Innovation Examples
Mar 06, 2024
By Ari Manor , CEO at ZOOZ

This is one in a series of articles that provide detailed and updated information about Innovation. In this specific article, which focuses on Innovation Examples, you can read about:
- Innovation for Kids
- Innovation for Seniors
- Innovation Born out of Necessity
- Innovation to Reduce Air Pollution
- Innovation with Purpose Lockheed Martin
- Innovation with AWS
- Innovation with Amazon
- Innovations in Foods
- Innovations in Furniture
- Which Innovation is Attributed to Geoffrey Chaucer
- Which Innovation Gave the Sumerians
- Which Innovation Helped Both the Ottoman
- What is the Next Big Innovation
- What is the Best Innovation
For additional articles about Innovation, see the Topic Menu.

Innovation for Kids
Innovations for kids are designed to enhance learning, safety, and fun. Exploring the landscape of children's innovation reveals a dynamic fusion of education, technology, and creativity aimed at nurturing young minds. From safety gadgets that offer peace of mind to parents, to educational apps that transform learning into an adventure, these inventions embody the spirit of modern childhood. They cater to diverse aspects of a child's development, ensuring that learning, safety, and play go hand in hand.
30 Breakthrough Inventions for Kids
Here are examples for innovation for Kids, arranged according to category.
Educational Tools
- Early Learning apps: ABCmouse.com offers comprehensive curriculums for early learning through interactive activities.
- Learning Platforms: Khan Academy Kids offers free and engaging learning resources across subjects for children of various ages.
- Language Apps: Duolingo for Kids helps children learn new languages through playful interactions and games.
- Educational Video Games: Minecraft Education Edition builds creativity and problem-solving skills.
- Educational Subscription Boxes: KiwiCo Crates delivers hands-on science and art projects.
- Interactive E-books: E-books with interactive elements make reading more engaging for kids.
- Augmented Reality Books: These books bring stories to life and enhance the reading experience.
- Tablets Designed for Kids: Amazon Fire Kids Edition offers robust parental controls and educational content.
Platforms and Learning Resources
- Digital Reading Tools: Epic! digital library provides access to thousands of books for kids.
- Adaptive Math Games: Prodigy Math Game adapts in real-time to the child's skill level.
- STEM Subscription Services: Mel Science offers monthly science experiments.
- Music Learning Apps: Yousician uses interactive lessons to teach kids how to play musical instruments.
Technology and Engineering
- Smart Toys: LEGO Mindstorms allows kids to build and program their own robots.
- Programmable Drones: Tello EDU introduces kids to the basics of aerodynamics and coding.
- DIY Computer Kits: Kano Computer Kit enables kids to build and code their own computers.
- Interactive Robots: Cozmo by Anki teaches coding through play.
- Smart Building Blocks: Intelino Smart Train Set introduces coding concepts.
- Electronic Coding Toys: Botley 2.0 teaches the basics of coding logic.
- Educational Robotics Kits: LEGO Boost Creative Toolbox makes building robots accessible.
- Child-Friendly Coding Apps: ScratchJr introduces children to programming.
Creative and Interactive Learning
- Smartwatches for Kids: VTech Kidizoom Smartwatch combines learning tools with fun.
- 3D Printers for Kids: Toybox 3D Printer stimulates design and engineering skills.
 Augmented Reality Globes: Orboot Earth by PlayShifu offers geography learning.
Augmented Reality Globes: Orboot Earth by PlayShifu offers geography learning.- Artificial Intelligence Learning Companions: Miko 3 engages kids with content.
- Interactive Language Learning Toys: Talkie by Toymail lets kids send voice messages.
- Virtual Reality Educational Experiences: Merge Cube enables interaction with digital objects.
- Digital Art Platforms: Osmo Creative Kit fosters creativity in drawing.
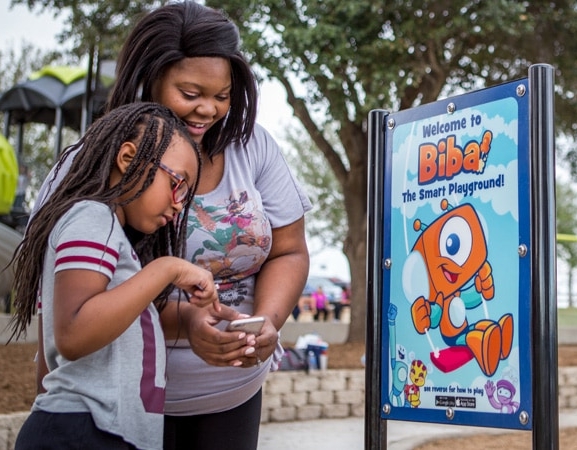 Case Study: Biba Ventures' Augmented Reality Playground Games
Case Study: Biba Ventures' Augmented Reality Playground Games- Company: Biba Ventures, Vancouver, Canada (First launched in 2014)
- What Was Done: Biba developed augmented reality mobile games to encourage outdoor physical play. These games transform traditional playground equipment into interactive gaming experiences.
- Results/Impact: By integrating digital play into outdoor activities, Biba has made playgrounds more appealing to the tech-savvy younger generation, promoting physical activity and imaginative play.
Health and Safety
- Safety Gadgets: The Jiobit location tracker enables parents to keep tabs on children's safety.
- Wearable Fitness Trackers: Garmin Vivofit Jr. motivates kids to stay active.
- Sun Exposure Monitor: L’Oréal’s My UV Patch helps protect kids from sunburn by monitoring UV exposure.
Leaders in Innovation for Kids
Several organizations and companies are at the forefront of creating innovative products and services for children, driving forward the market with new ideas and technologies.
- Nintendo: With products like Labo, Nintendo combines video gaming with hands-on building, providing a unique interactive experience.
- Vtech: Specializes in educational electronics for children, making learning fun and accessible.
- Fisher-Price: Known for its innovative toys that stimulate learning through play for various developmental stages.
- Mattel: Continuously evolves its toy lines with a focus on both education and entertainment, keeping in step with children's changing interests.
- LEGO: Continues to lead with its STEAM kits that blend play with education, teaching kids about engineering and programming.
Case Study: LEGO Braille Bricks for Visually Impaired Children
- Company: The LEGO Foundation, Billund, Denmark
- Product: Braille Bricks (launched in 2019)
- What Was Done: oundation and LEGO Group, in collaboration with associations for the blind, developed LEGO Braille Bricks. The bricks are molded with studs that correspond to letters and numbers in the braille alphabet.
- Results/Impact: The braille bricks were launched in several languages and distributed free to institutions, reaching children in multiple countries. They not only aid in literacy but also foster inclusivity in play, allowing visually impaired and sighted.
How to Apply Innovation for Kids
To apply innovation effectively for kids, one must understand the intersection of education, entertainment, and technology, often referred to as "edutainment."
- User-Centered Design Approach: Focus on the needs, wants, and limitations of kids as end-users.
- Iterative Prototyping and Testing: Develop prototypes and engage kids in testing to gather feedback and ensure the product resonates with them.
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Work with educators, psychologists, designers, and technologists to create holistic products.
- Incorporate Storytelling: Use narratives to make the product more engaging and memorable for kids.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize AR, VR, and AI to create immersive and interactive learning experiences.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Kids
- Developmental Suitability: Products are designed to match the cognitive and motor skills of children at different ages.
- Safety and Durability: Given the propensity for kids to explore with all their senses, innovations must be built to be safe and withstand rough handling.
- Engagement and Fun: To hold children's attention, innovations often include elements of play and storytelling.
- Educational Value: Many innovations aim to teach new skills or concepts, from basic numeracy to problem-solving.
- Parental Involvement: Encouraging shared activities between parents and kids, fostering bonding and learning together.
What to Avoid When Inventing for Kids
When inventing for kids, it is crucial to avoid certain pitfalls to ensure the product is appropriate and successful.
- Over-Complexity: Avoid making the product too complicated for the intended age group.
- Small Parts for Young Children: Be mindful of choking hazards and always follow age-appropriate guidelines.
- Short Lifespan and Obsolescence: Design products that grow with the child, offering longevity and adaptability.
- Ignoring Educational Value: Innovations should have a component of learning, no matter how subtle.
- Neglecting Parental Insights: Parents are often the purchasers, so their needs and concerns must be considered.
Innovation for kids is a specialized field that requires a delicate balance between educational value and the intrinsic need for play. By understanding these unique characteristics and following the examples set by leaders in the field, inventors and designers can create meaningful and enduring products for children. Innovators in this field will continue delivering solutions that not only captivate young imaginations but also equip them with the skills and knowledge for a thriving future.

Innovation for Seniors
Innovations designed for seniors aim to enhance quality of life, promote independence, and ensure safety for older adults. Catering to the unique needs and challenges of the elderly population, these advancements offer convenience, safety, connectivity, and greater independence. By merging technology with empathy and understanding, such inventions successfully bridge the gap between seniors' needs and the digital world, ensuring that age does not prevent a fulfilling life.
30 Breakthrough Inventions for Seniors
Over the years, numerous inventions have significantly impacted seniors' lives. Following are some examples, in several categories.
Emergency Response and Health Monitoring
- Personal Emergency Response Systems (PERS): LifeFone PERS enables seniors to alert caregivers or emergency services with a button press.
- Hearing Aids with Bluetooth Connectivity: The Phonak Audeo Marvel allows for clearer calls and audio streaming directly.
- Fall Detection Wearables: The Apple Watch Series 4 (and later) includes fall detection and automatic emergency calling if the user is unable.
- Smart Pillboxes: The MedMinder Maya organizes medications and alerts seniors when it's time to take their pills.
- Wearable Health Monitors: Fitbit devices track heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels, encouraging a healthier lifestyle.
- Telehealth Services: Teladoc offers virtual consultations with doctors, reducing the need for physical office visits.
Mobility and Accessibility Solutions
- Motorized Wheelchairs: Invacare's Pronto M51 provides mobility for those with limited physical capabilities.
- Adjustable Beds: The Craftmatic Adjustable Bed allows seniors to adjust sleeping positions with a remote, aiding in better sleep and comfort.
- Automated Stair Lifts: Stannah Stairlifts provide a safe and easy way up and down the stairs for those with limited mobility.
- Electric Lift Chairs: The Pride Mobility Infinite Position Lift Chair helps seniors stand up and sit down with ease.
Home Safety and Daily Living Aids
- High-Contrast Keyboards: The LogicKeyboard Large Print facilitates computer use for those with vision impairments.
- Walk-In Tubs: American Standard's Liberation tub ensures safe bathing without the risk of stepping over a high edge.
- Robotic Vacuum Cleaners: iRobot Roomba helps maintain cleanliness, minimizing the physical strain of vacuuming.
- Automatic Jar Openers: Hamilton Beach’s Open Ease Automatic Jar Opener makes opening jars effortless, preserving independence in the kitchen.
- Non-Slip Shoes: Propet offers a range of non-slip footwear to reduce the risk of falls among seniors.
- Long-Handled Cleaning Tools: OXO Good Grips extendable cleaning products (e.g. - Extendable Tub & Tile Scrubber) minimize the need for bending and stretching.
Cognitive Stimulation and Social Engagement
- Video Calling Devices: The GrandPad tablet simplifies video calling for seniors, helping them stay connected with family.
- Educational Tablets for Seniors: The GrandPad comes preloaded with apps designed for senior learning and entertainment, fostering continued cognitive engagement.
- Virtual Reality Experiences for Cognitive Stimulation: Oculus Go provides engaging activities that help maintain cognitive function.
- Memory Aid Devices: The Joy for All Companion Pet by Hasbro offers comfort and companionship, stimulating cognitive function through interaction.
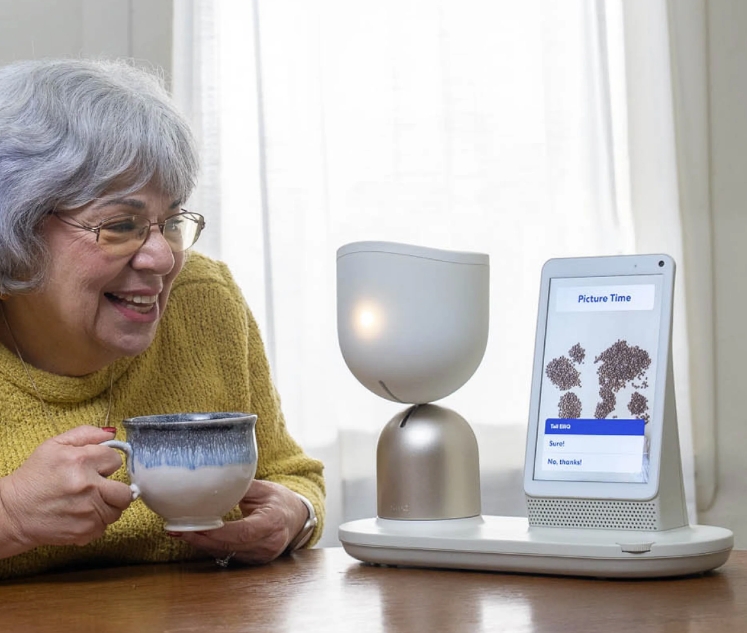 Case Study: ElliQ - The Companion Robot for the Elderly
Case Study: ElliQ - The Companion Robot for the Elderly
- Company: Intuition Robotics, Tel Aviv, Israel (Launched in 2018)
- What Was Done: ElliQ is a companion robot designed to engage and assist elderly individuals with daily routines, communication, and staying active, using AI to adapt to user preferences.
- Results/Impact: In trials, ElliQ improved seniors' quality of life by reducing social isolation and encouraging a more active and connected lifestyle, demonstrating the potential of robotics in elderly care.
Smart Home Technology
- Medication Dispensers with Alarms: The Philips Lifeline medication dispensing service aids in managing complex schedules, reducing missed doses.
- Smart Home Devices: The Google Nest Hub allows voice-activated control of lights, thermostats, and other appliances, simplifying daily tasks.
- Smart Canes: The CAN Go smart cane detects falls and alerts caregivers, providing an extra layer of security.
- Voice-Activated Smart Home Hubs: Amazon Echo allows users to control various smart home devices using voice commands.
- GPS Trackers for Seniors: The AngelSense tracker offers families peace of mind by providing real-time location updates of their loved ones.
- Digital Magnifiers: The Eschenbach SmartLux Digital is a portable device that enlarges text for those with vision impairments.
Health and Well-being
- Light Therapy Lamps: The Carex Day-Light Classic Plus provides bright light therapy to combat seasonal affective disorder and improve sleep.
- Fitness Equipment for Seniors: The Stamina InStride Folding Cycle provides low-impact exercise, promoting cardiovascular health.
- Ergonomic Gardening Tools: Radius Garden tools are designed to reduce strain on hands and wrists, making gardening more enjoyable.
- Elderly-Friendly Smartphone Apps: Oscar Senior app simplifies smartphone interfaces, making them more accessible for the elderly.
Case Study: Silvernest's Home Sharing for Aging Adults
- Company: Silvernest, Denver, USA (Founded in 2015)

- What Was Done: Silvernest provides a home sharing platform that matches older homeowners with compatible housemates, incorporating tools for agreement management and rent processing.
- Results/Impact: The service has provided seniors with financial stability and social interaction, tackling senior housing affordability and loneliness, while promoting intergenerational living.
Leaders in Innovation for Seniors
Several companies and organizations are recognized for their contributions to enhancing seniors' lives through innovative products and services:
- GreatCall: Offers senior-friendly mobile phones and wearable alert devices, emphasizing ease of use and emergency response services.
- SilverSneakers: Provides fitness programs specifically designed for older adults, promoting an active lifestyle and social engagement.
- Stannah Stairlifts: Manufactures stairlifts that help seniors navigate multi-story homes safely and independently.
- CaptionCall: Delivers captioned telephone service for seniors with hearing loss, ensuring clear communication.
How to Apply Innovation for Seniors
Applying innovation to products and services for seniors involves several key steps:
- Engage with Seniors: Directly involve seniors in the design process to ensure their needs and preferences are met.
- Conduct Thorough Market Research: Understand the challenges and pain points seniors face in their daily lives.
- Iterate and Test: Prototype and test with real users to refine products and ensure they truly benefit the end-user.
- Focus on Training and Support: Provide clear instructions and customer support to assist seniors in adopting new technologies.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation for Seniors
- Ease of Use: Products and services must feature simple interfaces, avoiding complex configurations that can cause confusion.
- Accessibility: Innovations should be accessible to seniors with varying degrees of mobility and tech-savviness.
- Safety Focus: A key characteristic of senior-focused innovations is the emphasis on safety, from slip-resistant materials to emergency response features.
- Adaptive Design: Recognizing that seniors' abilities may change over time, products need to be adaptable to a range of physical capabilities.
- Social Connection: Many innovations aim to address loneliness, which is common in older age, by facilitating communication with friends, family, and caregivers.
What to Avoid When Inventing for Seniors
Inventing for seniors requires sensitivity to potential barriers:
- Overcomplication: Innovations should not be too technologically complex for the average senior user.
- Small, Indistinct Buttons: Can be difficult for seniors with limited dexterity or vision to use.
- Ignoring Privacy Concerns: Seniors are particularly concerned about their privacy and security.
- Neglecting Comfort and Ergonomics: Discomfort can deter seniors from using a product, regardless of its innovative features.
- Assuming One-Size-Fits-All: Seniors are a diverse group with a wide range of abilities and preferences.
Innovation for seniors should be carried out with a clear understanding of the demographic's specific needs. It should prioritize simplicity, safety, and enhancement of everyday life. As the senior population grows, so does the opportunity for meaningful and impactful innovation. As we look to the future, the potential for innovation in senior care and lifestyle enhancement is boundless.
Companies and inventors are urged to continue their focus on this demographic, ensuring that the tools and services they develop truly resonate with the needs and desires of older adults. Through continued collaboration, research, and creativity, we can look forward to a world where seniors are not left behind by technology but are empowered by it, leading to a society that values inclusivity and the well-being of its eldest members

Innovation Born out of Necessity
Innovation born out of necessity, often referred to as "frugal innovation" or "constraint-based innovation," occurs when limitations or pressing challenges drive the development of creative solutions. These innovations are characterized by their cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and focus on meeting basic needs in challenging or resource-limited environments.
30 Breakthrough Inventions Born Out of Necessity
Here are 30 examples of applying innovation out of Necessity, in various categories.
Healthcare Innovations
- Paper Microscopes: The Foldscope, an inexpensive, durable microscope made mostly of paper, is used to identify diseases in remote areas.
- Portable Ultrasound Devices: The Butterfly iQ handheld ultrasound device makes prenatal care more accessible in remote regions.
- Affordable Prosthetics: Low-cost prosthetic limbs, like the Jaipur Foot, provide mobility for amputees in developing countries.
- Affordable Eye Care: Aravind Eye Care System offers high-quality, low-cost eye care services in India, making vision care accessible to millions.
- Telemedicine Platforms: MD Consults enables remote medical consultations in areas lacking medical facilities.
- Mobile Apps for Healthcare: Medic Mobile offers health-focused mobile apps to support community health workers in remote areas of Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
- Wearable Health Monitors: Fitbit trackers offer affordable ways to monitor health metrics, encouraging proactive health management in populations with limited access to healthcare services.
Water and Energy Solutions
- Portable Water Purifiers: LifeStraw's personal water filters ensure safe drinking water in any environment, addressing the critical need for clean water in remote and disaster-stricken areas.
- Drip Irrigation Systems: Netafim provides solutions that maximize water efficiency for agriculture in arid regions.
- Sustainable Energy Solutions: SELCO India provides solar lighting and power to underprivileged communities in India.
- Solar Cookers: The SolSource by One Earth Designs utilizes the sun's energy for cooking, beneficial in regions with limited fuel sources.
- Wind-Powered Water Pumps: The WindWise system provides affordable irrigation and drinking water solutions by harnessing wind energy, especially useful in remote, off-grid locations.
- Solar-Powered Desalination Units: The SunSpring system, designed for coastal communities, provides clean drinking water by converting seawater into freshwater using solar energy.
- Low-Cost Solar Lighting: d.light provides affordable solar lanterns to people in developing countries, offering a safer alternative to kerosene lamps and improving quality of life.
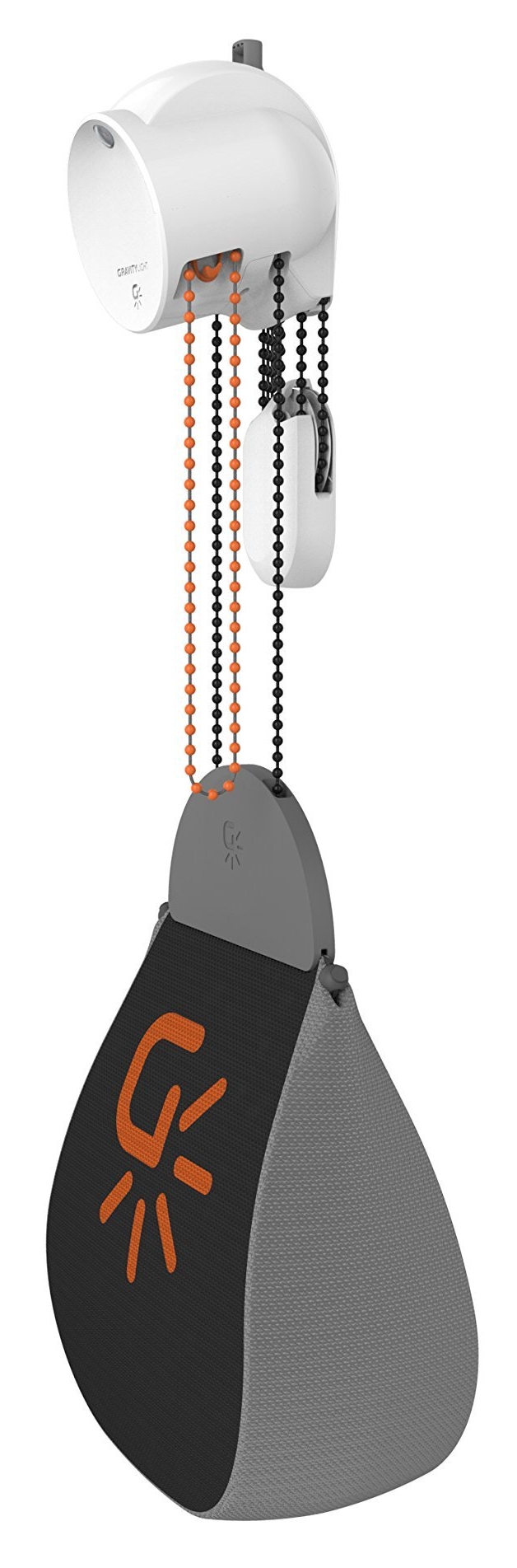 Case Study: GravityLight - Lighting Up Lives without Electricity
Case Study: GravityLight - Lighting Up Lives without Electricity- Company: The GravityLight Foundation, London, UK (Founded in 2012)
- What Was Done: The GravityLight Foundation developed an innovative device that generates light from gravity. It was designed for regions without reliable electricity, using a weight to generate energy as it descends.
- Results/Impact: GravityLight provided a safe, reliable, and renewable source of light to communities where traditional electricity is not available, costly, or reliant on harmful kerosene lamps, significantly improving living conditions and safety.
Sustainable Living and Building
- Bamboo Housing: Bamboo Living uses bamboo as a strong, sustainable building material for constructing affordable housing in earthquake-prone areas.
- Low-Cost Building Materials: EcoBricks transform plastic waste into durable construction materials, offering an environmentally friendly solution to building in resource-limited settings.
- Upcycled Materials: PlasticRoad creates new products from waste materials, such as using discarded plastic to pave roads, providing both an environmental and infrastructural solution.
- Emergency Shelter Solutions: The Better Shelter, a flat-packed, easy-to-assemble shelter developed in partnership with IKEA, offers immediate housing for refugees and disaster victims.
- Biodegradable Planters: EcoForms creates sustainable plant pots from renewable agricultural by-products, reducing plastic use in gardening and agriculture.
Education and Connectivity
- Solar-Powered Textbooks: Bridge International Academies utilize solar-powered tablets for education in remote African regions.
- Mobile Education Platforms: Khan Academy's app delivers free, high-quality educational content to students worldwide, breaking barriers to education in underserved communities.
- Portable Solar Chargers: The Solio Bolt charger allows individuals in off-grid areas to charge mobile devices using only the power of the sun, facilitating communication and access to information.
- Mesh Network Classrooms: In remote Peruvian villages, mesh networks link schools digitally, allowing lesson sharing and online resources access without mainstream internet infrastructure.
- Broadcast Educational Radio: Utilized in rural African regions, radio broadcasts deliver educational content to students without access to the internet or television, ensuring continuity of learning during school closures.
Environmental and Health Impact
- Recycled Footwear: The Ecoalf foundation creates shoes from recycled ocean plastics, addressing pollution while providing footwear for those in need.
- Manual Laundry Machines: The GiraDora, a foot-powered washing machine, offers an affordable and efficient laundry solution for low-income families without access to electricity.
- Composting Toilets: Peepoo's single-use, biodegradable toilets provide a sanitary solution for areas without sewer systems, improving public health by preventing fecal-oral diseases.
- Solar Water Purification: Solar-powered systems by companies like Solar Water Solutions provide clean drinking water, combating water scarcity in remote regions.
- Innovative Mosquito Traps: The Mosquito Magnet traps and kills mosquitoes without chemicals, helping to reduce the spread of mosquito-borne diseases in tropical regions.
- Affordable Insulin: Biocon's Basalog provides a more accessible biosimilar insulin option, making diabetes management more affordable in low-income countries.
Unique Characteristics of Innovation Born Out of Necessity
- Resourcefulness: Making the most of limited resources and finding value in materials or technologies that are readily available or discarded.
- Simplicity: Solutions that are simple to implement and use, often due to the constraint of needing to address the problem immediately.
- Affordability: Offering economical solutions that are accessible to those with limited financial means.
- Localization: Adapting to local conditions, cultures, and markets, ensuring that innovations are relevant to the community's specific needs.
- Sustainability: Creating solutions with minimal environmental impact, often utilizing renewable or recycled materials.
Case Study: Mobile Banking in Kenya with M-PESA
- Company: Safaricom, Nairobi, Kenya (Launched in 2007)
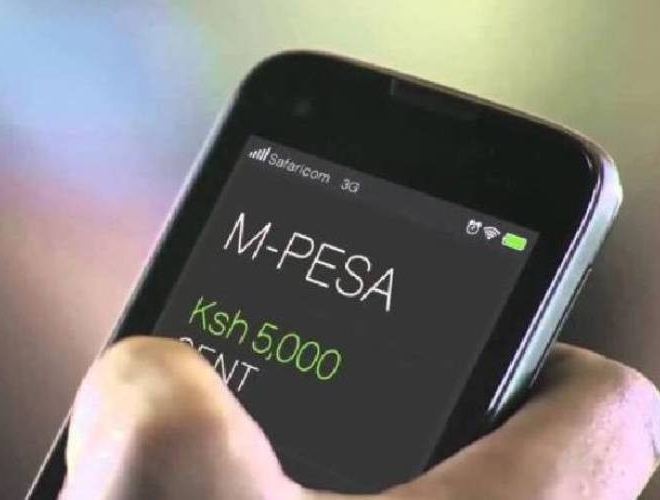

- What Was Done: Safaricom launched M-PESA, a mobile phone-based money transfer, financing, and microfinancing service. It was created to serve the unbanked population of Kenya, allowing users to deposit, withdraw, and transfer money easily with a mobile device.
- Results/Impact: M-PESA revolutionized the banking industry in Kenya and other countries, providing financial services to millions who previously had no bank access. It has significantly impacted economic activity and financial inclusion in the region.
What to Avoid When Inventing for Necessity
- Over-Engineering: Avoid creating solutions that are more complex than necessary, which can drive up costs and reduce usability.
- Cultural Insensitivity: Solutions must be developed with a deep understanding of local customs and needs to ensure acceptance and integration within communities.
- Ignoring User Feedback: The target users are the best source of feedback; their input should guide the innovation process.
- Neglecting Scalability: While solutions should be localized, they should also be designed with the potential for scaling to other areas with similar challenges.
- Underestimating Sustainability: It’s important to consider the long-term sustainability of the solution, both economically and environmentally.
Five Key Areas Where Necessity Drives Innovation
Here are 25 examples, in 5 areas of global problems that require creative solutions
Healthcare Innovations in Remote Areas
- Mobile Clinics: Provide essential healthcare services directly to remote and underserved communities, offering screenings, treatments, and vaccinations.
- Telehealth Services: Utilize digital platforms to connect patients with healthcare professionals for consultations, diagnostics, and treatment planning without the need for physical travel.
- Portable Diagnostic Tools: Devices like the Foldscope allow for on-the-spot disease diagnosis in field conditions, enabling rapid response to health crises.
- Vaccine Delivery Innovations: Novel methods such as drone deliveries to distribute vaccines in hard-to-reach areas, ensuring wider immunization coverage.
- Affordable Prosthetics: Solutions like the Jaipur Foot give amputees in low-income countries access to mobility aids, enhancing their quality of life.
Sustainable Water Solutions
- Water Purification Innovations: Ensure clean drinking access in drought-impacted communities with portable and efficient filtration systems like LifeStraw.
- Advanced Irrigation Systems: Technologies such as drip irrigation maximize water efficiency for agriculture in arid regions, conserving precious water resources.
- Rainwater Harvesting Techniques: Systems for collecting and storing rainwater for domestic and agricultural use, providing a sustainable water source in dry areas.
- Desalination Technologies: Convert seawater into drinkable water, supplying fresh water to communities in coastal and arid environments.
- Greywater Recycling: Reuse of household wastewater for gardening and agricultural purposes, reducing the demand for fresh water.
Energy Solutions in Off-grid Communities
- Biogas Systems: Transform organic waste into a clean, renewable energy source for cooking and lighting, benefiting rural households.
- Hand-cranked Generators: Offer an immediate power solution in emergency situations or where electricity is not available.
- Wind Turbines: Small-scale installations provide localized energy production, suitable for off-grid communities.
- Solar Cookstoves: Utilize the sun's energy for cooking, decreasing dependence on wood and fossil fuels.
- Hydroelectric Micro-grids: Generate electricity for small communities through water-powered systems, harnessing local river currents.
Agricultural Techniques for Arid Lands
- Aquaponics Systems: Combine fish farming with hydroponic agriculture to produce food efficiently with minimal water use.
- Soil Moisture Conservation Practices: Techniques to retain soil humidity and improve water use efficiency in crop production.
- Climate-Resistant Farming Practices: Adoption of crops and cultivation methods that withstand extreme weather conditions, securing food production.
- Seed Banks: Preserve genetic diversity of plants, ensuring availability of seeds for future planting in changing environmental conditions.
- Mobile Apps for Precision Farming: Utilize data and technology to optimize planting, watering, and harvesting, increasing yields with fewer resources.
Educational Tools for Underserved Populations
- Offline Digital Content Libraries: Access to educational materials without the need for internet connectivity, supporting learning in remote locations.
- Low-bandwidth Educational Platforms: Online learning tools designed to function with minimal internet speeds, making education more accessible.
- Mobile Classrooms: Schools on wheels that bring educational opportunities directly to children in distant or nomadic communities.
- Bilingual Education Materials: Resources for non-native speakers to learn in their own language while acquiring a new one, fostering inclusivity.
- Vocational Training Programs via Mobile Apps: Offer practical skills and job training to youths and adults, enhancing employability and supporting economic development.
Strategies for Innovating Out of Necessity
- Identify Pressing Problems: Recognize the most urgent needs within a community or environment.
- Following natural disasters, organizations identify immediate survival needs, such as shelter and clean water, deploying rapid-response solutions like emergency housing units and water purification systems.
- Following natural disasters, organizations identify immediate survival needs, such as shelter and clean water, deploying rapid-response solutions like emergency housing units and water purification systems.
- Utilize Local Resources: Innovate using locally available materials and knowledge.
- In sun-rich, fuel-scarce regions, local communities adopt solar cookers made from easily accessible materials, reducing dependence on traditional fuel sources.
- In sun-rich, fuel-scarce regions, local communities adopt solar cookers made from easily accessible materials, reducing dependence on traditional fuel sources.
- Leverage Community Knowledge: Incorporating local traditions and knowledge into modern innovations.
- Traditional knowledge of medicinal plants in the Amazon is utilized to develop new pharmaceutical treatments, marrying ancestral wisdom with modern medical research.
- Traditional knowledge of medicinal plants in the Amazon is utilized to develop new pharmaceutical treatments, marrying ancestral wisdom with modern medical research.
- Foster Community Engagement: Work closely with local communities to ensure solutions are culturally and practically relevant.
- Addressing the lack of sanitation facilities, NGOs work with villages to build and maintain locally sourced composting toilets, ensuring adoption and proper use.
- Addressing the lack of sanitation facilities, NGOs work with villages to build and maintain locally sourced composting toilets, ensuring adoption and proper use.
- Simplify Technology for Accessibility: Making technology user-friendly and accessible to all, regardless of background.
- Basic mobile phones with pre-loaded educational content are distributed in rural Africa, enabling access to learning resources without the need for internet connectivity.
- Basic mobile phones with pre-loaded educational content are distributed in rural Africa, enabling access to learning resources without the need for internet connectivity.
- Utilize Open Source Solutions: Sharing and adapting open-source technologies to fit local needs.
- Communities in developing countries customize open-source software to create educational platforms that are tailored to local languages and curricula.
- Communities in developing countries customize open-source software to create educational platforms that are tailored to local languages and curricula.
- Build on Modular Design: Creating solutions that are easily adjustable and scalable.
- Modular housing units designed for rapid assembly are deployed in refugee camps, offering a flexible and scalable approach to emergency shelter.
- Modular housing units designed for rapid assembly are deployed in refugee camps, offering a flexible and scalable approach to emergency shelter.
- Adopt Rapid Prototyping: Quickly develop and test prototypes to adapt solutions based on real-world feedback.
- Health startups rapidly prototype mobile apps for remote diagnostics, testing them in field conditions with healthcare workers for immediate feedback.
- Health startups rapidly prototype mobile apps for remote diagnostics, testing them in field conditions with healthcare workers for immediate feedback.
- Scale and Adapt Solutions: Ensure innovations can be scaled or modified to address broader applications or different challenges.
- In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, educational organizations scaled up radio-based learning to reach students in areas without internet access, adapting content for broad age ranges and subjects.
- In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, educational organizations scaled up radio-based learning to reach students in areas without internet access, adapting content for broad age ranges and subjects.
- Emphasize Sustainability: Ensuring solutions are environmentally sustainable and economically viable.
- Innovative solar-powered water pumps are introduced in dry regions, providing a sustainable and cost-effective solution for irrigation, significantly reducing the dependency on diesel-fueled generators.
- Innovative solar-powered water pumps are introduced in dry regions, providing a sustainable and cost-effective solution for irrigation, significantly reducing the dependency on diesel-fueled generators.
Innovation born out of necessity demonstrates that some of the most impactful solutions stem from addressing fundamental needs under constrained circumstances. By prioritizing affordability, simplicity, and local applicability, such innovations can have a profound and lasting impact on communities worldwide.

Innovation to Reduce Air Pollution
Innovations designed to reduce air pollution tackle one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time. By implementing novel technologies and strategies, both public and private sectors aim to improve air quality and reduce the health impacts associated with polluted air.
Technological Advancements to Combat Air Pollution
- Alternative Energy Vehicles: A shift from fossil fuel-based transportation to electric and hydrogen vehicles to decrease roadside emissions.
- Tesla's electric cars and buses like Proterra are reducing urban transportation emissions.
Case Study: Tesla Semi - Electrifying Freight Transport
- Company: Tesla, Inc., Palo Alto, USA (Tesla Semi launched in 2017)
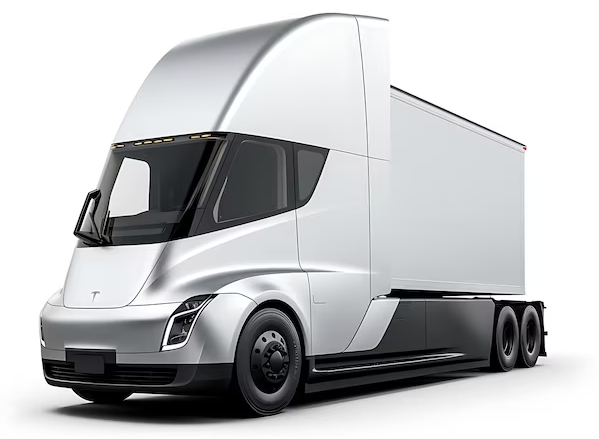

- What Was Done: Tesla unveiled the Tesla Semi, an all-electric semi-truck, aiming to reduce air pollution and the carbon footprint of freight transport. The Semi boasts impressive performance figures while producing zero tailpipe emissions.
- Results/Impact: The Tesla Semi is poised to transform the freight industry by reducing dependence on diesel, with potential significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and fuel costs for operators, pending its anticipated widespread adoption.
- Company: Tesla, Inc., Palo Alto, USA (Tesla Semi launched in 2017)
- Tesla's electric cars and buses like Proterra are reducing urban transportation emissions.
- Emissions Control in Industry: Upgrading factories with scrubbers and filters to capture harmful emissions before they reach the atmosphere.
- Steel plants implementing carbon capture technologies to minimize their carbon footprint.
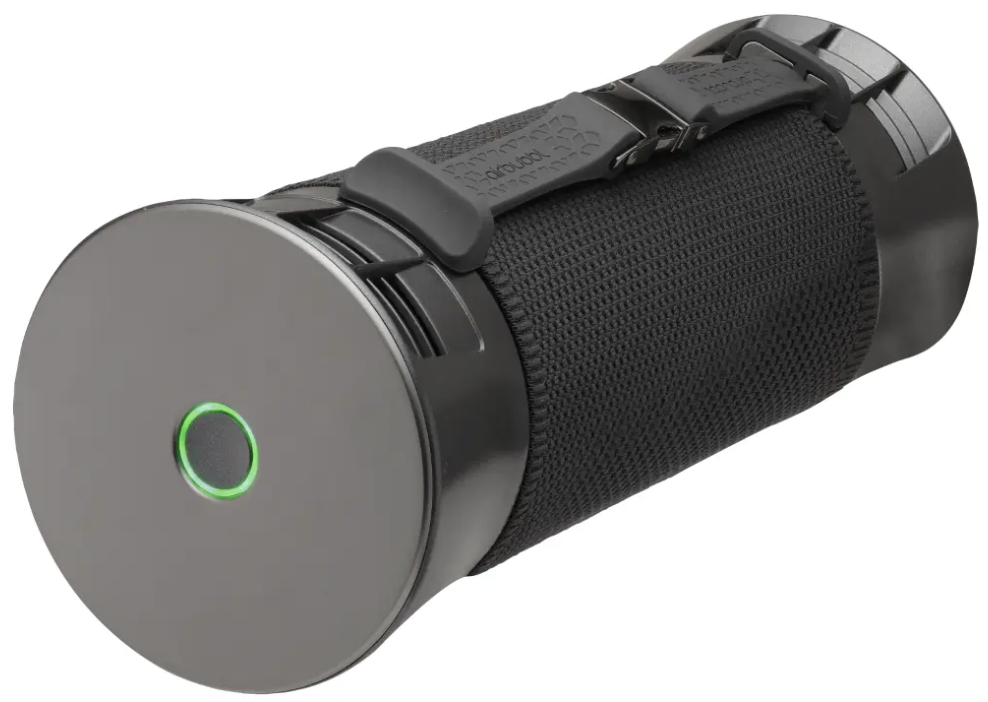 Case Study: Airlabs’ Airbubbl - Clean Air in Vehicles
Case Study: Airlabs’ Airbubbl - Clean Air in Vehicles- Company: Airlabs, London, UK (Launched in 2018)
- What Was Done: Airlabs created the Airbubbl, an in-car air purifier that removes more than 95% of nitrogen dioxide and other pollutants inside vehicles, which is vital in urban areas with high traffic emissions.
- Results/Impact: The Airbubbl has been adopted by private car owners and fleets, offering a solution to reduce the health impact of air pollution during commutes and proving particularly beneficial for professional drivers in polluted cities.
- Steel plants implementing carbon capture technologies to minimize their carbon footprint.
- Green Urban Planning: Designing cities with green spaces that can absorb CO2 and other pollutants, improving urban air quality.
- Singapore's integration of vertical gardens in urban development to act as natural air filters.
- Singapore's integration of vertical gardens in urban development to act as natural air filters.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Increasing the use of solar, wind, and other renewable energy forms to reduce reliance on coal and natural gas.
- SolarCity's widespread deployment of solar panels to replace traditional electricity generation methods.
- SolarCity's widespread deployment of solar panels to replace traditional electricity generation methods.
- Public Transportation Systems: Developing and expanding public transport networks to reduce the number of private vehicles on the road.
- Copenhagen's investment in cycling infrastructure and public transit to cut down vehicular pollution.
Policies and Programs to Reduce Air Pollution
- Cap and Trade Systems: Imposing limits on emissions and allowing the trading of allowances to incentivize reduction.
- Urban Congestion Pricing: Charging fees for vehicles entering congested areas to discourage driving and lower emissions.
- Air Quality Regulations: Enforcing strict air quality standards that industries and vehicles must comply with.
- Subsidies for Clean Technology: Offering financial incentives for companies and individuals to adopt cleaner technologies.
- Educational Campaigns: Raising public awareness about the sources and impacts of air pollution and how to reduce personal contributions.
These measures, when effectively implemented, can lead to significant improvements in air quality. While technology provides the tools for cleaner air, policies and public engagement ensure these tools are used widely and effectively. The battle against air pollution is ongoing, but through innovative approaches, we can work towards a cleaner, healthier atmosphere.

Innovation with Purpose Lockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin, renowned for its role in aerospace, defense, and security, places a strong emphasis on purpose-driven innovation. With projects spanning from advanced fighter jets to space exploration, their commitment to cutting-edge technology is foundational to their operations.
Areas of Innovation by Lockheed Martin
Here are major fields of development, and related inventions for each of these field.
- Aeronautics: Development of aircraft like the F-35 Lightning II, incorporating stealth technology and advanced avionics. The F-35 program represents a leap in combat capabilities and multirole functions.
- F-35 Lightning II Stealth Technology: Lockheed Martin's F-35 Lightning II incorporates advanced stealth technology, including patented features like radar-absorbing materials and aerodynamic designs. These innovations reduce the aircraft's radar cross-section, enhancing its stealth capabilities and survivability in combat situations.
- F-35 Lightning II Stealth Technology: Lockheed Martin's F-35 Lightning II incorporates advanced stealth technology, including patented features like radar-absorbing materials and aerodynamic designs. These innovations reduce the aircraft's radar cross-section, enhancing its stealth capabilities and survivability in combat situations.
 Space Systems: Engagement in space exploration initiatives, such as the Orion spacecraft, designed for deep space missions. Orion is set to play a key role in NASA's Artemis program, aiming to return humans to the Moon and beyond.
Space Systems: Engagement in space exploration initiatives, such as the Orion spacecraft, designed for deep space missions. Orion is set to play a key role in NASA's Artemis program, aiming to return humans to the Moon and beyond.
- Orion Spacecraft Thermal Protection System: Lockheed Martin's Orion spacecraft, designed for deep space exploration, features a patented thermal protection system. This system utilizes innovative materials and heat-resistant coatings to shield the spacecraft from extreme temperatures encountered during re-entry into Earth's atmosphere.
- Orion Spacecraft Thermal Protection System: Lockheed Martin's Orion spacecraft, designed for deep space exploration, features a patented thermal protection system. This system utilizes innovative materials and heat-resistant coatings to shield the spacecraft from extreme temperatures encountered during re-entry into Earth's atmosphere.
- Missile and Fire Control: Creation of precision weaponry and missile defense systems to enhance national security. For example, Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) systems, designed to protect against ballistic missiles attacks.
- THAAD Missile Defense System: Lockheed Martin's Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system includes patented technologies for intercepting and destroying incoming ballistic missiles. These technologies encompass advanced radar systems, tracking algorithms, and kinetic energy interceptors, providing a highly effective defense against a variety of missile threats.
- THAAD Missile Defense System: Lockheed Martin's Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system includes patented technologies for intercepting and destroying incoming ballistic missiles. These technologies encompass advanced radar systems, tracking algorithms, and kinetic energy interceptors, providing a highly effective defense against a variety of missile threats.
 Rotary and Mission Systems: Advancements in rotary-wing aircraft and maritime systems for global military, commercial, and rescue operations. For example, Sikorsky helicopters, like the UH-60 Black Hawk, offer reliable performance for diverse missions.
Rotary and Mission Systems: Advancements in rotary-wing aircraft and maritime systems for global military, commercial, and rescue operations. For example, Sikorsky helicopters, like the UH-60 Black Hawk, offer reliable performance for diverse missions.
- Sikorsky X2 Technology: Developed by Sikorsky, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, the X2 Technology incorporates several patented innovations for rotary-wing aircraft. This technology enables helicopters like the Sikorsky S-97 Raider to achieve high speeds and maneuverability through features such as coaxial rotors and active vibration control systems.
- Sikorsky X2 Technology: Developed by Sikorsky, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, the X2 Technology incorporates several patented innovations for rotary-wing aircraft. This technology enables helicopters like the Sikorsky S-97 Raider to achieve high speeds and maneuverability through features such as coaxial rotors and active vibration control systems.
- Emerging Technologies: Investment in breakthrough technologies such as hypersonic flight, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy solutions. For example, Hypersonic technology was developed for ultra-fast, long-range missile systems.
- Hypersonic Vehicle Propulsion Systems: Lockheed Martin has patented several technologies related to hypersonic flight and propulsion systems. These innovations include scramjet engines, air-breathing propulsion systems, and thermal management solutions designed to power hypersonic vehicles capable of traveling at speeds exceeding Mach 5.
Key Characteristics of Lockheed Martin Innovation Management
The following characteristics collectively contribute to Lockheed Martin's success in driving innovation, delivering high-performance solutions, and addressing complex challenges in the aerospace, defense, and security sectors:
- Strategic Vision: Lockheed Martin maintains a clear strategic vision that guides its innovation efforts, aligning with its mission to deliver advanced technology solutions for defense, aerospace, and security.
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: The company fosters collaboration across diverse teams and disciplines, bringing together experts from engineering, science, technology, and other fields to drive innovation and problem-solving.
- Investment in Research and Development: Lockheed Martin allocates significant resources to research and development (R&D), investing in cutting-edge technologies, facilities, and talent to stay at the forefront of innovation.
- Focus on Customer Needs: The company prioritizes understanding customer requirements and challenges, leveraging insights to develop tailored solutions that address specific mission needs and deliver value to customers.
- Agile and Iterative Approach: Lockheed Martin embraces an agile and iterative approach to innovation, enabling rapid prototyping, testing, and iteration to quickly validate concepts and bring innovations to market efficiently.
- Intellectual Property Protection: The company places importance on protecting its intellectual property through patents, trademarks, and trade secrets, safeguarding its innovative technologies and solutions from unauthorized use or replication.
- Continuous Improvement: Lockheed Martin fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees to identify opportunities for innovation, streamline processes, and enhance the effectiveness of products and services.
Lockheed Martin's dedication to purpose-driven innovation, spanning from cutting-edge aircraft to space exploration, underscores its pivotal role in advancing technology for aerospace, defense, and security. With a strategic vision guiding its cross-disciplinary collaboration and significant investment in research and development, Lockheed Martin continues to deliver high-performance solutions tailored to address evolving challenges. By prioritizing customer needs, embracing agile methodologies, and safeguarding intellectual property, Lockheed Martin exemplifies excellence in innovation management, driving continuous improvement and ensuring its position at the forefront of technological innovation in the aerospace and defense sectors.

Innovation with AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has been a trailblazer in cloud computing, enabling organizations to innovate by offering a broad set of global cloud-based products including computing power, storage options, and networking capabilities. AWS's broad service offering supports businesses across virtually every industry sector with the tools needed for digital transformation, enabling them to innovate more quickly and at a scale.
Innovation with AWS: Examples in Key Industries
- Healthcare: Leveraging AWS cloud to manage patient data and analytics.
- Cerner uses AWS for its health analytics, improving patient care outcomes.
- Cerner uses AWS for its health analytics, improving patient care outcomes.
- Finance: Banks use AWS for real-time fraud detection and financial modeling.
- Intuit uses AWS to power its financial software with machine learning for personalized financial advice.
- Intuit uses AWS to power its financial software with machine learning for personalized financial advice.
- Retail: Enhancing customer experiences through personalized recommendations.
- Netflix utilizes AWS capabilities to deliver content and recommend shows and movies.
- Netflix utilizes AWS capabilities to deliver content and recommend shows and movies.
- Education: AWS provides a secure, scalable platform for online learning.
- Coursera hosts its e-learning platform on AWS, offering courses to millions of learners.
- Coursera hosts its e-learning platform on AWS, offering courses to millions of learners.
- Government: Governments employ AWS to improve the scalability and security of their digital services.
- The UK’s Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA) uses AWS to manage vehicle records for citizens.
- The UK’s Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA) uses AWS to manage vehicle records for citizens.
- Manufacturing: Utilizing AWS IoT services for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- Siemens employs AWS IoT services to monitor industrial machinery and streamline production processes.
- Siemens employs AWS IoT services to monitor industrial machinery and streamline production processes.
- Energy: Implementing AWS analytics for optimizing energy generation and distribution.
- ENGIE uses AWS analytics tools to analyze energy consumption patterns and improve operational efficiency in power plants.
- ENGIE uses AWS analytics tools to analyze energy consumption patterns and improve operational efficiency in power plants.
- Media and Entertainment: Deploying AWS for content creation, storage, and distribution.
- The Walt Disney Company leverages AWS for digital asset management and content delivery of its streaming services like Disney+.
- The Walt Disney Company leverages AWS for digital asset management and content delivery of its streaming services like Disney+.
- Transportation: Integrating AWS for fleet management and logistics optimization.
- Uber utilizes AWS for real-time tracking of vehicles and route optimization to improve ride-sharing services.
- Uber utilizes AWS for real-time tracking of vehicles and route optimization to improve ride-sharing services.
- Agriculture: Employing AWS for crop monitoring and precision agriculture solutions.
- The Climate Corporation, a subsidiary of Bayer, uses AWS to analyze weather data and provide farmers with insights for optimal crop management.
Advantages of Using AWS
- Scalability: AWS offers scalable resources that can seamlessly accommodate fluctuations in demand, allowing businesses to scale up or down quickly without incurring high costs.
- Cost-effectiveness: With a pay-as-you-go pricing model, AWS enables organizations to pay only for the resources they use, eliminating the need for upfront investments in infrastructure.
- Reliability: AWS provides high availability and fault tolerance across its global infrastructure, ensuring that services remain accessible, and data remains secure even in the event of failures.
- Flexibility: AWS offers a wide range of services and deployment options, allowing businesses to choose the tools and configurations that best suit their specific requirements and use cases.
- Innovation: AWS continuously introduces new services and features, enabling businesses to leverage cutting-edge technologies and stay ahead of the competition in rapidly evolving markets.
Innovation examples at AWS
- AWS Lambda (2014): Introduced serverless computing, allowing developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
- Amazon SageMaker (2017): A fully managed service for building, training, and deploying machine learning models, enabling developers to accelerate the development cycle and scale their ML initiatives.
- Amazon Aurora (2014): A high-performance, fully managed relational database service, offering compatibility with MySQL and PostgreSQL, along with advanced features such as automatic scaling and high availability.
- Amazon Redshift (2012): A fast, fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service, enabling organizations to analyze large datasets and derive valuable insights for decision-making.
- Amazon Polly (2016): A text-to-speech service that uses advanced deep learning technologies to generate lifelike speech from text, enhancing user experiences in various applications such as virtual assistants and accessibility tools.
In conclusion, innovation with AWS has transformed the landscape of cloud computing, empowering organizations across various industries to innovate and scale their operations efficiently. With a diverse array of services tailored to different use cases, AWS facilitates digital transformation and fosters innovation at every level of business. By leveraging AWS's advanced capabilities, companies can drive growth, enhance customer experiences, and stay at the forefront of technological innovation.

Innovation with Amazon
Amazon, a global leader in e-commerce, has revolutionized online shopping and retail through continuous innovation. From pioneering new delivery methods to redefining customer experiences, Amazon's innovations have reshaped the way people buy and sell goods online.
Examples of Users Leveraging Amazon for Innovation
- Education: Educators and students utilize Amazon's Kindle Direct Publishing platform to self-publish educational materials and textbooks, democratizing access to knowledge.
- Independent authors leverage Kindle Direct Publishing to create and distribute educational resources, bypassing traditional publishing barriers and reaching a global audience.
- Independent authors leverage Kindle Direct Publishing to create and distribute educational resources, bypassing traditional publishing barriers and reaching a global audience.
- Small Businesses: Entrepreneurs leverage Amazon's Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program to outsource order fulfillment and logistics, allowing them to focus on product development and growth.
- Small businesses use FBA to access Amazon's vast customer base and logistics infrastructure, expanding their reach and accelerating their business growth.
- Small businesses use FBA to access Amazon's vast customer base and logistics infrastructure, expanding their reach and accelerating their business growth.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers integrate Amazon's voice assistant, Alexa, into patient care workflows to improve efficiency and patient outcomes.
- Hospitals and clinics deploy Alexa-enabled devices to assist with administrative tasks, medication reminders, and patient education, enhancing the overall healthcare experience.
- Hospitals and clinics deploy Alexa-enabled devices to assist with administrative tasks, medication reminders, and patient education, enhancing the overall healthcare experience.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers utilize Amazon's Machine Learning services to optimize production processes and improve product quality.
- Companies leverage Amazon's SageMaker platform to develop custom machine learning models for predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization.
- Companies leverage Amazon's SageMaker platform to develop custom machine learning models for predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization.
- Nonprofits: Nonprofit organizations leverage Amazon's donation platform, AmazonSmile, to raise funds for charitable causes with every eligible purchase.
- Nonprofits register with AmazonSmile to receive donations from Amazon at no additional cost to customers, providing a simple way for supporters to contribute to their mission while shopping online.
- Nonprofits register with AmazonSmile to receive donations from Amazon at no additional cost to customers, providing a simple way for supporters to contribute to their mission while shopping online.
- Food and Beverage: Restaurants and food service providers utilize Amazon's Whole Foods Market stores and delivery services to expand their reach and offer online ordering options.
- Independent restaurants partner with Whole Foods Market to sell prepared meals through Amazon's delivery platform, providing customers with convenient dining options.
- Independent restaurants partner with Whole Foods Market to sell prepared meals through Amazon's delivery platform, providing customers with convenient dining options.
- Real Estate: Real estate developers and property managers use Amazon's smart home devices and services to enhance the value and appeal of residential and commercial properties.
- Developers incorporate Amazon's Alexa-enabled devices and smart home technology into new construction projects, offering residents seamless control over home automation and security systems.
- Developers incorporate Amazon's Alexa-enabled devices and smart home technology into new construction projects, offering residents seamless control over home automation and security systems.
- Travel and Hospitality: Hotels and travel agencies leverage Amazon's cloud services and data analytics tools to personalize guest experiences and optimize operations.
- Hospitality businesses use Amazon Web Services (AWS) to analyze guest preferences and behavior, enabling targeted marketing campaigns and tailored service offerings.
- Hospitality businesses use Amazon Web Services (AWS) to analyze guest preferences and behavior, enabling targeted marketing campaigns and tailored service offerings.
- E-commerce: Online retailers and e-commerce startups utilize Amazon's marketplace platform and advertising services to reach new customers and drive sales.
- Small businesses launch storefronts on Amazon.com and leverage Amazon Advertising to promote their products to millions of shoppers, increasing visibility and sales.
- Small businesses launch storefronts on Amazon.com and leverage Amazon Advertising to promote their products to millions of shoppers, increasing visibility and sales.
- Education Technology: EdTech startups and educational institutions leverage Amazon's cloud infrastructure and machine learning tools to develop innovative learning platforms and personalized educational content.
- Companies use AWS to host and scale their educational applications, while leveraging Amazon's AI and natural language processing capabilities to deliver adaptive learning experiences to students.
Advantages of Using Amazon
- Convenience: Amazon offers a wide selection of products and services that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, providing unparalleled convenience to customers.
- Accessibility: Amazon's platform is accessible to sellers of all sizes, democratizing access to global markets and enabling small businesses to reach customers around the world.
- Innovation: Amazon is constantly innovating and experimenting with new technologies and business models, driving industry-wide change and shaping the future of e-commerce.
- Customer Focus: Amazon prioritizes customer satisfaction and loyalty, continuously improving its services based on customer feedback and preferences.
- Scalability: Amazon's infrastructure is designed to scale seamlessly to accommodate fluctuations in demand, ensuring reliability and performance even during peak periods.
Innovation examples at Amazon
- Amazon Go (2018): Amazon's chain of cashier-less convenience stores, utilizing computer vision and sensor fusion to enable frictionless shopping experiences.
- Alexa (2014): Amazon's virtual assistant powered by artificial intelligence, offering voice-controlled interactions and smart home integration.
- Kindle (2007): Amazon's e-reader device, revolutionizing the way people read and access digital books.
- Amazon Fresh (2007): Amazon's grocery delivery and pickup service, providing customers with convenient access to fresh produce and household essentials.
- Amazon Prime (2005): Amazon's subscription service offering benefits such as free two-day shipping, streaming video, and exclusive deals, driving customer loyalty and retention.
In conclusion, the examples showcased highlight the transformative impact of Amazon's platform on various industries, empowering users to innovate and thrive in today's digital economy. By leveraging Amazon's diverse range of services and technologies, businesses and individuals alike can unlock new opportunities, enhance efficiency, and deliver value to customers in innovative ways. As Amazon continues to drive innovation and push the boundaries of what's possible, its influence on global commerce and society will only continue to grow.

Innovations in Foods
The food industry has been a hotbed of innovation, particularly as consumer preferences shift toward sustainability, health, and convenience.
Breakthroughs in the Food Industry
- Plant-Based Alternatives: The rise of plant-based meat alternatives addressing environmental and ethical concerns.
- Tivol's plant-based burger patties offer a sustainable and delicious alternative to traditional meat options, catering to environmentally conscious consumers.
 Case Study: Beyond Meat's Plant-Based Protein Revolution
Case Study: Beyond Meat's Plant-Based Protein Revolution- Company: : Beyond Meat, El Segundo, USA (Founded in 2009)
- What Was Done: Beyond Meat developed plant-based meat substitutes designed to replicate the taste, texture, and cooking experience of beef. They utilize proteins from peas, beans, and other plants to create products that have a lower environmental footprint than traditional livestock products.
- Results/Impact: Beyond Meat products are now sold worldwide, contributing to the rising popularity and acceptance of plant-based diets. Their success has encouraged a significant shift in consumer behavior and spurred innovation within the food industry, impacting sustainability and health.
- Tivol's plant-based burger patties offer a sustainable and delicious alternative to traditional meat options, catering to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Lab-grown Meat: Cultivating meat from cells to meet demand while reducing the environmental impact of animal farming.
- Memphis Meats produces cultured meat products by farming animal cells directly, bypassing traditional livestock methods.
- Memphis Meats produces cultured meat products by farming animal cells directly, bypassing traditional livestock methods.
- Food Preservation: Advanced preservation techniques extending the shelf life of food without the need for additives.
- Apeel Sciences creates plant-derived coatings that keep produce fresh twice as long as traditional methods.
- Apeel Sciences creates plant-derived coatings that keep produce fresh twice as long as traditional methods.
- Functional Foods: Development of foods enhanced with additional health benefits.
- Foods fortified with vitamins, probiotics, and omega-3s cater to health-conscious consumers.
- Foods fortified with vitamins, probiotics, and omega-3s cater to health-conscious consumers.
- Sustainable Packaging: Creating compostable and biodegradable packaging to reduce plastic waste.
- Notpla has innovated seaweed-based packaging, offering an alternative to plastic.
Leaders in Food Innovation
- Nestlé: Pioneering research in nutrition and sustainability.
- Impossible Foods: Leading in plant-based meat alternatives.
- Soylent: Innovating in complete meal replacements.
- Blue Apron: Revolutionizing meal kit delivery with a focus on fresh ingredients.
- LocalBounty: Advancing controlled-environment agriculture.
 Case Study: Imperfect Foods' Ugly Produce Delivery
Case Study: Imperfect Foods' Ugly Produce Delivery
- Company: Imperfect Foods, San Francisco, USA (Founded in 2015)
- What Was Done: Imperfect Foods started a direct-to-consumer delivery service that offers 'ugly' fruits and vegetables that don't meet the cosmetic standards of traditional grocers, preventing food waste at the farm level.
- Results/Impact: Imperfect Foods has expanded its reach across the US, saving thousands of tons of food from going to waste. It has also educated consumers on the value of reducing waste, contributing to a more sustainable food system.
How to Apply Food Innovation
- Consumer Research: Understanding preferences for targeted product development.
- Sustainability Focus: Emphasizing eco-friendly production methods.
- Nutritional Science: Fortifying foods with essential nutrients.
- Collaboration: Working with agricultural tech startups for new methods.
- Technology Adoption: Integrating IoT for supply chain transparency.
Unique Characteristics of Food Innovation
- Customization: Catering to individual dietary needs and preferences.
- Sensory Enhancement: Improving taste, texture, and visual appeal.
- Convenience: Simplifying preparation and consumption.
- Traceability: Ensuring source and process transparency.
- Nutrient Retention: Maximizing health benefits during processing.
What to Avoid When Inventing Food Solutions
- Over-Processing: Retain nutritional value and avoid excessive additives.
- Ignoring Local Tastes: Consider cultural food preferences.
- Unsustainable Practices: Avoid methods harmful to the environment.
- Neglecting Allergens: Be aware of common dietary restrictions.
- Forgetting Accessibility: Ensure solutions are scalable and affordable.
Innovation in food is a testament to our ability to adapt and improve our relationship with what we eat. This journey underscores a commitment to health, pleasure, and care for the planet.

Innovations in Furniture
The furniture industry is embracing innovation to meet the demands of modern consumers, focusing on sustainability, functionality, and design.
Breakthroughs in the Furniture Industry
- Sustainable Materials: Using recycled and eco-friendly materials for production.
- Emeco creates chairs from recycled aluminum, promoting sustainability in furniture design.
- Emeco creates chairs from recycled aluminum, promoting sustainability in furniture design.
- Smart Furniture: Integrating technology for enhanced functionality.
- Ori Systems develops robotic furniture that transforms small spaces with automated, space-saving solutions.
- Ori Systems develops robotic furniture that transforms small spaces with automated, space-saving solutions.
- Modular Designs: Allowing customization and adaptability to different spaces.
- Vitsoe offers modular shelving systems that can be easily reconfigured to suit changing needs and spaces.
- Vitsoe offers modular shelving systems that can be easily reconfigured to suit changing needs and spaces.
- Ergonomic Focus: Prioritizing comfort and health in design.
- Humanscale designs ergonomic chairs and accessories to promote healthier sitting postures and reduce fatigue.
- Humanscale designs ergonomic chairs and accessories to promote healthier sitting postures and reduce fatigue.
- Flat-Pack Innovations: Improving ease of transport and assembly.
- Floyd produces modular furniture pieces that are shipped flat-packed for easy transportation and assembly, minimizing environmental impact.
Case Study: Greycork Furniture
- Company: Greycork, Providence, USA (Launched in 2014)

- What Was Done: Greycork developed an alternative to traditional flat-pack furniture that's designed to be assembled and disassembled easily, aimed at the urban lifestyle. Their products are shipped in compact boxes, reducing shipping volume and costs.
- Results/Impact: : Although Greycork eventually ceased operations, their innovations in design for easy assembly and minimal hardware influenced the furniture industry, particularly targeting the needs of a mobile, environmentally conscious generation.
- Floyd produces modular furniture pieces that are shipped flat-packed for easy transportation and assembly, minimizing environmental impact.
Leaders in Furniture Innovation
- IKEA: Trailblazing in affordable, modular, and eco-friendly designs.
- Steelcase: Innovating workspace solutions for collaboration and well-being.
- Wayfair: Utilizing AR for virtual furniture placement in homes.
- Burrow: Offering easy-to-assemble, customizable furniture options.
- Herman Miller: Focusing on ergonomic and sustainable office furniture.
Case Study: Herman Miller's Eco-Friendly Furniture Design
- Company: Herman Miller, Zeeland, USA (Environmental goals set in 2009)

- What Was Done: Herman Miller set ambitious sustainability goals and integrated eco-friendly practices into its furniture production, using biodegradable materials and designing products for disassembly and recycling.
- Results/Impact: The company has reduced its environmental impact and established itself as a leader in sustainable furniture design, influencing the industry and changing customer expectations regarding the environmental responsibility of their furniture choices.
- Company: Herman Miller, Zeeland, USA (Environmental goals set in 2009)
How to Apply Furniture Innovation
- Consumer-Centric Design: Crafting furniture based on customer feedback.
- Sustainable Practices: Reducing carbon footprint throughout production.
- Adaptive Functionality: Designing for multiple use-cases and versatility.
- Collaborative Development: Partnering with designers for fresh perspectives.
- Tech Integration: Incorporating smart technology for user interaction.
Unique Characteristics of Furniture Innovation
- Aesthetics and Function: Balancing beauty with practicality.
- Cultural Relevance: Reflecting local tastes and traditions in designs.
- Space Efficiency: Addressing the needs of urban living spaces.
- Health and Comfort: Designing with user well-being in mind.
- Environmental Impact: Minimizing waste and promoting recyclability.
What to Avoid When Inventing Furniture Solutions
- One-Size-Fits-All Approach: Acknowledge the diversity in consumer needs.
- Ignoring Ergonomics: Prioritize comfort to prevent health issues.
- Overcomplicating Assembly: Keep customer convenience in mind.
- Forgetting Durability: Ensure long-term usability and quality.
- Neglecting Trends: Stay updated on evolving design preferences.
Innovative furniture solutions are shaping modern interiors, ensuring sustainability and functionality align with the evolving lifestyle needs of consumers. In this pursuit of innovation, designers and manufacturers are advised to avoid overlooking the individuality of consumer preferences, the importance of ergonomic designs, oversimplification in assembly that compromises structure, neglecting durability, and missing out on current and emerging design trends. These principles guide the industry towards creating products that not only enhance living spaces but also advocate for environmental consciousness and user well-being. The balance of form, function, and sustainability is the hallmark of contemporary furniture innovation.

Which Innovation is Attributed to Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer, often referred to as the "Father of English literature," is best known for his work "The Canterbury Tales." Chaucer's innovation lies not in a technological invention but in his significant contributions to English literature and language. He is credited with helping to popularize the use of the English vernacular in literary works at a time when French and Latin were the dominant languages of literature and scholarship in England.
"The Canterbury Tales" was innovative in its use of the English vernacular and its narrative structure, comprising a collection of stories told by pilgrims from different social classes on a journey from London to Canterbury. Chaucer's work is also recognized for its rich and diverse character development and for using the pilgrimage as a literary device to present a slice of 14th-century English society.
Through his literary works, Chaucer brought forth characters that represented various aspects of society, from the nobility to the peasantry, and gave them distinct voices that conveyed their personal stories and perspectives. This approach allowed for a variety of themes, including love, betrayal, humor, and morality, to be explored in a relatable and engaging manner.
Chaucer's pioneering use of iambic pentameter in his rhyming couplets was also a key innovation in English poetry. This rhythmic pattern consists of ten syllables per line, with alternating stressed and unstressed syllables, and sound like this - da-DUM da-DUM da-DUM da-DUM da-DUM. This metric scheme became a standard in English poetry and is considered one of Chaucer's lasting legacies. It not only enhanced the rhythmic quality of English poetry but also expanded its expressive range, making it more flexible and dynamic.
Overall, Geoffrey Chaucer's innovation was in his storytelling, his development of English literary style, and the elevation of the English language in literature. His works have had a lasting impact on English literature and remain studied and celebrated for their creative brilliance and historical importance.

Which Innovation Gave the Sumerians
The Sumerians, known for their pioneering contributions to civilization, are credited with a myriad of innovations, but perhaps their most notable is the invention of cuneiform writing. Developed around 3200 BC, this system of writing is recognized as one of the earliest forms of written expression.
Cuneiform began as a series of pictograms, which eventually evolved into a series of impressions made on clay tablets using a reed stylus. This innovation was crucial not only for record-keeping and the administration of the Sumerian city-states but also for preserving knowledge, laws, literature, and history.
Moreover, the Sumerians are also celebrated for their advancements in agriculture, architecture, and mathematics. They developed sophisticated irrigation techniques, enabling them to cultivate land in the arid Mesopotamian environment. In architecture, they constructed ziggurats, which were massive step-pyramid structures that served as temples. In mathematics, they utilized a base-60 numerical system, which is still reflected in how we measure hours and angles today.
The legacy of Sumerian innovation is deeply embedded in the foundations of modern society, influencing various aspects of contemporary life and underscoring the lasting impact of their early advancements.

Which Innovation Helped Both the Ottoman
The Ottoman Empire's strategic mastery in military technology and organization was pivotal in its expansion and longevity from the 14th to the early 20th century. One of the key innovations that the Ottomans harnessed was gunpowder weaponry. They refined the use of cannons and firearms, which were crucial during their sieges and in battles, most notably during the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The fall of Constantinople marked a significant shift in power and trade, largely due to the Ottoman's effective use of gunpowder to breach the city's formidable Theodosian Walls.
Beyond weaponry, the Ottomans introduced the Janissary corps, an elite infantry unit that began as the Sultan's personal guard and became a powerful military force. The Janissaries were known for their rigorous training, discipline, and loyalty, which stemmed from the devşirme system that recruited boys from Christian territories, converted them to Islam, and educated them for service in the empire.
In terms of governance, the Ottomans established a sophisticated administrative system that allowed them to control a vast and diverse empire. The millet system enabled religious communities to govern themselves in matters of personal law, education, and religion, which was innovative in its approach to handling a multi-ethnic and multi-religious empire.
The Ottomans were also noted for their contributions to architecture, with the development of unique structures that combined Islamic and Byzantine architectural elements. The most famous example is the Hagia Sophia, which was converted into a mosque following the conquest of Constantinople and featured Ottoman architectural additions like minarets.
These military, administrative, and cultural innovations enabled the Ottoman Empire to become a dominant force in the Mediterranean and beyond, influencing the course of history in the regions they controlled. Their innovative use of technology, combined with strategic governance and cultural patronage, facilitated the empire's growth and left a lasting legacy that continued to influence the modern era.

What is the Next Big Innovation
Predicting the "next big innovation" is a fascinating endeavor, as it requires looking at current trends and technologies that have the potential to transform our lives significantly.
Current Innovations with Significant Impact
- Internet of Things (IoT): The interconnectivity of everyday devices has and will continue to improve efficiency, safety, and convenience.
- Renewable Energy Technologies: Solar and wind power innovations are already contributing significantly to a sustainable future.
- CRISPR Gene Editing: This revolutionary technology allows for precise editing of the DNA in living organisms, opening doors to curing genetic diseases and agricultural advancements.
- 5G Networks: The rollout of 5G technology promises ultra-fast internet speeds, lower latency, and the capacity to connect more devices simultaneously, enhancing mobile networks.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars and drones are set to revolutionize transportation, reducing accidents caused by human error and optimizing logistics and delivery services.
 Case Study: Full Cycle Bioplastics
Case Study: Full Cycle Bioplastics
- Company: Full Cycle Bioplastics, Richmond, USA (2014)
- What Was Done: Full Cycle Bioplastics developed a proprietary technology to convert organic waste into PHA, a type of biodegradable plastic. This process offers a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
- Results/Impact: The innovation by Full Cycle Bioplastics has the potential to address the global plastic waste crisis significantly. Their technology turns waste into a valuable resource, thereby reducing pollution and dependence on fossil fuels.
Emerging Areas Poised for Breakthrough Innovations
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems that are currently intractable for classical computers, revolutionizing fields like cryptography, materials science, and optimization.
- Biotechnology: Advancements in gene editing, particularly CRISPR technology, could lead to cures for genetic diseases and improvements in food security.
- Sustainable Energy: Innovations in fusion energy promise a potential source of nearly limitless and clean energy if current technical challenges can be overcome.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI has the potential to automate complex tasks, provide insights from big data, and create more personalized experiences in technology.
- Space Exploration: Advancements in space technology may soon make space travel more accessible and lead to new discoveries about our universe and resources.
 Case Study: Quantum Computing Breakthrough by IBM
Case Study: Quantum Computing Breakthrough by IBM
- Company: IBM, Armonk, USA
- Product: Quantum computer (Announced in 2016)
- What Was Done: : IBM has been pioneering in the development of quantum computing. Their IBM Q System One represents significant advancements, aiming to solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
- Results/Impact: IBM's continuous progress in quantum computing is expected to revolutionize industries by enabling new ways to model financial data, optimize supply chains, speed up discoveries in drug research, and solve complex optimization problems.
10 Mind-Bending Predictions for the Future of Humanity and Technology
- Neural Interface Communication: People communicate through thought alone, using advanced neural interfaces that translate brain waves into digital messages, making language barriers obsolete.
- Autonomous Construction: Robot swarms autonomously construct buildings and infrastructure, adapting real-time to environmental changes, dramatically reducing construction times and costs.
- Personal Health Avatars: AI-powered avatars monitor individual health metrics 24/7, predicting potential illnesses before symptoms appear and suggesting personalized treatments or lifestyle adjustments.
- Quantum Internet: A global quantum communication network offers unprecedented levels of security and speed, revolutionizing how information is shared and drastically reducing cyber threats.
- Space-Based Solar Power: Solar power stations in space beam clean energy back to Earth, providing a limitless source of power and significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Genetic Memory Uploads: Techniques to encode digital information into DNA allow individuals to "upload" knowledge and memories, making learning instantaneous and creating a new form of inheritance.
- Ocean City-States: Self-sustaining, floating cities in international waters, operating as independent city-states, offer new living and governance models on the ocean frontier.
- Atmospheric Water Harvesting: Advanced materials and technologies capture water vapor directly from the air in arid regions, solving water scarcity issues and transforming deserts into arable land.
- Nano-Robotic Healthcare: Swarms of nanorobots perform surgeries and deliver targeted drug therapies within the human body, offering treatments without the need for incisions or traditional medical interventions.
- Mind Cloning: Digital copies of human consciousness are created, allowing individuals' personalities, memories, and experiences to exist in virtual environments or be transferred to artificial bodies, challenging concepts of identity and mortality.
Common Strategies to Identify and Support the Next Big Innovation
- Investment in R&D: Continuous funding for research and development can hasten the arrival of breakthrough innovations.
- Education and Training: Equipping the future workforce with skills in emerging technologies ensures readiness for upcoming changes.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments and companies can pool resources and expertise to tackle big challenges.
- Innovation Ecosystems: Creating environments that foster creativity and experimentation can lead to the birth of significant innovations.
- Leveraging TRIZ for Predictive Innovation: Utilizing the Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) principles to predict technological convergence and future innovations. By analyzing patterns of technological evolution, companies can anticipate the next big breakthroughs and position themselves as leaders in innovation.
Methodologies for Predicting the Future of Technology
- TRIZ (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving): A systematic approach based on patterns of invention within the global patent literature, TRIZ enables the prediction of technological evolution by analyzing past innovations.
- Delphi Method: A structured communication technique, which relies on a panel of experts. The experts answer questionnaires in two or more rounds. After each round, a facilitator provides an anonymous summary of the experts' forecasts and reasons. This process continues until reaching a consensus.
- Technology Road Mapping: A planning technique to create a strategic roadmap that outlines the trajectory of technological advances and the desired future state, helping organizations align their technological capabilities with their business objectives.
- Scenario Planning: Involves envisioning different future scenarios based on various factors and uncertainties. It helps organizations anticipate possible futures and develop strategies that are robust across multiple possible outcomes.
- Horizon Scanning: A technique used to detect early signs of potentially important developments through a systematic examination of potential threats and opportunities. It involves looking at the wider picture beyond the current operations to anticipate future trends.
- Futures Studies (Futurology): An interdisciplinary field that seeks to hypothesize possible, probable, and preferable futures. Futurology uses a variety of methods, from quantitative and qualitative to normative and exploratory.
- Cross-Impact Analysis: A method used to determine how different economic, technological, political, and social variables affect each other and the future development of a particular scenario.
- Trend Extrapolation: Analyzing historical data and trends to project future developments. This method assumes that existing trends will continue into the future but may not account for sudden changes or new innovations.
- Patent Analysis: Examining the trends in patent filings and grants to identify emerging technologies and predict future technological breakthroughs. This method provides insights into where companies and countries are investing their research and development efforts.
- Expert Workshops: Bringing together industry experts, technologists, futurists, and policymakers to discuss and debate future technological advancements. These workshops provide a platform for sharing insights and perspectives that can shape understanding of future trends.
- Crowdsourcing and Open Innovation: Leveraging the collective intelligence of a large group of people, often from the public or an online community, to predict trends, solve problems, and gather ideas for future technologies.
Explaining TRIZ and Predictive Innovation
- TRIZ Fundamentals: TRIZ is a problem-solving, analysis, and forecasting methodology based on data derived from the study of patterns of invention in the global patent literature. It offers a systematic approach to creativity for generating innovative solutions.
- Identifying Patterns of Evolution: TRIZ studies how systems and technologies evolve over time, identifying specific patterns that can predict future developments in any technological or engineering field.
- Problem Solving with TRIZ: Utilizes a set of 40 inventive principles and a contradiction matrix to find innovative solutions to difficult problems, bypassing traditional trial-and-error approaches.
- Technology Forecasting: By understanding the evolution of systems, TRIZ enables practitioners to forecast technological changes and develop products or solutions that meet future needs.
- Ideality and Innovation: TRIZ promotes the concept of ideality, where the best solution is one that eliminates the problem without introducing new problems, guiding towards more efficient and innovative designs.
- Resource Utilization: Emphasizes the use of available resources in the environment, system, or process to solve problems creatively and cost-effectively, reducing waste and increasing sustainability.
- Function Analysis: A tool within TRIZ that helps to understand and break down the problem at hand, identifying what functions are needed and how they can be provided in innovative ways.
- Conflict Resolution: TRIZ provides strategies for resolving conflicts or contradictions without compromise, leading to breakthrough innovations that do not trade off one benefit for another.
- Innovation Algorithms: Offers a structured approach to creativity that can be systematically applied to generate innovative solutions, making the process of invention more predictable and accessible.
- Global Collaboration: TRIZ encourages the sharing of solutions across industries and borders, leveraging the collective intelligence and creativity of the global innovation community to solve complex challenges.
Predicting the "next big innovation" is a fascinating endeavor, as it requires looking at current trends and technologies that have the potential to transform our lives significantly. With advancements in areas like quantum computing, biotechnology, and sustainable energy, coupled with methodologies like TRIZ for predictive innovation, we're on the brink of a new era of technological breakthroughs that promise to reshape our future in unimaginable ways. As we navigate this landscape of innovation, embracing collaboration, foresight, and creativity will be key to unlocking the next wave of revolutionary developments that will shape the course of humanity and technology for generations to come.

What is the Best Innovation
Defining "the best innovation" is inherently subjective, as it can vary greatly depending on individual values, the impact on society, and the context of the innovation's application. However, if we consider the following criteria, certain innovations consistently rise to the top.
Criteria for Evaluating Innovations
- Scope of Impact: How widely an innovation affects the population and daily life (longevity and quality of life).
- Sustainability: Innovations that allow for progress without depleting resources.
- Accessibility: The best innovations are often those that can be accessed and utilized by a broad range of people.
- Transformational: Innovations that fundamentally change industries, behaviors, or societal norms
- Impactful: Innovations that create significant positive change in communities and industries.
Top 10 Transformative Innovations in Human History
- The Wheel (circa 3500 BC): Often cited as the hallmark of human progress, facilitating transportation and machinery development.
- Electricity (late 19th century): The cornerstone of modern life, powering countless devices and technologies.
- The Internet (1960s-1980s): Revolutionized communication, access to information, and the global economy.
- Penicillin (1928): Marked the beginning of the antibiotic era, saving countless lives.
- Agricultural Revolution (circa 10,000 BC): Advances in farming techniques that allowed civilizations to flourish.
- Printing Press (1440): Revolutionized the spread of information and literacy.
- Steam Engine (1698): Ignited the Industrial Revolution, changing manufacturing forever.
- Airplane (1903): Shrunk the world by making long-distance travel fast and accessible.
- Computer (20th century): Revolutionized every aspect of work, communication, and entertainment.
- Generative AI (2010s-present): Revolutionizing creative and analytical processes by generating new content, from text to images, based on learned data patterns.
Top 10 Life-Saving Innovations in History
- Hand Hygiene in Medical Settings (19th century onwards): dramatically reduced the transmission of infections, particularly in childbirth.
- Antibiotics (1928 onwards): Penicillin and subsequent antibiotics have drastically reduced deaths from bacterial infections.
- Sanitation Systems (19th century onwards): Clean water and sewage systems have significantly reduced deaths from waterborne diseases.
- Agricultural Innovations (Neolithic period onwards): Improved farming techniques and GMOs have increased food production, reducing starvation.
- Medical Imaging (Late 19th century onwards): Technologies like X-rays and MRIs enable early detection and treatment of diseases.
- Anesthesia (19th century onwards): Made surgeries less risky and more bearable, saving countless lives.
- Oral Rehydration Therapy (1960s onwards): Simple treatment for dehydration has saved millions of children from diarrheal diseases.
- Blood Transfusion (19th century onwards): Enables life-saving surgeries and treatments for diseases.
- Contraceptives (20th century onwards): Improved family planning and reduced maternal mortality.
- Pasteurization (19th century onwards): Reduced deaths from foodborne illnesses.
Top 10 Innovations Improving Quality of Life
- Fire (1.5 million years ago onwards): The controlled use of fire transformed human civilization by providing warmth, cooking food, protection from predators, and enabling the development of various technologies.
- Clean Water and Sanitation (1854): Implementation of modern sanitation systems and access to clean water significantly reduced waterborne diseases, enhancing public health and well-being.
- Electricity (late 19th century): Electrification improved living conditions by providing lighting, heating, and powering appliances, revolutionizing daily life.
- Antibiotics (1928): The discovery of penicillin and subsequent antibiotics transformed medicine, treating bacterial infections and reducing mortality rates.
- Internet (late 20th century): Connecting people worldwide, the internet revolutionized communication, access to information, and opportunities for education and employment.
- Air Conditioning (early 20th century): Providing relief from extreme temperatures, air conditioning systems improved comfort and productivity in various climates.
- Transportation Networks (19th century onwards): The development of railways, highways, and public transportation systems facilitated travel, trade, and mobility, enhancing quality of life.
- Agricultural Innovations (various dates): Modern farming techniques, including mechanization, fertilizers, and crop rotation, increased food production and security, reducing hunger and malnutrition.
- Personal Computing (1970s onwards): Access to personal computers and digital technology transformed work, entertainment, and communication, increasing efficiency and connectivity.
- Medical Imaging (20th century): Advancements in medical imaging technologies, such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, revolutionized diagnosis and treatment, improving health outcomes and quality of life.
Criteria for Evaluating Innovations
- Scope of Impact: How widely an innovation affects the population and daily life.
- Sustainability: Innovations that allow for progress without depleting resources.
- Accessibility: The best innovations are often those that can be accessed and utilized by a broad range of people.
- Transformational: Innovations that fundamentally change industries, behaviors, or society norms.
- Impactful: Innovations that create significant positive change in communities and industries.
Challenges in Assessing Innovations
- Cultural Bias: Different cultures may value certain innovations over others based on their specific needs and historical context.
- Temporal Relevance: What is considered the "best" innovation can change over time as society evolves.
- Ethical Considerations: Innovations may raise ethical concerns related to privacy, consent, and societal implications, complicating their assessment.
- Technological Complexity: Assessing the impact of highly technical innovations can be challenging for individuals without specialized knowledge or expertise.
 Case Study: Direct Wafer Process by 1366 Technologies
Case Study: Direct Wafer Process by 1366 Technologies
- Company: 1366 Technologies, Bedford, USA (Founded in 2008)
- What Was Done: 1366 Technologies has created a breakthrough process called Direct Wafer that manufactures silicon wafers for solar panels more efficiently than traditional methods, significantly reducing waste and cost.
- Results/Impact: By making solar power more cost-effective and sustainable, 1366 Technologies' innovation has the potential to accelerate the transition to renewable energy sources on a global scale. Their process could play a critical role in combating climate change and making solar energy more accessible.
In conclusion, while it's challenging to definitively name a single "best" innovation, those that have dramatically improved human capabilities, longevity, quality of life, and our understanding of the world are often revered as the most significant. Each major innovation stands on the shoulders of countless small advancements, reflecting the cumulative nature of progress.
Systematic innovation
Interested in getting help with systematic innovation processes and developing new products and services?
Contact us: info@zooz.co.il ,+972-9-958-5085
Innovation Articles
- Innovation overview
- Innovation management
- Innovation methods
- Innovation tools
- Innovation and creativity
- Innovation and other disciplines
- Innovation in organizations
- Innovation career
- Innovation importance
- Innovation goals
- Innovation values
- Inspiration for innovation
- Innovation education
- Product innovation
- Service innovation
- Technological innovation
- Innovation examples
- Innovations across various industries
- Innovation glossary (200 terms)





