work and personal life.
- "Lateral Thinking" by Edward de Bono: Introduces the concept of lateral thinking as a way to solve problems through an indirect and creative approach.
Innovation in Practice
Practical guides that take readers from theory to practice, emphasizing real-world application and providing insight into what works and what doesn't.
- "Making Ideas Happen" by Scott Belsky: Outlines practical strategies for moving ideas from conception to realization, emphasizing the execution phase of innovation.
- "The Other Side of Innovation" by Vijay Govindarajan and Chris Trimble: Focuses on the execution of innovation within organizations, offering a systematic approach to bringing ideas to life.
- "The Ten Faces of Innovation" by Tom Kelley: Describes the roles people can play in an organization to foster innovation and new ideas.
- "Innovating for People" by LUMA Institute: Provides a handbook of human-centered design methods for solving problems and discovering new opportunities.
- "Experimentation Works" by Stefan H. Thomke: Highlights the power of experimentation in driving innovation within companies, using examples from Amazon, Google, and Netflix.
Emerging Technologies
Keeping pace with the rapidly changing technological landscape, these books provide an analysis of emerging trends and their potential impact on business and society.
- "The Fourth Industrial Revolution" by Klaus Schwab: Examines the current period of technological advancements and their transformative impact on society and the global economy.
- "The Singularity Is Near" by Ray Kurzweil: Discusses the future of human and machine intelligence, predicting a merging point that will transform society.
- "Life 3.0" by Max Tegmark: Explores the future of artificial intelligence and its impact on the fabric of human existence.
- "The Industries of the Future" by Alec Ross: Offers insights into the next wave of global innovation, including robotics, genomics, and cybersecurity.
- "The Inevitable" by Kevin Kelly: Describes the twelve technological forces that will shape our future, from virtual reality to artificial intelligence.
Global Perspectives on Innovation
Understanding how different cultures approach innovation can provide a broader view of what is possible and inspire new ways of thinking.
- "The World Is Flat" by Thomas L. Friedman: A global analysis of the advancements in communication and technology, and their effects on globalization.
- "Innovation and Its Enemies" by Calestous Juma: Explores the history and future of innovation and how it is often resisted by societies.
- "How We Got to Now" by Steven Johnson: Investigates the history of innovation and how seemingly unrelated ideas connect to spark significant advancements.
- "The Third Wave" by Steve Case: Discusses the next era of the internet and how it will transform business, society, and governance.
- "Jugaad Innovation" by Navi Radjou, Jaideep Prabhu, and Simone Ahuja: Introduces the concept of frugal innovation practiced in emerging markets, offering lessons on doing more with less.
Sustainability and Innovation
With a growing emphasis on sustainability, books are increasingly focusing on how to innovate responsibly and create solutions that are not only profitable but also beneficial to the planet.
- "Cradle to Cradle" by William McDonough & Michael Braungart: Rethinks the way we make things, advocating for a circular economy and sustainable product designs.
- "The Blue Economy" by Gunter Pauli: Presents a sustainable development model that uses nature's resources efficiently and in a way that is beneficial to the economy and the environment.
- "Sustainable Innovation" by Andrew Hargadon: Focuses on how to create sustainable products, services, and technologies that solve both economic and environmental challenges.
- "Natural Capitalism" by Paul Hawken, Amory Lovins, and L. Hunter Lovins: Proposes a new business model that capitalizes on the economic value of nature and its resources.
- "Green Giants" by E. Freya Williams: Examines companies that have built billion-dollar businesses while putting sustainability at the heart of their strategy.
Innovation Policy and Economics
These works examine how governmental policies and economic systems can foster or impede innovation, offering insights into the complex relationship between regulation, economic incentives, and technological advancement.
- "The Entrepreneurial State" by Mariana Mazzucato: Debunks the myth of a sluggish state versus a dynamic private sector, arguing for the critical role of the state in driving innovation.
- "Innovation and Its Discontents" by Adam B. Jaffe and Josh Lerner: Looks at how poorly designed patent systems can stifle innovation.
- "The Third Pillar" by Raghuram G. Rajan: Explores the role of communities in a global economy and how they can be revitalized to foster innovation and growth.
- "Jump-Starting America" by Jonathan Gruber and Simon Johnson: Proposes how public investment in science and technology can lead to a new wave of economic growth.
- "The Code of Capital" by Katharina Pistor: Examines how the law creates wealth and inequality through the coding of capital, and its implications for innovation and economic development.
Innovation books are invaluable resources for anyone looking to delve deeper into the realms of creativity, strategy, and transformative thinking. They encapsulate the essence of human ingenuity, offering narratives that inspire, frameworks that guide, and insights that challenge the conventional. From the biographical sketches of pioneers who dared to think differently and change the world, to the systematic approaches that demystify the innovation process, these books cover a broad spectrum of knowledge. They not only cater to those seeking to foster a culture of innovation within organizations but also to individuals curious about the future of technology and its social implications.
Through detailed case studies, literature reviews, and discussions on policy and economics, these works illuminate the multifaceted nature of innovation, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of its dynamics. Whether you're an aspiring entrepreneur, a seasoned leader, or simply an enthusiast of progress, the recommended readings across various categories of innovation literature offer a treasure trove of wisdom and tools to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of innovation.

Innovation Journals
In the academic and professional world, innovation journals stand as pillars of knowledge dissemination, chronicling the latest research, case studies, and theoretical advancements in the field of innovation. These journals are critical for anyone looking to stay abreast of the newest trends, understand the empirical evidence behind innovation practices, and gain insights into the future direction of innovation.
Following are various topics related to innovation covered in such magazines, with 5 top recommended journals known for their contributions to these topics about innovation:
Peer-Reviewed Research
They provide rigorously vetted articles that offer fresh insights into the science and practice of innovation.
- Journal of Product Innovation Management: Focuses on the latest research in the development, introduction, and improvement of new products and services.
- Research Policy: Covers a wide range of topics in innovation research, including technology, science policy, and the economic impact of innovation.
- Innovation: Management, Policy & Practice: Offers insights into the management and policy aspects of innovation, blending practical and theoretical research.
- Technovation: Dedicated to understanding the role of technology in innovation and the impact of technological change on society.
- R&D Management: Explores the interaction between research, development, and innovation management, offering multidisciplinary perspectives.
Case Studies
Many journals include detailed case studies that illustrate the practical application of innovative strategies in various industries.
- Harvard Business Review: While not exclusively an academic journal, HBR provides in-depth case studies on innovation in practice across industries.
- MIT Sloan Management Review: Offers case studies and articles on how businesses can develop and implement innovative strategies.
- Journal of Business Venturing: Focuses on entrepreneurial and innovation case studies, examining the challenges and successes of new ventures.
- Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal: Publishes research and case studies on the strategic aspects of entrepreneurship and innovation.
- California Management Review: Presents case studies and research on management innovations and business strategies.
Literature Reviews
These comprehensive reviews summarize current knowledge on particular aspects of innovation, identifying trends and gaps in the research.
- Annual Review of Psychology: Includes comprehensive reviews on topics related to innovation and creativity within the field of psychology.
- International Journal of Management Reviews: Offers literature reviews on a broad range of management topics, including innovation management.
- The Journal of Technology Transfer: Features literature reviews on the process of technology transfer and its role in innovation.
- Academy of Management Annals: Provides extensive literature reviews and syntheses on various aspects of management and innovation.
- Journal of Economic Literature: Covers reviews and syntheses of economic research, including studies on innovation and its economic implications.
Methodological Advances
For those interested in the 'how' of innovation research, these journals discuss new methodologies, metrics, and evaluation techniques.
- Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Publishes articles on statistical methods that can be applied to the study of innovation.
- Quantitative Marketing and Economics: Offers insights into new quantitative methods in marketing, relevant to analyzing and understanding innovation.
- Structural Equation Modeling: A multidisciplinary journal that discusses methodological advances relevant to studying innovation.
- Journal of Research in Marketing and Entrepreneurship: Focuses on methodological issues in marketing and entrepreneurship research, including innovation.
- Innovation: Organization & Management: Discusses new methodologies for studying organizational aspects of innovation.
Cross-Disciplinary Insights
Innovation is inherently interdisciplinary, and these journals often include articles that draw from multiple fields of study, such as technology, business, psychology, and design.
- Journal of Innovation & Knowledge: Encourages cross-disciplinary research on innovation, drawing from fields such as business, engineering, and social sciences.
- Technological Forecasting and Social Change: Offers articles that integrate technological, social, and environmental aspects of innovation.
- Journal of Creative Behavior: Focuses on creativity as a component of innovation, incorporating insights from psychology, education, and business.
- Creativity and Innovation Management: Publishes research that bridges gaps between creativity and innovation management across disciplines.
- Industry and Innovation: Covers innovation from an industrial perspective, including cross-disciplinary insights into technological and organizational innovation.
Policy and Regulation Discussions
Understanding the policy landscape is crucial, and innovation journals frequently address the implications of policy decisions on innovation ecosystems.
- Science and Public Policy: Explores the interface between innovation, technology, and policy-making.
- Research Evaluation: Discusses how policy decisions influence the evaluation, funding, and direction of scientific research and innovation.
- Innovation and Development: Offers insights into how innovation policies impact development and growth, particularly in emerging economies.
- Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management: Focuses on the implications of science and technology policies for innovation.
- Technology in Society: Examines the societal and policy aspects of technology and innovation, including regulatory challenges.
Book Reviews and Critiques
Journals also offer reviews of recent books on innovation, providing critical analysis and discussions of their contributions to the field.
- Science, Technology, & Human Values: Includes book reviews on the latest publications in the field of science and technology studies, with implications for innovation.
- Journal of Economic Literature: Regularly features book reviews and critiques relevant to economics, including works on innovation.
- Minerva: A journal of science, learning, and policy, offering book reviews on a wide range of topics related to innovation.
- Research-Technology Management: Provides reviews of books focused on technology and innovation management.
- The Information Society: Reviews books on the societal aspects of information technology and innovation.
Interviews with Thought Leaders
Interviews and conversations with leading innovators and scholars offer personal perspectives and advice.
- Innovations: This journal features interviews with leading figures in the field of global innovation, offering unique insights and perspectives.
- Leadership Quarterly: While broader in scope, it occasionally includes interviews with leaders known for innovative approaches in their fields.
- Strategy & Leadership: Offers interviews and discussions with thought leaders on strategic innovation and leadership.
- Technology Analysis & Strategic Management: Presents conversations with experts on the strategic management of technology and innovation.
- Journal of Product Innovation Management: Occasionally includes dialogues with practitioners and academics renowned for their contributions to innovation.
Thematic Special Issues
Often, journals will dedicate entire issues to a specific theme, delving deep into subjects like social innovation, sustainability, or digital transformation.
- Social Innovation Journal: Dedicated to exploring social innovation through special issues on various themes.
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Frequently publishes special issues focusing on sustainability and innovation in production and consumption.
- Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice: Offers thematic special issues on entrepreneurial aspects of innovation.
- Journal of Business Research: Periodically dedicates issues to specific innovation topics, such as digital transformation or consumer innovation.
- Sustainability: A multidisciplinary journal that often features special issues on sustainability-related innovations.
Future Outlooks
Articles that offer predictions about the future of innovation, discussing emerging technologies and potential societal shifts.
- Futures: Focuses on forecasting and the exploration of future trends, including technological and social innovations.
- Foresight: Dedicated to future studies and predictions about innovation and its impact on society.
- Technological Forecasting and Social Change: Provides articles on the future of technology and innovation, including predictive analyses.
- Journal of Future Studies: Explores various futures, including the implications of current innovations on tomorrow's world.
- Long Range Planning: Offers insights into strategic planning for future innovation, including technological and organizational perspectives.
To summarize, innovation journals stand as beacons of knowledge, guiding both theorists and practitioners through the ever-evolving landscape of innovation. They not only document groundbreaking research but also serve as a dynamic conduit for the exchange of ideas that challenge and expand our understanding of innovation. For anyone looking to navigate the complexities of modern innovation, these journals offer invaluable insights, practical applications, and a platform for contributing to the ongoing dialogue that shapes our future.

Innovation Board Game
Innovation board games are a creative and interactive way to engage people in the principles and challenges of innovation. They simulate the innovation process, allowing players to experience the thrill of discovery, the challenges of development, and the strategy behind implementation, all within the risk-free environment of gameplay.
Key Elements in Innovation Board Games
- Idea Generation Mechanics: Players may be required to come up with creative solutions to problems presented within the game, mimicking the brainstorming phase of innovation.
- Resource Management: Just like in real-world innovation, board games often include the need to manage limited resources effectively, be it time, money, or materials.
- Risk and Reward: Games usually incorporate elements of risk, where players must decide whether to invest in an uncertain idea that could yield high rewards.
- Collaboration and Competition: Some games encourage teamwork to achieve a common goal, while others are based on out-innovating your competitors.
- Patents and Intellectual Property: Players might have to navigate the world of intellectual property, balancing the benefits of patents against their cost and potential limitations.
- Market Dynamics: Many innovation games involve simulating market forces, requiring players to adapt their strategies in response to changing market demands.
- Problem-Solving Challenges: The gameplay often includes challenges or barriers to innovation that players must overcome, such as technological limitations or regulatory hurdles.
- Adaptation and Pivot: The ability to pivot or adapt an initial idea to respond to feedback or new information is a common feature, reflecting the iterative nature of real-world innovation.
- Narrative and Storytelling: Some games incorporate a strong narrative element, taking players through a story of innovation that can be historically based or set in a fictional future.
- Educational Content: While playing, participants often learn about key innovation concepts and historical innovations, making these games not only fun but also informative.
Recommended Innovation Board Games
- Catan - A popular strategy board game where players collect resources and build settlements to earn points. Innovators Edition specifically does not exist, but the base game encourages strategic innovation.
- Innovation - A card game that focuses on building a civilization through technological advancements.
- Terraforming Mars - A highly acclaimed board game where players work to make Mars habitable through strategic resource management and technological development.
- Pandemic - While not specifically "Rapid Response," Pandemic is a cooperative board game where players work together to stop global pandemics, requiring innovative strategy and teamwork.
- Rory’s Story Cubes - A real storytelling game that encourages creativity and can be used as a tool for innovation and idea generation.
- Disruptus - This is an actual game designed to encourage innovation and creativity by challenging players to think of new uses for everyday objects.
- Evolution - A game that challenges players to adapt their species to survive and thrive, involving strategic innovation to deal with changing environments.
Innovation board games serve as an excellent tool for education and team-building. They provide a microcosm of the innovation process, allowing players to experience and learn about the complexities of innovation in a tangible, hands-on manner. Through play, these games break down the abstract components of innovation into understandable and engaging activities, making the concept of innovation accessible and entertaining for a wide audience.

Innovation Museum
The concept of an Innovation Museum captures the essence of human ingenuity and creativity through the ages. It serves as a physical and interactive space where visitors can explore the history of innovation, from early tools and inventions to the latest technological advancements. Such museums aim to educate, inspire, and provoke thought about the process of innovation and its impact on society.
- Historical Inventions: Showcases inventions that have significantly impacted human life, detailing their development and the problems they solved.
- Interactive Technology Displays: Allows visitors to engage with cutting-edge technologies, such as virtual reality, robotics, and artificial intelligence, providing a hands-on learning experience.
 Case Study: The Tech Interactive
Case Study: The Tech Interactive- Museum: The Tech Interactive, San Jose, California, USA (Opened in 2021)
- Highlights: : Featured an augmented reality tour that guides visitors through the history of computing, from the first mechanical calculators to quantum computing.
- Impact: The gallery has become a hub for tech enthusiasts and school groups, significantly increasing public interest in STEM fields and inspiring a new generation of innovators.
- Innovator Profiles: Highlights the stories of notable inventors and innovators, their thought processes, challenges, and contributions to their fields.
- Innovation Workshops: Offers workshops and seminars that encourage visitors to think creatively and work on their own innovation projects.
 Case Study: MIT Museum
Case Study: MIT Museum- Museum: MIT Museum, at MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA (Established in 1971)
- Highlights: The MIT Museum showcases the cutting-edge research and innovation stemming from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It features exhibits on robotics, artificial intelligence, holography, and much more. One of the museum's notable attractions is its collection of holograms, one of the largest in the world, alongside exhibits on robotics that include interactive demonstrations. The museum also highlights the history of MIT's contributions to science, technology, and engineering, including the work of its faculty and alumni.
- Impact: The MIT Museum plays a crucial role in inspiring the next generation of engineers, scientists, and innovators. By making complex topics accessible and engaging to the public, the museum fosters a deeper understanding of the importance of science and technology in solving global challenges. It serves as a bridge between the academic community and the public, encouraging visitors to explore the possibilities of technology and its impact on our future.
- Future Concepts Gallery: A section dedicated to speculative designs and concepts that could shape the future, encouraging visitors to think about the possibilities of tomorrow.
- Global Innovation Impact: Explores how innovation affects global challenges and contributes to sustainable development goals.
- Patent Library: A comprehensive archive of patents that visitors can explore to understand the legal aspects of innovation and its evolution over time.
- Art and Design Intersection: Showcases how art and design influence and are influenced by technological innovation, highlighting the importance of aesthetics in functional inventions.
Innovation museums are more than just repositories of knowledge; they are incubators for future innovators. By engaging with the exhibits, visitors are encouraged to see themselves as potential innovators who can solve the challenges of the future. These museums play a crucial role in demystifying the innovation process, making it accessible and relatable to people from all walks of life.

Innovation Park
Innovation Parks, also known as Science Parks or Research Parks, are designed to foster collaboration between universities, research institutions, start-ups, and established companies to drive technological advancements and innovation. These parks provide a conducive environment for research and development, offering state-of-the-art facilities, business support services, and networking opportunities to encourage the growth of high-tech businesses and industries.
Key Features of Innovation Parks
- Collaborative Spaces: Facilities that encourage collaboration among researchers, entrepreneurs, and businesses to share ideas and resources.
Case Study: Stanford Research Park (SRP)
- Innovation Park: Stanford Research Park (SRP), Palo Alto, California, USA (Founded in 1951)

- Highlights: Stanford Research Park is one of the first and most influential models of an innovation park in the world. Home to over 150 companies across various sectors, including Tesla, HP, and VMware, SRP has been instrumental in the development of Silicon Valley. The park facilitates collaborations between Stanford University and high-tech companies, fostering an ecosystem where innovation thrives.
- Impact: SRP has been pivotal in numerous technological breakthroughs and has contributed significantly to the global prominence of Silicon Valley as a tech hub. Its success has inspired the creation of similar innovation parks worldwide.
- Innovation Park: Stanford Research Park (SRP), Palo Alto, California, USA (Founded in 1951)
- Access to Research Institutions: Close proximity to universities and research institutions provides easy access to academic expertise, talent, and resources.
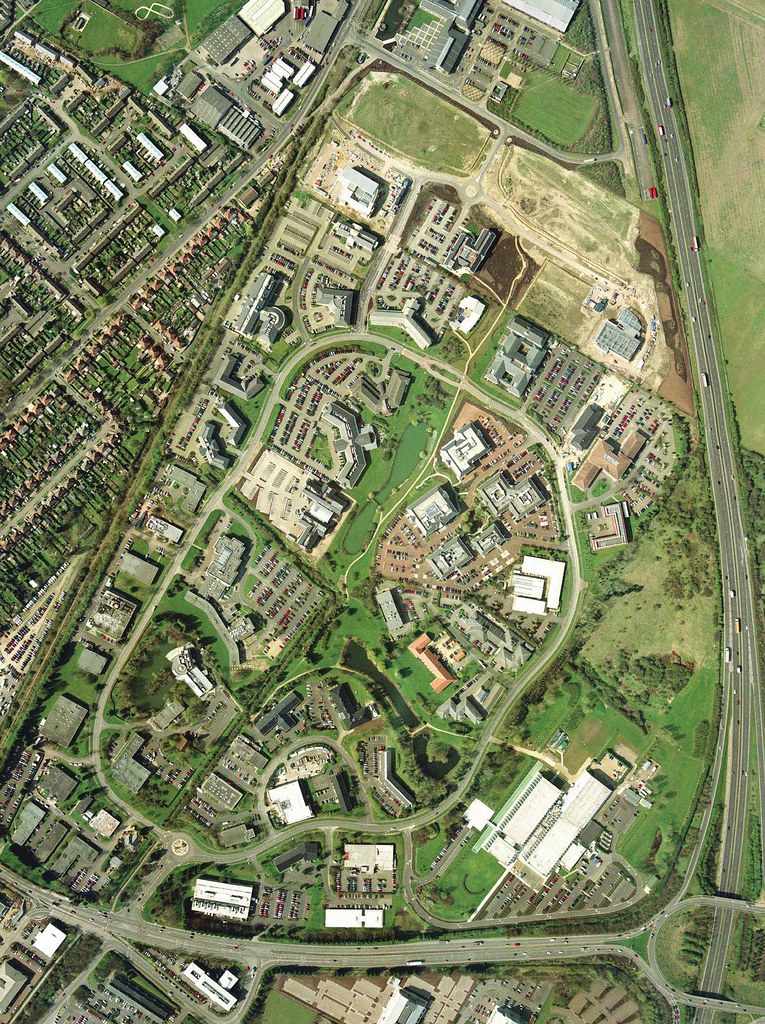 Case Study: Cambridge Science Park
Case Study: Cambridge Science Park- InnovaInnovation Park: Cambridge Science Park, at Cambridge, England, UK (Founded in 1970)
- Highlights: Etablished by Trinity College, Cambridge Science Park is the oldest science park in the United Kingdom. It houses over 100 companies specializing in various fields of science and technology, from startups to multinational corporations. The park benefits from its proximity to the University of Cambridge, facilitating collaboration between academia and industry.
- Impact: Cambridge Science Park has played a crucial role in the Cambridge Phenomenon, the city's transformation into one of the leading technology hubs in the world. It has supported the growth of numerous successful companies and has been a key factor in the region's economic development.
- Startup Incubators and Accelerators: Programs designed to support startups and entrepreneurs through mentorship, funding opportunities, and business services.
- Advanced Technological Infrastructure: State-of-the-art laboratories, high-speed internet, and other technological resources necessary for cutting-edge research and development.
- Networking and Community Events: Regular events, workshops, and seminars that foster community engagement and professional networking.
- Access to Capital: Connections with venture capitalists, angel investors, and other funding sources to help emerging companies scale.
- Talent Pool: Access to a skilled workforce from nearby universities and the local community.
To summarize, Innovation Parks serve as critical hubs for technological growth and innovation, providing an ecosystem where academia, startups, and established companies converge to push the boundaries of what's possible. Through fostering collaboration, offering access to cutting-edge facilities, and supporting new ventures, these parks catalyze the development of breakthrough technologies and products.
The exemplary models of Stanford Research Park and Cambridge Science Park highlight the global impact of these innovation ecosystems, demonstrating their pivotal role in driving economic development, creating jobs, and positioning regions at the forefront of technological advancement. As such, Innovation Parks are not just physical spaces but vibrant communities that embody the spirit of discovery and progress.

Innovation Programs
Innovation programs are structured initiatives designed by academic institutions, corporations, or government bodies to foster creativity, support the development of new products and services, and encourage entrepreneurial thinking. These programs often serve as catalysts for economic growth and technological advancement, providing participants with the resources, mentorship, and network needed to turn innovative ideas into reality.
Key Components of Effective Innovation Programs
- Mentorship and Guidance: Access to experienced mentors who can provide advice, feedback, and guidance throughout the innovation process.
Case Study: Y Combinator
- Program: Y Combinator, Mountain View, California, USA (Founded in 2005)

- Highlights: : Y Combinator is one of the most prestigious startup accelerators globally. It offers a three-month program where startups receive funding, mentorship, and access to a vast network of investors and entrepreneurs. The program culminates in a Demo Day, where startups pitch to a selected audience of investors.
- Impact: Y Combinator has funded over 2,000 startups, including notable companies like Airbnb, Dropbox, and Stripe. Its model has been widely replicated, significantly influencing the startup ecosystem worldwide.
- Program: Y Combinator, Mountain View, California, USA (Founded in 2005)
- Funding and Resources: Financial support, office space, and access to necessary technologies and materials to develop prototypes and test ideas.
 Case Study: Innovate UK
Case Study: Innovate UK- Program: Innovate UK, UK Research and Innovation , Swindon, UK (Independent body since 2007)
- Highlights: : Innovate UK is the UK's innovation agency, part of UK Research and Innovation (UKRI). It provides funding and support for businesses and research organizations to drive science and technology innovations that will grow the UK economy.
- Impact: Since its establishment in 2007, Innovate UK has invested around £2.5 billion to help businesses across a variety of sectors, generating up to £18 billion in gross value added (GVA) and creating approximately 70,000 jobs, demonstrating the critical role of government-supported innovation programs in national economic development.
- Educational Workshops and Seminars: Training sessions covering various aspects of innovation, entrepreneurship, and business management to equip participants with the knowledge needed to succeed.
- Networking Opportunities: Events and meetings that connect participants with potential collaborators, investors, and industry experts.
- Research Collaboration: Partnerships with universities and research institutions to access academic expertise and resources.
- Market Exposure: Opportunities to showcase innovations through competitions, trade shows, and media coverage to attract interest and investment.
Innovation programs play an instrumental role in bridging the gap between visionary ideas and market realities, propelling forward the engines of growth and change. Through a combination of mentorship, funding, educational resources, and networking opportunities, these programs cultivate environments where creativity flourishes and entrepreneurial ventures can thrive. The success stories of initiatives like Y Combinator and Innovate UK underscore the transformative potential of well-structured innovation programs. They not only foster individual success stories but also contribute significantly to the broader economic and technological landscape, highlighting the essential role such programs play in fostering a culture of innovation and progress on a global scale.

Innovation and Entrepreneurship Minor
The Innovation and Entrepreneurship Minor is an academic program designed for students who wish to complement their major field of study with the skills, knowledge, and experience necessary to innovate, start new businesses, or bring entrepreneurial thinking to existing organizations. This minor typically combines coursework in business fundamentals, innovation processes, and entrepreneurial strategy with hands-on experience through projects, internships, and startup incubators.
Key Components of the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Minor
- Foundational Business Courses: Introduction to key business concepts such as marketing, finance, and operations management.
- Innovation Workshops: Hands-on workshops that teach creative thinking techniques, design thinking, and problem-solving strategies.
Case Study: Innovation and Entrepreneurship Minor, Stanford University
- Program: Innovation and Entrepreneurship Minor, Stanford University , USA (Ongoing)

- Highlights: Stanford's program encourages students from any major to apply entrepreneurial thinking to their passions. It offers an interdisciplinary curriculum that includes courses from the Stanford Graduate School of Business and the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design (d.school). The program is known for its unique approach that bridges theory with practical application, fostering a culture of innovation.
- Impact: The minor has produced a notable number of graduates who have made significant contributions to the startup ecosystem, both in Silicon Valley and globally. Alumni have founded companies across various sectors, bringing innovative solutions to the market and addressing critical societal challenges. The program's success underscores Stanford's commitment to cultivating entrepreneurial talent capable of driving meaningful change.
- Program: Innovation and Entrepreneurship Minor, Stanford University , USA (Ongoing)
- Entrepreneurial Strategy: Courses on developing business models, understanding market dynamics, and strategic planning for new ventures.
- Technology Commercialization: Understanding the process of bringing technological innovations to market, including patenting, licensing, and product development.
- Startup Experience: Opportunities to work directly with startups or to develop one's own business ideas in a supportive, mentor-driven environment.
Case Study: Entrepreneurship & Innovation Minor, MIT Sloan School of Management
- Program: Entrepreneurship & Innovation Minor, MIT Sloan School of Management, USA (Ongoing)
- Highlights: The program at MIT Sloan provides an interdisciplinary approach that combines coursework, workshops, and hands-on experiences. It covers the entire innovation and entrepreneurship spectrum, from ideation and concept development to venture execution. The curriculum is designed to equip students with critical thinking skills and practical tools necessary for leading innovative ventures.
- Impact: Graduates of the program have gone on to successfully launch startups, lead innovation within established companies, and contribute to the entrepreneurial ecosystem. The program's emphasis on practical experience, supported by MIT's robust innovation network, has positioned its alumni as leaders in the fields of technology, business, and social impact.
- Program: Entrepreneurship & Innovation Minor, MIT Sloan School of Management, USA (Ongoing)
- Networking Events: Access to a network of entrepreneurs, investors, and industry leaders through guest lectures, networking events, and mentorship programs.
10 Recommended Entrepreneurship & Innovation Minor Programs, Globally
- Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA - Offers a minor in Management Science & Engineering that includes courses in entrepreneurship and innovation, teaching students how to bring technological inventions to market.
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, MA, USA - The Martin Trust Center for MIT Entrepreneurship provides extensive resources and courses for students interested in entrepreneurship, complementing various study fields.
- University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA - The Sutardja Center for Entrepreneurship & Technology offers a Certificate in Entrepreneurship & Technology that undergraduates from any major can pursue alongside their degree.
- Imperial College London, London, UK - Offers an Entrepreneurship minor available to students across various departments, focusing on the practical aspects of starting and running a business.
- National University of Singapore (NUS), Singapore - The NUS Overseas Colleges program is a unique combination of coursework and internships designed to immerse students in global entrepreneurial hubs.
- ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland - Provides a minor in Management, Technology, and Economics for students keen on complementing their technical or scientific major with entrepreneurship and innovation knowledge.
- University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK - Through the Judge Business School, students can access various entrepreneurship and innovation management courses that can complement their studies.
- Tsinghua University, Beijing, China - Offers an innovation and entrepreneurship minor program that equips students with the knowledge and skills to start new ventures and innovate within existing organizations.
- Technical University of Munich (TUM), Munich, Germany - The TUM School of Management offers an Entrepreneurship & Innovation minor, focusing on turning scientific findings into business models.
- University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada - Offers a Cross-Disciplinary Certificate in Entrepreneurship for undergraduate students through the Impact Centre, aiming to foster entrepreneurial thinking.
The Innovation and Entrepreneurship Minor offers a versatile and dynamic education path that equips students with the necessary tools to navigate the complexities of the modern business world. By blending academic rigor with practical experience, this minor prepares students to become leaders in innovation, capable of transforming ideas into impactful ventures. Whether aiming to launch a startup or innovate within established organizations, students gain a competitive edge in their careers, ready to contribute creatively and effectively to their industries.

Innovation Fellowship
Innovation fellowships are prestigious programs designed to nurture and support emerging leaders, innovators, and change-makers across various fields and industries. These fellowships provide talented individuals with unique opportunities for professional development, mentorship, and networking, enabling them to drive meaningful innovation, tackle complex challenges, and effect positive change within their organizations and communities. By fostering a culture of innovation and leadership excellence, innovation fellowships contribute to building a diverse pipeline of visionary leaders equipped to shape the future and address pressing global issues.
ey Components of Innovation Fellowships
- Structured Learning Experiences: Innovation fellowships typically offer structured learning experiences, such as workshops, seminars, and training sessions, focused on developing critical skills in innovation, leadership, entrepreneurship, and problem-solving. These learning opportunities equip fellows with the knowledge, tools, and frameworks needed to drive innovation and lead change in their respective fields.
- Mentorship and Coaching: Fellows often receive mentorship and coaching from experienced leaders, industry experts, and seasoned innovators who provide guidance, feedback, and support throughout the fellowship journey. Mentorship relationships help fellows navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and unlock their full potential as innovative leaders.
- Project-Based Assignments: Many innovation fellowships include project-based assignments or innovation challenges where fellows collaborate on real-world problems, develop innovative solutions, and implement initiatives that address societal, environmental, or organizational challenges. These hands-on experiences allow fellows to apply their skills, creativity, and expertise to make tangible impact and drive meaningful change.
- Networking and Collaboration: Innovation fellowships provide fellows with opportunities to connect, collaborate, and build relationships with a diverse community of peers, mentors, and industry leaders. Networking events, conferences, and community-building activities facilitate knowledge sharing, idea exchange, and collaboration, fostering a supportive ecosystem for innovation and learning.
- Access to Resources and Funding: Fellows may gain access to resources, funding, and support services to advance their innovative projects or ventures. Innovation fellowships often provide seed funding, grants, or access to incubators and accelerators to help fellows turn their ideas into actionable projects or scalable ventures with real-world impact.
Innovation fellowships play a crucial role in cultivating a new generation of visionary leaders, innovators, and changemakers who are equipped to tackle complex challenges, drive innovation, and create positive social and economic impact. By investing in talent development, leadership capacity, and cross-sector collaboration, innovation fellowships contribute to building resilient, inclusive, and sustainable communities and organizations poised to thrive in an ever-changing world.

Innovation Academy
An Innovation Academy is an educational institution or a specific program within a larger university that focuses on teaching students the principles of innovation, creativity, and entrepreneurship. These academies are designed to equip students with the skills needed to drive technological advancements, start new ventures, and solve complex problems in modern society.
Core Elements of an Innovation Academy
- Interdisciplinary Curriculum: Courses that span across different fields such as business, engineering, design, and computer science to encourage a holistic understanding of innovation.
Case Study: Olin College of Engineering
- Institution: Olin College of Engineering, Needham, MA, USA

- Overview: Olin College is dedicated to preparing students to become exemplary engineering innovators who recognize needs, design solutions, and engage in creative enterprises for the good of the world. Through its interdisciplinary curriculum, project-based learning, and a strong entrepreneurial ecosystem, Olin embodies the essence of an Innovation Academy.
- Unique Features: What sets Olin apart is its foundational belief in engineering as a creative enterprise that begins with people and their needs. The curriculum is designed around real-world projects from day one, encouraging students to develop innovative solutions with direct societal impact. Olin’s partnership with nearby Babson College also provides students with access to world-class entrepreneurial training.
- Institution: Olin College of Engineering, Needham, MA, USA
- Project-Based Learning: Emphasis on hands-on projects that allow students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world challenges.
 Case Study: Aalto University
Case Study: Aalto University- Institution: Aalto University, Espoo, Finland
- Overview: Aalto University stands out for its strong emphasis on innovation and design thinking, integrating business, technology, and art to foster an environment conducive to innovation. The university houses the Aalto Design Factory, Startup Sauna, and Aalto Ventures Program, making it a hub for entrepreneurial activities in Northern Europe.
- Unique Features: Aalto's multidisciplinary approach offers students an expansive network of industry partnerships, providing practical experiences alongside their academic studies. The Aalto Design Factory is particularly noteworthy for its project-based learning environment, where students work on real-life challenges presented by global companies, promoting a hands-on approach to innovation and entrepreneurship. Aalto's global network and emphasis on creativity and sustainability prepare students to be forward-thinking leaders in their fields.
- Entrepreneurial Ecosystem: Access to incubators, accelerators, and mentorship programs that support the development of student-led startups.
- Industry Partnerships: Collaborations with companies and organizations to provide students with internships, co-op opportunities, and real-world insights.
- Global Network: Opportunities for students to connect with a global network of innovators, entrepreneurs, and alumni.
- Innovation Labs and Maker Spaces: State-of-the-art facilities equipped with the latest technology and tools for prototyping and experimentation.
- Leadership and Management Skills: Courses and workshops designed to develop leadership, team management, and communication skills essential for successful innovation.
Innovation Academies play a pivotal role in shaping the innovators and entrepreneurs of tomorrow. By providing a comprehensive education that bridges theory and practice, these academies not only prepare students for the challenges of the future but also instill in them a mindset of continuous learning and improvement. Graduates of Innovation Academies are well-equipped to lead change, create sustainable solutions, and contribute positively to the global economy, making these institutions vital to the advancement of society.

Innovation Campus
An Innovation Campus is a dedicated space where academia, industry, and research converge to foster innovation, collaboration, and entrepreneurship. These campuses are designed to create a vibrant ecosystem that supports the development of new technologies, startups, and partnerships, driving economic growth and technological advancements. By integrating academic research with commercial opportunities, Innovation Campuses offer a unique environment that encourages the cross-pollination of ideas across different disciplines.
Key Features of an Innovation Campus
- Collaborative Workspaces: Open and flexible workspaces that encourage collaboration among students, researchers, entrepreneurs, and industry professionals.
Case Study: NC State University Centennial Campus
- Institution: North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA

- Overview: The Centennial Campus at NC State University exemplifies the concept of an Innovation Campus by blending academic departments, corporate partners, government agencies, and non-profits in a single community focused on technological innovation and research. Spanning over 1,000 acres, this campus houses more than 70 corporate, government, and non-profit partners alongside NC State research and academic units.
- Unique Features: Centennial Campus is distinguished by its collaborative research environment, fostering partnerships that translate into real-world applications and job creation. It hosts the Hunt Library, renowned for its advanced technological resources, and the Venture Place, which supports startups and entrepreneurship within the campus ecosystem. This integrated approach not only enhances the educational experience for students but also drives economic development in the region.
- Institution: North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA
- Research and Development Facilities: State-of-the-art laboratories and research centers equipped with advanced technologies for cutting-edge research.
- Startup Incubators and Accelerators: Programs and services that support early-stage startups, including mentorship, funding, and business development resources.
Case Study: Google Campus
- Institution: Google, global locations in about 100 cities, including New-York, San-Francisco, São Paulo, London, Madrid, Milan, Bangkok, Tokyo, Tel-Aviv, Dubai, and more.

- Overview: Google Campus is not a traditional academic institution, but a network of spaces run by Google for Entrepreneurs. These campuses serve as a hub for startups and innovators, offering workspace, events, and mentorship opportunities to help entrepreneurs grow their businesses.
- Unique Features: Each Google Campus is designed to foster community and innovation, providing access to Google’s resources and network. The campuses host regular workshops, talks, and networking events led by successful entrepreneurs and industry leaders. While it operates differently from a university-based innovation campus, Google Campus exemplifies the role of corporate entities in supporting the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Institution: Google, global locations in about 100 cities, including New-York, San-Francisco, São Paulo, London, Madrid, Milan, Bangkok, Tokyo, Tel-Aviv, Dubai, and more.
- Corporate Partnerships: Strong connections with leading companies and industries that provide students and researchers with access to real-world projects and challenges.
- Entrepreneurial Education: A range of courses and workshops focused on entrepreneurship, innovation management, and business strategy.

Case Study: Cornell Tech
- Institution: Cornell University, New York City, NY, USA
- Overview: Cornell Tech is an innovative campus that blends technology, business, law, and design education to spur innovation. Established as a partnership between Cornell University and the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, it's located on Roosevelt Island in New York City and aims to integrate the entrepreneurial spirit of Silicon Valley with the diverse and dynamic culture of New York.
- Unique Features: The campus is designed with collaboration in mind, featuring open workspaces and state-of-the-art facilities to encourage interaction among students, faculty, and industry partners. It hosts a variety of programs, including a startup studio and product studio, which bridge academia and industry by enabling students to work directly on company-sponsored projects.
- Community Engagement: Events, seminars, and networking opportunities that bring together members of the campus community with external experts and thought leaders.
 Case Study: Skolkovo Innovation Center
Case Study: Skolkovo Innovation Center- Institution: Skolkovo, Moscow, Russia
- Overview: Skolkovo Innovation Center, often referred to as the "Russian Silicon Valley," is a comprehensive development project aimed at promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in Russia. The center focuses on key areas such as information technology, energy efficiency, nuclear technology, biomedical research, and space. It offers a dynamic ecosystem that includes educational institutions like the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech), corporate R&D centers, startups, and investment firms.
- Unique Features: Skolkovo's approach to fostering innovation includes substantial government and private investment, tax incentives for resident companies, and a regulatory framework designed to facilitate rapid growth and development. The campus encourages international collaboration, hosting numerous global conferences and competitions to connect Russian innovators with worldwide networks. Skolkovo Innovation Center serves as a pivotal force in Russia's mission to diversify its economy and stimulate the growth of knowledge-intensive industries.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Commitment to sustainability and green technologies, often featuring eco-friendly buildings and infrastructure.
Innovation Campuses represent the frontier of modern education and research, embodying the principles of openness, collaboration, and interdisciplinary learning. They serve as catalysts for economic development, nurturing the next generation of entrepreneurs and innovators who will drive societal progress. By breaking down traditional barriers between academia and industry, Innovation Campuses create a dynamic environment where ideas can flourish, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and transformative solutions.
Systematic innovation
Interested in getting help with systematic innovation processes and developing new products and services?
Contact us: info@zooz.co.il ,+972-9-958-5085
Innovation Articles
- Innovation overview
- Innovation management
- Innovation methods
- Innovation tools
- Innovation and creativity
- Innovation and other disciplines
- Innovation in organizations
- Innovation career
- Innovation importance
- Innovation goals
- Innovation values
- Inspiration for innovation
- Innovation education
- Product innovation
- Service innovation
- Technological innovation
- Innovation examples
- Innovations across various industries
- Innovation glossary (200 terms)





